Your What does a kinked demand curve mean images are ready in this website. What does a kinked demand curve mean are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the What does a kinked demand curve mean files here. Find and Download all free photos and vectors.
If you’re searching for what does a kinked demand curve mean images information connected with to the what does a kinked demand curve mean interest, you have visit the ideal blog. Our website always gives you suggestions for viewing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and locate more enlightening video articles and graphics that match your interests.
What Does A Kinked Demand Curve Mean. In an oligopolistic market the kinked demand curve hypothesis states that the firm faces a demand curve with a kink at the prevailing price level. This is demand curve for Oligopolistic competition in which there are less than 10 producers and there are huge number of consumers. Kinked Demand Curve Econfix What Is Kinked Demand Idea In Economics Quora Kinked Demand Curve Idea Graphical Illustration Examples And so forth Theories Of Oligopoly. The kinked demand curve model predicts there will be periods of relative price stability under an oligopoly with businesses focusing on non-price competition as a means of reinforcing their market position and increasing their supernormal profits.
![]() Education Resources For Teachers Schools Students Ezyeducation From ezyeducation.co.uk
Education Resources For Teachers Schools Students Ezyeducation From ezyeducation.co.uk
In an oligopolistic market the kinked demand curve hypothesis states that the firm faces a demand curve with a kink at the prevailing price level. EXERCISE3 a Explain the difference between monopoly duopoly and oligopoly. Short-lived price wars between rival firms can still happen under the kinked demand curve model. A kinked demand curve occurs when the demand curve is not a straight line but has a different elasticity for higher and lower prices. Shows stable prices in an oligopoly. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly.
A kinked demand curve.
Shows stable prices in an oligopoly. The kinked demand curve model seeks to explain the reason of price rigidity under oligopolistic market situations. A kinked demand curve represents the behavior pattern of oligopolistic organizations in which rival organizations lower down the prices to secure their market share but restrict an increase in the prices. Short-lived price wars between rival firms can still happen under the kinked demand curve model. For the term kinked-demand curve may also exist other definitions and meanings the meaning and definition indicated above are indicative not be used for medical and legal or special purposes. Starting from point K if one firm felt that if it were to charge a higher unmatched price than its rivals it would lose sales to these rivals then its relevant perceived demand curve.
