Your What causes supply curve to shift to the left images are available in this site. What causes supply curve to shift to the left are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the What causes supply curve to shift to the left files here. Find and Download all free vectors.
If you’re looking for what causes supply curve to shift to the left images information related to the what causes supply curve to shift to the left interest, you have visit the ideal blog. Our site frequently gives you hints for refferencing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more informative video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
What Causes Supply Curve To Shift To The Left. The shape of the curve is a function of taxable income elasticity ie taxable income changes in response to changes in the rate of taxation. With more resources it is possible. A graph that illustrates the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied. Nobel laureate economist Simon Kuznets argues that as an economy develops a natural cycle of economic inequality occurs represented by an inverted U-shape curve called the Kuznets curve see Fig.

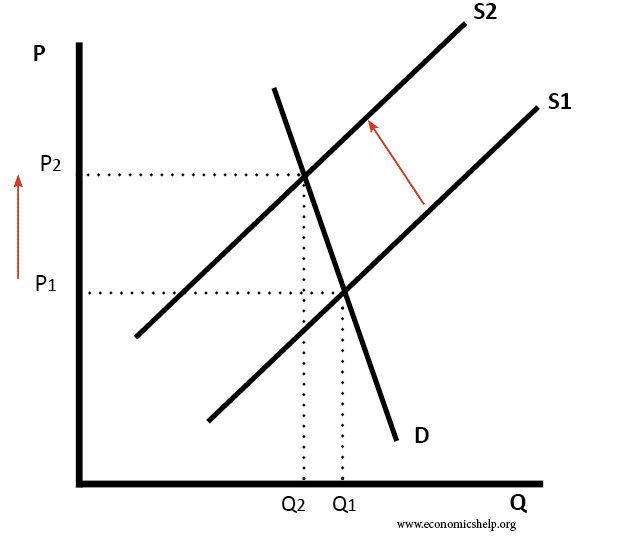
In general adverse supply shocks cause the price level for a given amount of output to increase. When the suppliers decide to collaborate and supply less oil for every price this causes a backwards shift in the supply curve to supply curve 2. The the total demand for final goods and services in the economy at a given time and price level. The Laffer curve assumes that no tax revenue is raised at the extreme tax rates of 0 and 100 and that there is a tax rate between 0 and 100 that maximizes government tax revenue. A shift to the right of the aggregate demand curve. Shift in Supply and Demand For a real world example consider the market for oil.
The shape of the curve is a function of taxable income elasticity ie taxable income changes in response to changes in the rate of taxation.
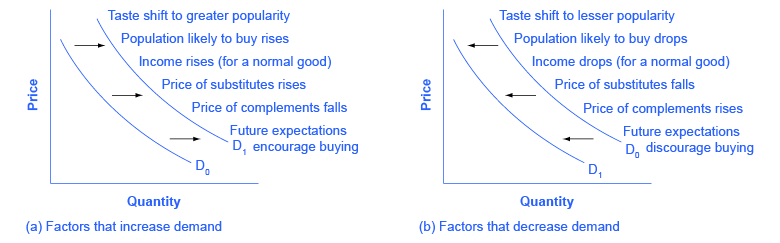
Chocolate ice cream at any given price. Positive supply shocks include things like decreases in oil prices or an unexpected great crop season. Show in a diagram the effect on the demand curve the supply curve the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity of each of the following events. A supply curve is a relationship between two and only two variables when all other variables are kept constant. Any given supply curve is based on the ceteris paribus assumption that all else is held equal. A graph that illustrates the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied.

