Your What happens if both supply and demand increase images are ready in this website. What happens if both supply and demand increase are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the What happens if both supply and demand increase files here. Find and Download all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re searching for what happens if both supply and demand increase images information connected with to the what happens if both supply and demand increase topic, you have come to the ideal blog. Our site frequently gives you suggestions for downloading the highest quality video and image content, please kindly surf and locate more informative video articles and graphics that match your interests.
What Happens If Both Supply And Demand Increase. If demand decreases and supply increases then equilibrium quantity could go up down or stay the same and equilibrium price will go down. Although it all depends on the price elasticity which is the degree of change in demand in response to the relative change in price. If the increase in both demand and supply is exactly equal there occurs a proportionate shift in the demand and supply curve. According to the model of demand and supply if a good has a simultaneous increase in demand and decrease in supply what happens to the equilibrium quantity of the good sold.
 This Pin Explains The Law Of Demand And Supply And Its Effect On Price Read The Complete Article Below Teaching Economics Economics Lessons Economics Notes From pinterest.com
This Pin Explains The Law Of Demand And Supply And Its Effect On Price Read The Complete Article Below Teaching Economics Economics Lessons Economics Notes From pinterest.com
Equilibrium price and quantity are determined by the intersection of supply and demand. If supply rises more than demand we get a decrease in price. If an increase in demand increases equilibrium quantity and anincrease in supply increases equilibrium quantity then an increasein both MUST increase equilibrium quantity. If demand decreases and supply remains unchanged then it leads to lower equilibrium price and lower quantity. In order to know for sure we would need to know the magnitudes of both shifts. Quantity supplied will decrease.
However the equilibrium quantity rises.
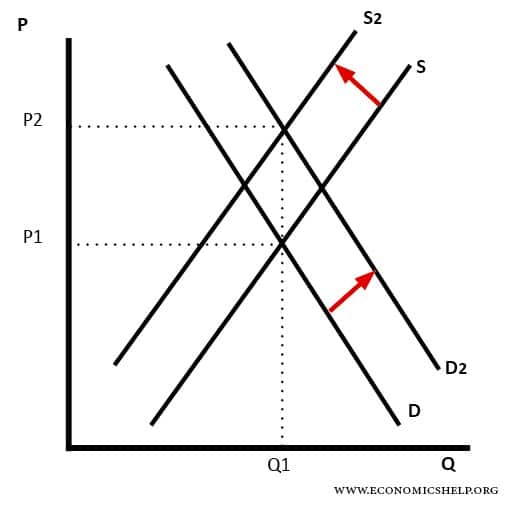
If supply and demand both increase at about the same rate the price of. If demand increases more than supply does we get an increase in price. The same inverse relationship holds for the demand for goods and services. What we do know is that quantity demanded will go up and you can confirm this by looking at the three red equilibrium points each of them are located to the right of the original equilibrium. Supply and demand will attain an equilibrium price where both the supplier and consumer agree to the same price. While supply for the product has not changed all of the determinants of supply are the same producers incur higher cost which is why we will see a new equilibrium point further up the demand curve at a higher.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
If the increase in both demand and supply is exactly equal there occurs a proportionate shift in the demand and supply curve. An increase in demand and a decrease in supply will cause an increase in equilibrium price but the effect on equilibrium quantity cannot be detennined. If demand decreases and supply increases then equilibrium quantity could go up down or stay the same and equilibrium price will go down. If demand increases more than supply does we get an increase in price. Quantity supplied will decrease.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
If demand decreases and supply remains unchanged then it leads to lower equilibrium price and lower quantity. Quantity demanded will increase. An increase in demand all other things unchanged will cause the equilibrium price to rise. Consequently the equilibrium price remains the same. The increase in demand increase in supply.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Secondly what happens to equilibrium when supply and demand both increase. Changes in price levels holding other things constant ceteris paribus causes movements along both aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves. Quantity supplied will decrease. If demand increases more than supply does we get an increase in price. So the answer is it depends when both supply and demand increase and you want to know what happens to price.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Both an increase in supply and an increase in demand will result in the quantity traded eg both supplied and demanded going up so there is no ambiguity there. In the past few years increased supplies of US. An increase in demand all other things unchanged will cause the equilibrium price to rise. This increased supply has lead to decreases in the price of gas at the pump. Consequently the equilibrium price remains the same.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Quantity supplied will decrease. If an increase in demand increases equilibrium quantity and anincrease in supply increases equilibrium quantity then an increasein both MUST increase equilibrium quantity. Quantity supplied will increase. A decrease in demand will cause the equilibrium price to fall. Reason- When demand increases Quantity increases and supply decreases there is a decrease in quantity so c View the full answer Transcribed image text.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