 Source: amosweb.com
Source: amosweb.com
The kinkeddemand theory of oligopoly illustrates the high degree of interdependence that exists among the firms that make up an oligopoly. The kinked demand curve model predicts there will be periods of relative price stability under an oligopoly with businesses focusing on non-price competition as a means of reinforcing their market position and increasing their supernormal profits. Starting from point K if one firm felt that if it were to charge a higher unmatched price than its rivals it would lose sales to these rivals then its relevant perceived demand curve. This means that the response to a price increase is less than the response to a price decrease. This model of oligopoly suggests that prices are rigid and that firms will face different effects for both increasing price or decreasing price.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
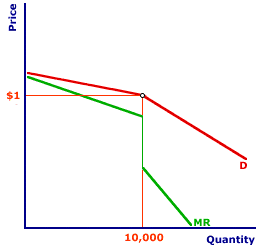
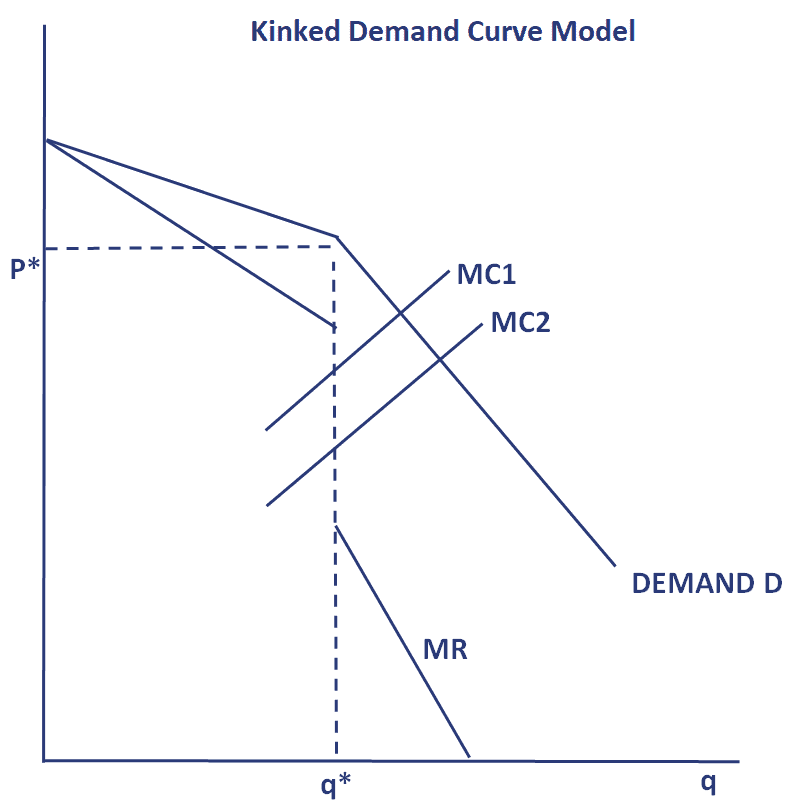
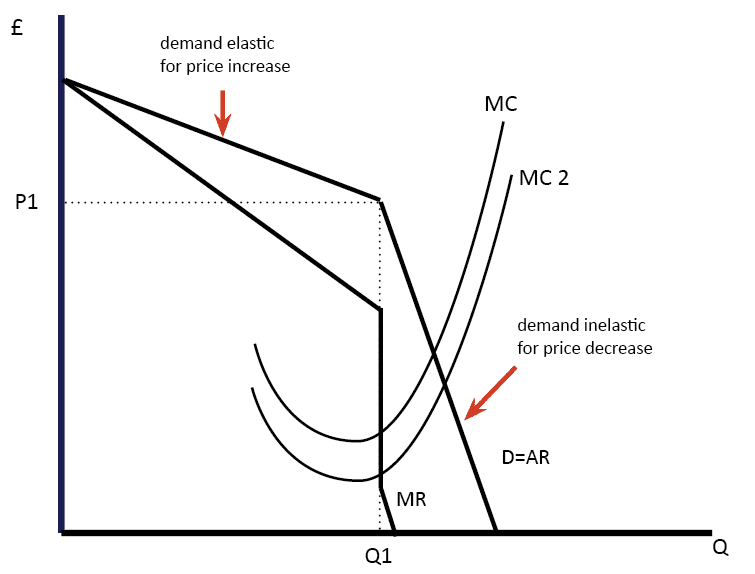
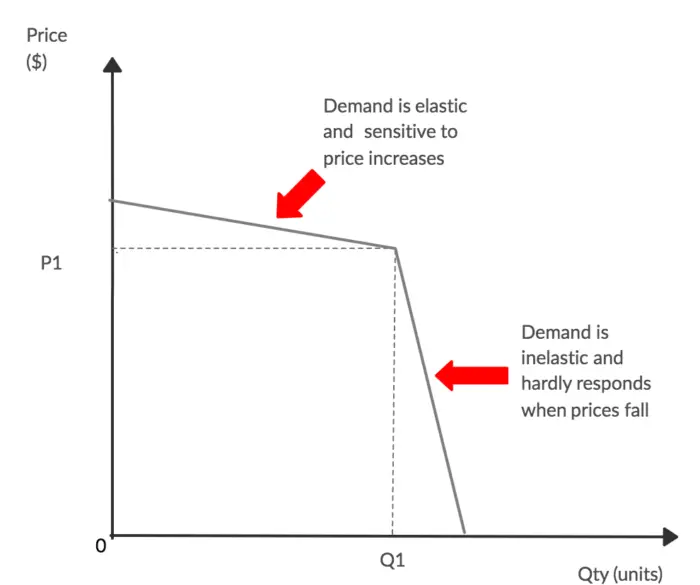
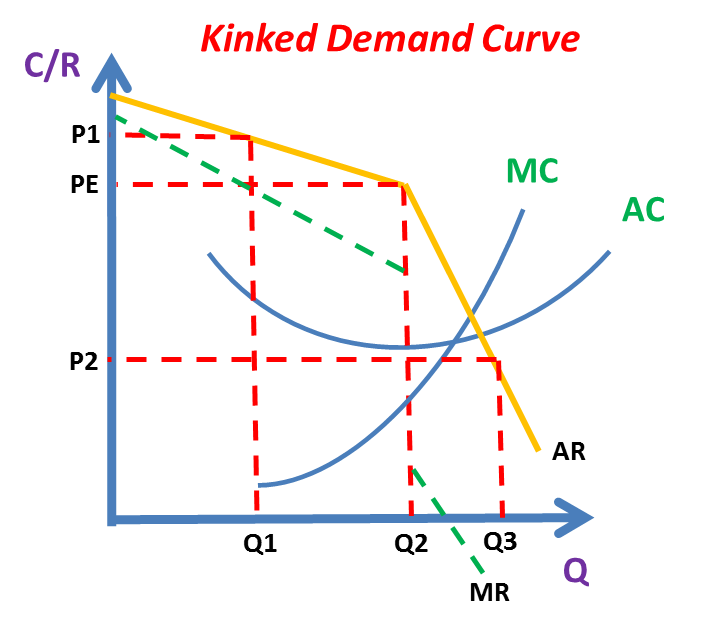
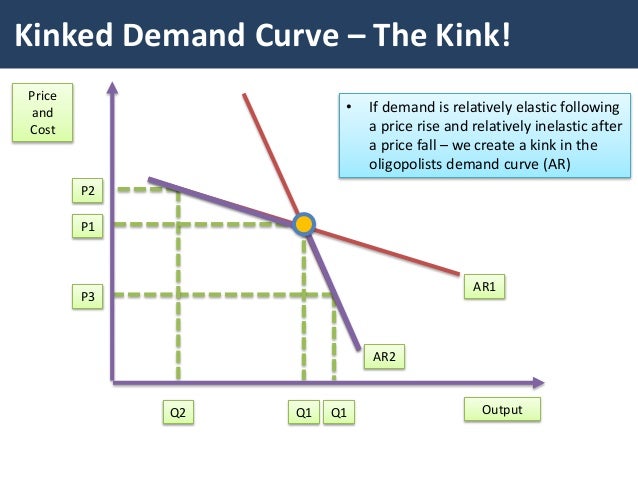
Therefore in the case of the kinked demand curve dRD the firms MR curve up. If variable costs change a profit maximizing oligopolist will not change price or quantity as long as the marginal cost curve crosses the marginal revenue curve within this gap. At a price higher than the prevailing market price a firm faces a more elastic demand curve but at a price below the prevailing market price the demand curve is relatively less elastic. In an oligopolistic market the kinked demand curve hypothesis states that the firm faces a demand curve with a kink at the prevailing price level. - An increase in price will lead to a more than proportionate decrease in quantity demanded.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
This means that the response to a price increase is less than the response to a price decrease. The kink is formed at the prevailing price level because the segment of the demand curve above the prevailing price level is highly elastic and the segment of the demand curve below the prevailing price level is inelastic. And to explain the price rigidity in this market conventional demand curve is not used. This is the major contribution of the kinkeddemand theory. The curve is more elastic above the kink and less elastic below it.
 Source: breakingdownfinance.com