The the total demand for final goods and services in the economy at a given time and price level. A graph that illustrates the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied. We will discuss a total of six factors which cause the supply curve to shift. Positive supply shocks include things like decreases in oil prices or an unexpected great crop season. From the curve we observe as the economy develops inequality first increases then decreases after a certain level of average income is attained.
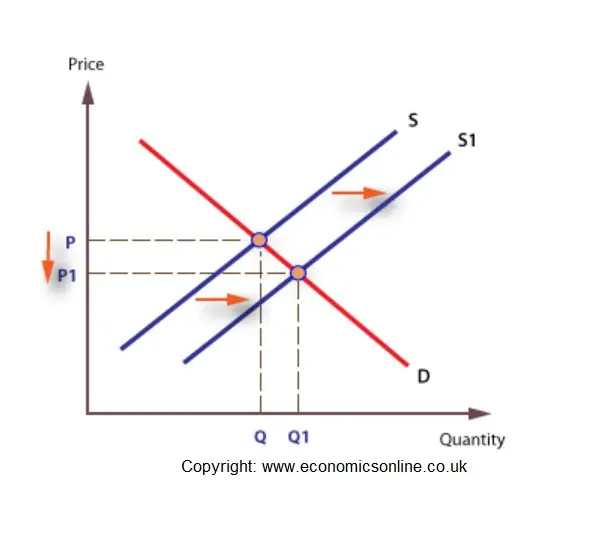 Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Source: economicsonline.co.uk
A graph that illustrates the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied. From AD 1 to AD 2 means that at the same price levels the quantity demanded of real GDP has increased. Positive supply shocks include things like decreases in oil prices or an unexpected great crop season. Show in a diagram the effect on the demand curve the supply curve the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity of each of the following events. When the suppliers decide to collaborate and supply less oil for every price this causes a backwards shift in the supply curve to supply curve 2.
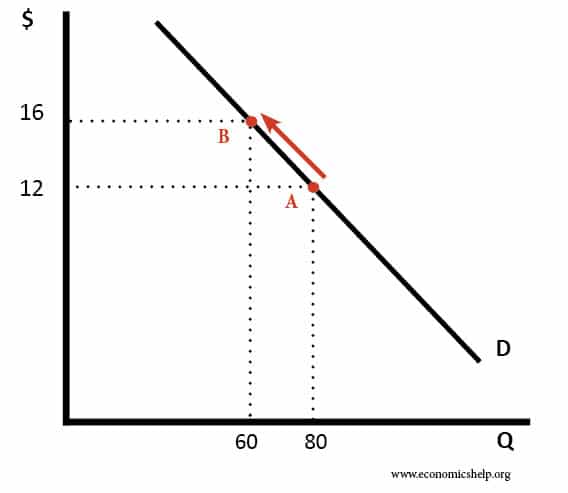 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
The initial supply and demand curves would be at position 1 p1. A graph that illustrates the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied. A shift to the right of the aggregate demand curve. The Laffer curve assumes that no tax revenue is raised at the extreme tax rates of 0 and 100 and that there is a tax rate between 0 and 100 that maximizes government tax revenue. When the suppliers decide to collaborate and supply less oil for every price this causes a backwards shift in the supply curve to supply curve 2.
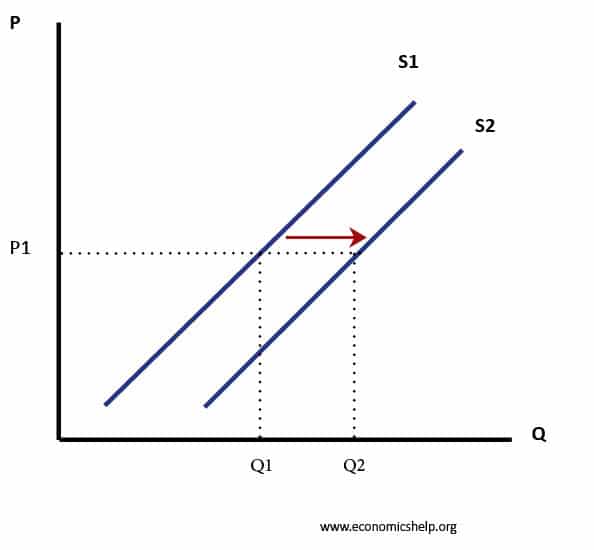 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Positive economic growth results from an increase in productive resources such as labor and capital. Positive supply shocks include things like decreases in oil prices or an unexpected great crop season. From AD 1 to AD 2 means that at the same price levels the quantity demanded of real GDP has increased. The curve shifts in the direction of decreasing quantity with respect to the horizontal axis. With more resources it is possible.

An increase in aggregate supply due to a decrease in input prices is represented by a shift to the right of the SAS curve. From AD 1 to AD 2 means that at the same price levels the quantity demanded of real GDP has increased. Any given supply curve is based on the ceteris paribus assumption that all else is held equal. Show in a diagram the effect on the demand curve the supply curve the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity of each of the following events. A second factor that causes the aggregate supply curve to shift is economic growth.
 Source: investopedia.com
Source: investopedia.com
A supply curve is a relationship between two and only two variables when all other variables are kept constant. With more resources it is possible. If the monetary supply decreases the demand curve will shift to the left. Increases in aggregate supply like these will shift the short run Phillips Curve to the left so that less inflation is seen at each unemployment. A graph that illustrates the relationship between the price of a good and the quantity supplied.
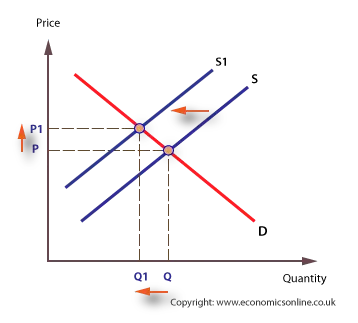 Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Positive supply shocks include things like decreases in oil prices or an unexpected great crop season. The shape of the curve is a function of taxable income elasticity ie taxable income changes in response to changes in the rate of taxation. Conversely a shift to the left displays a decrease in demand at whatever price because another factor such as number of buyers has slumped. We will discuss a total of six factors which cause the supply curve to shift. If the monetary supply decreases the demand curve will shift to the left.
 Source: ibguides.com
Source: ibguides.com
The Laffer curve assumes that no tax revenue is raised at the extreme tax rates of 0 and 100 and that there is a tax rate between 0 and 100 that maximizes government tax revenue. The shape of the curve is a function of taxable income elasticity ie taxable income changes in response to changes in the rate of taxation. If the monetary supply decreases the demand curve will shift to the left. Increases in aggregate supply like these will shift the short run Phillips Curve to the left so that less inflation is seen at each unemployment. Shift in Supply and Demand For a real world example consider the market for oil.