For any quantity consumers now place a higher value on the goodand producers must have a higher price in order to supply the good. According to the model of demand and supply if a good has a simultaneous increase in demand and decrease in supply what happens to the equilibrium quantity of the good sold. An increase in supply all other things unchanged will cause the equilibrium price to fall. For any quantity consumers now place a higher value on the goodand producers must have a higher price in order to supply the good. If demand decreases and supply remains unchanged then it leads to lower equilibrium price and lower quantity.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In order to know for sure we would need to know the magnitudes of both shifts. This encourages consumers to purchase more. Supply and demand will attain an equilibrium price where both the supplier and consumer agree to the same price. Reason- When demand increases Quantity increases and supply decreases there is a decrease in quantity so c View the full answer Transcribed image text. Quantity demanded will increase.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Quantity supplied will decrease. Fig 21 Short Run Aggregate Supply curve SRAS Fig 22 Long Run Aggregate Supply. An increase in demand all other things unchanged will cause the equilibrium price to rise. If demand decreases and supply increases then equilibrium quantity could go up down or stay the same and equilibrium price will go down. Quantity supplied will increase.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Consequently the equilibrium price remains the same. If an increase in demand increases equilibrium quantity and anincrease in supply increases equilibrium quantity then an increasein both MUST increase equilibrium quantity. Supply and demand will attain an equilibrium price where both the supplier and consumer agree to the same price. An increase in demand all other things unchanged will cause the equilibrium price to rise. Consequently the equilibrium price remains the same.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
If supply and demand both increase we know that the equilibrium quantity bought and sold will increase. The increase in demand increase in supply. Quantity supplied will increase. It is highly unlikely that the change in supply and demand perfectly offset one another so that equilibrium remains the same. Quantity supplied will decrease.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
What we do know is that quantity demanded will go up and you can confirm this by looking at the three red equilibrium points each of them are located to the right of the original equilibrium. If the price decreases the demand will increase. If supply rises more than demand we get a decrease in price. Quantity demanded will increase. A decrease in demand and an increase in supply will cause a fall in equilibrium price but the effect on equilibrium quantity cannot be determined.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
This encourages consumers to purchase more. If an increase in demand increases equilibrium quantity and anincrease in supply increases equilibrium quantity then an increasein both MUST increase equilibrium quantity. If the supply increases the price will decrease. If demand decreases and supply increases then equilibrium quantity could go up down or stay the same and equilibrium price will go down. Therefore price will increase.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
If demand decreases and supply remains unchanged then it leads to lower equilibrium price and lower quantity. If there is an increase in supply for goods and services while demand remains the same prices tend to fall to a lower equilibrium price and a higher equilibrium quantity of goods and services. The same inverse relationship holds for the demand for goods and services. Supply and demand will attain an equilibrium price where both the supplier and consumer agree to the same price. If demand decreases and supply remains unchanged then it leads to lower equilibrium price and lower quantity.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
If the increase in both demand and supply is exactly equal there occurs a proportionate shift in the demand and supply curve. In order to know for sure we would need to know the magnitudes of both shifts. The increase in demand increase in supply. If demand increases and supply stays the same then equilibrium quantity goes up and equilibrium price goes up. Quantity supplied will decrease.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Fig 21 Short Run Aggregate Supply curve SRAS Fig 22 Long Run Aggregate Supply. The same inverse relationship holds for the demand for goods and services. Quantity supplied will increase. When supply and demand both increase the quantity of goods sold will also increase. However the equilibrium quantity rises.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
If supply and demand both increase at about the same rate the price of. Quantity demanded will increase. The increase in demand increase in supply. A change in supply or demand or both will necessarily change the equilibrium price quantity or both. This video shows the potential outcomes for equilibrium price if both the supply and demand curves shift right.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Changes in price levels holding other things constant ceteris paribus causes movements along both aggregate demand and aggregate supply curves. A decrease in demand and an increase in supply will cause a fall in equilibrium price but the effect on equilibrium quantity cannot be determined. Consequently the equilibrium price remains the same. If supply rises more than demand we get a decrease in price. As supply increases suppliers will lower their prices due to the abundance of product.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
A change in supply or demand or both will necessarily change the equilibrium price quantity or both. If an increase in demand increases equilibrium quantity and anincrease in supply increases equilibrium quantity then an increasein both MUST increase equilibrium quantity. According to the model of demand and supply if a good has a simultaneous increase in demand and decrease in supply what happens to the equilibrium quantity of the good sold. An increase in demand all other things unchanged will cause the equilibrium price to rise. Quantity supplied will increase.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title what happens if both supply and demand increase by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.