Source: breakingdownfinance.com
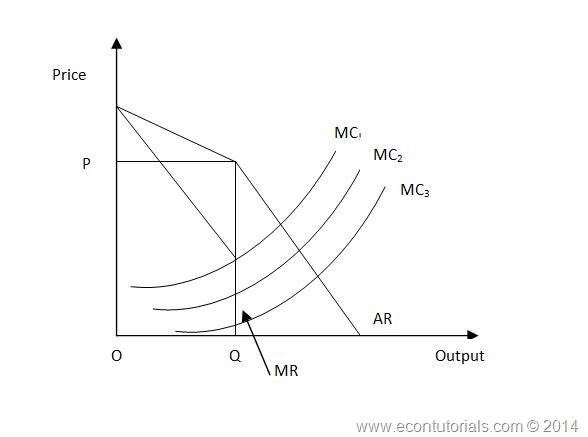
106 DD is the DEMAND CURVE if all firms charge the same price. This is demand curve for Oligopolistic competition in which there are less than 10 producers and there are huge number of consumers. Meaning and definition of kinked-demand curve. Kinked demand curve a curve that explains why the PRICES charged by competing oligopolists see OLIGOPOLY once established tend to be stable. In the case of the kinked demand curve model this interdepence works as follows.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
In the case of the kinked demand curve model this interdepence works as follows. C What is a reaction function. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. What does a kinked demand curve mean. - An increase in price will lead to a more than proportionate decrease in quantity demanded.
 Source: biznewske.com
Source: biznewske.com
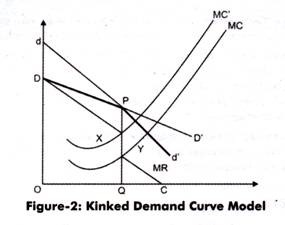
Meaning and definition of kinked-demand curve. In an oligopolistic market the kinked demand curve hypothesis states that the firm faces a demand curve with a kink at the prevailing price level. Bhaskar University College London March 15 2007 The kinked demand curve Sweezy 1939. The word Kink means a sudden turn. There is a kink at the point R p 1 q 1 on this curve because the curve consists of a segment dR of the relatively flatter curve dd and another segment RD of the relatively steeper curve DD.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. This model of oligopoly suggests that prices are rigid and that firms will face different effects for both increasing price or decreasing price. A kinked demand curve. Sweezy uses kinked demand curve to describe price rigidity in oligopoly market structure. C What is a reaction function.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
The kinked demand curve model predicts there will be periods of relative price stability under an oligopoly with businesses focusing on non-price competition as a means of reinforcing their market position and increasing their supernormal profits. The kinked demand curve model for oligopoly markets is based on the assumption that companies within the market are interdependent. A kinked demand curve occurs when the demand curve is not a straight line but has a different elasticity for higher and lower prices. In an oligopolistic market the kinked demand curve hypothesis states that the firm faces a demand curve with a kink at the prevailing price level. Kinked Demand Curve Econfix What Is Kinked Demand Idea In Economics Quora Kinked Demand Curve Idea Graphical Illustration Examples And so forth Theories Of Oligopoly.