Positive supply shocks include things like decreases in oil prices or an unexpected great crop season. The initial supply and demand curves would be at position 1 p1. From the curve we observe as the economy develops inequality first increases then decreases after a certain level of average income is attained. In general adverse supply shocks cause the price level for a given amount of output to increase. From AD 1 to AD 2 means that at the same price levels the quantity demanded of real GDP has increased.
 Source: college.cengage.com
Source: college.cengage.com
When the suppliers decide to collaborate and supply less oil for every price this causes a backwards shift in the supply curve to supply curve 2. A shift to the right of the aggregate demand curve. Conversely a shift to the left displays a decrease in demand at whatever price because another factor such as number of buyers has slumped. Positive economic growth results from an increase in productive resources such as labor and capital. This is represented by a shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve to the left.

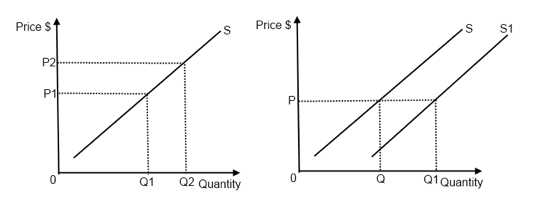
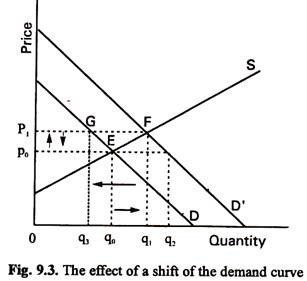
Show in a diagram the effect on the demand curve the supply curve the equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity of each of the following events. Because the supply curve is upward sloping a shift to the right produces a new curve that in a sense lies below the original curve. Positive supply shocks include things like decreases in oil prices or an unexpected great crop season. A shift to the left of the aggregate demand curve from AD 1 to AD 3 means that at the same price levels the quantity demanded of real GDP has decreased. The curve shifts in the direction of decreasing quantity with respect to the horizontal axis.
 Source: web.mnstate.edu
Source: web.mnstate.edu
A supply curve is a relationship between two and only two variables when all other variables are kept constant. A shift to the left of the aggregate demand curve from AD 1 to AD 3 means that at the same price levels the quantity demanded of real GDP has decreased. With more resources it is possible. Shift in Supply and Demand For a real world example consider the market for oil. This is represented by a shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve to the left.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Increases in aggregate supply like these will shift the short run Phillips Curve to the left so that less inflation is seen at each unemployment. In Figure 310 A Reduction in Supply a reduction in supply is shown as a shift of the supply curve to the left. When the suppliers decide to collaborate and supply less oil for every price this causes a backwards shift in the supply curve to supply curve 2. In general adverse supply shocks cause the price level for a given amount of output to increase. The curve shifts in the direction of decreasing quantity with respect to the horizontal axis.

Shift in Supply and Demand For a real world example consider the market for oil. The Laffer curve assumes that no tax revenue is raised at the extreme tax rates of 0 and 100 and that there is a tax rate between 0 and 100 that maximizes government tax revenue. If the monetary supply decreases the demand curve will shift to the left. The shape of the curve is a function of taxable income elasticity ie taxable income changes in response to changes in the rate of taxation. We will discuss a total of six factors which cause the supply curve to shift.
 Source: opentextbc.ca
Source: opentextbc.ca
Any given supply curve is based on the ceteris paribus assumption that all else is held equal. The curve shifts in the direction of decreasing quantity with respect to the horizontal axis. In Figure 310 A Reduction in Supply a reduction in supply is shown as a shift of the supply curve to the left. A supply curve is a relationship between two and only two variables when all other variables are kept constant. A second factor that causes the aggregate supply curve to shift is economic growth.
 Source: college.cengage.com
Source: college.cengage.com
We will discuss a total of six factors which cause the supply curve to shift. The the total demand for final goods and services in the economy at a given time and price level. We will discuss a total of six factors which cause the supply curve to shift. This is represented by a shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve to the left. The initial supply and demand curves would be at position 1 p1.

From AD 1 to AD 2 means that at the same price levels the quantity demanded of real GDP has increased. The Laffer curve assumes that no tax revenue is raised at the extreme tax rates of 0 and 100 and that there is a tax rate between 0 and 100 that maximizes government tax revenue. Positive economic growth results from an increase in productive resources such as labor and capital. This is represented by a shift of the short-run aggregate supply curve to the left. An increase in aggregate supply due to a decrease in input prices is represented by a shift to the right of the SAS curve.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Any given supply curve is based on the ceteris paribus assumption that all else is held equal. The initial supply and demand curves would be at position 1 p1. The curve shifts in the direction of decreasing quantity with respect to the horizontal axis. Increases in aggregate supply like these will shift the short run Phillips Curve to the left so that less inflation is seen at each unemployment. An increase in aggregate supply due to a decrease in input prices is represented by a shift to the right of the SAS curve.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title what causes supply curve to shift to the left by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