 Source: econtutorials.com
Source: econtutorials.com
This concept was propounded by Prof. Sweezy uses kinked demand curve to describe price rigidity in oligopoly market structure. A rm conjectures that its rivals will match its price if. And to explain the price rigidity in this market conventional demand curve is not used. In the case of the kinked demand curve model this interdepence works as follows.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. This means that the response to a price increase is less than the response to a. The demand curve for a noncollusive oligopolist which is based on the assumption that rivals will match a price decrease and will ignore a price increase. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. The idea of using a non-conventional demand curve to represent non-collusive oligopoly ie where sellers compete with their rivals was best explained by Paul Sweezy in 1939.
 Source: quizlet.com
Source: quizlet.com
What does a kinked demand curve mean. Then what is a kinked demand curve. This is demand curve for Oligopolistic competition in which there are less than 10 producers and there are huge number of consumers. 106 DD is the DEMAND CURVE if all firms charge the same price. 106 DD is the DEMAND CURVE if all firms charge the same price.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The kinkeddemand theory of oligopoly illustrates the high degree of interdependence that exists among the firms that make up an oligopoly. A rm conjectures that its rivals will match its price if. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. And to explain the price rigidity in this market conventional demand curve is not used. Starting from point K if one firm felt that if it were to charge a higher unmatched price than its rivals it would lose sales to these rivals then its relevant perceived demand curve.

Starting from point K if one firm felt that if it were to charge a higher unmatched price than its rivals it would lose sales to these rivals then its relevant perceived demand curve. This means that the behavior of one company is expected to impact the behavior of the other companies in the market. This means that the response to a price increase is less than the response to a price decrease. The kinked demand curve model for oligopoly markets is based on the assumption that companies within the market are interdependent. In an oligopolistic market the kinked demand curve hypothesis states that the firm faces a demand curve with a kink at the prevailing price level.
![]() Source: ezyeducation.co.uk
Source: ezyeducation.co.uk
EXERCISE3 a Explain the difference between monopoly duopoly and oligopoly. C What is a reaction function. A kinked demand curve occurs when the demand curve is not a straight line but has a different elasticity for higher and lower prices. The word Kink means a sudden turn. A kinked demand curve.
 Source: thetutoracademy.com
Source: thetutoracademy.com
The kink in the demand curve occurs because rival firms will behave differently to price cuts and price increases. At a price higher than the prevailing market price a firm faces a more elastic demand curve but at a price below the prevailing market price the demand curve is relatively less elastic. It was originally formulated as a theory of price rigidity. Bhaskar University College London March 15 2007 The kinked demand curve Sweezy 1939. Then what is a kinked demand curve.

B What does a kinked demand curve mean. The demand curve for a noncollusive oligopolist which is based on the assumption that rivals will match a price decrease and will ignore a price increase. Kinked demand curve a curve that explains why the PRICES charged by competing oligopolists see OLIGOPOLY once established tend to be stable. Sweezy uses kinked demand curve to describe price rigidity in oligopoly market structure. The kink in the demand curve occurs because rival firms will behave differently to price cuts and price increases.
 Source: es.slideshare.net
Source: es.slideshare.net
This is the major contribution of the kinkeddemand theory. Kinked demand curve a curve that explains why the PRICES charged by competing oligopolists see OLIGOPOLY once established tend to be stable. The kinked demand curve model does not explain all behavior in oligopoly but the. Starting from point K if one firm felt that if it were to charge a higher unmatched price than its rivals it would lose sales to these rivals then its relevant perceived demand curve. What does a kinked demand curve mean.
 Source: econfix.wordpress.com
Source: econfix.wordpress.com
Starting from point K if one firm felt that if it were to charge a higher unmatched price than its rivals it would lose sales to these rivals then its relevant perceived demand curve. Shows stable prices in an oligopoly. B What does a kinked demand curve mean. Kinked demand curve a curve that explains why the PRICES charged by competing oligopolists see OLIGOPOLY once established tend to be stable. Then what is a kinked demand curve.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title what does a kinked demand curve mean by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.