Your What affects the loanable funds market images are available. What affects the loanable funds market are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the What affects the loanable funds market files here. Get all free photos.
If you’re searching for what affects the loanable funds market images information connected with to the what affects the loanable funds market interest, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our website frequently gives you hints for seeing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more informative video content and images that match your interests.
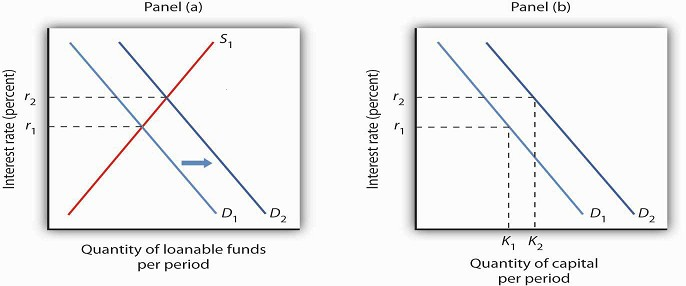
What Affects The Loanable Funds Market. A change in the demand for capital affects the demand for loanable funds and hence the interest rate in the loanable funds market. The change in the interest rate leads to a change in the quantity of capital demanded. The demand schedule for loanable funds is drawn with respect to their price. Changes in perceived business opportunities and in government borrowing shift the demand curve for loanable funds.

The Loanable Funds Market. Changes in private savings and capital inflows shift the supply curve. The higher the interest rate the greater the cost of paying it back. The logic of this point of view is that if the government runs a deficit it has to borrow money just like everyone else. Lets say that the government decides to increase government purchases which will increase the demand for loanable funds. The market for loanable funds describes how that borrowing happens.
These actions would be aimed at the money market and would simultaneously impact the market for loanable funds.
Lets say that the government decides to increase government purchases which will increase the demand for loanable funds. Deficits increase the demand for loanable funds. Secondly since people wants to convert their euros into a more secure currency supply of. Crowding out in the loanable funds market. The interaction between the supply of savings and the demand for loans determines the real interest rate and how much is loaned out. So the sign of the deflator depends on which direction the taxes are going.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
As the interest rate falls the quantity of loanable funds demanded decreasesincreases. When the real interest rate decreases investment spending increases. The supply of loanable funds is based on savings. This will affect both the market for loanable funds and the market for foreign currency exchange. First it will increase the demand for loanable funds in order to increase the purchase of assets overseas shifting the demand curve D LF to the right increasing the real interest rate.

When demand for investment decreases quantity quantity of loanable funds decreases and real interest rate decreases. Secondly since people wants to convert their euros into a more secure currency supply of. Higher interest rates and greater saving. If a change in the tax laws encouraged greater investment the result would be. In the loanable funds market the price is the interest rate and the thing being exchanged is money.

So when interest rates rise the demand for loanable funds decreases. The gdp deflator is negatively correlated with tax. First it will increase the demand for loanable funds in order to increase the purchase of assets overseas shifting the demand curve D LF to the right increasing the real interest rate. The price of loanable funds is the nominal interest rate. With a decrease in government spending your demand curve for the loan-able funds market will shift inward and push the interest rate lower.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
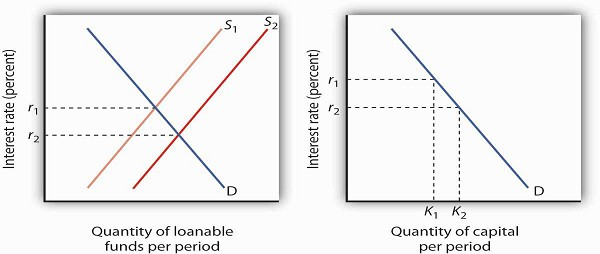
This rise in savings shifts the supply curve for loanable funds rightward and reducing the equilibrium interest rate in the loanable funds market. If there is an increase in savings by the private sector the supply of loanable funds increases shifts right causing the real interest rate to fall. With a decrease in government spending your demand curve for the loan-able funds market will shift inward and push the interest rate lower. So an increase in expected inflation will have the effect of increasing the nominal interest rate and nothing else. The ability to affect the money market the national bank may engage in open market operations to bring interest rates back up to pre-shock levels.
 Source: econowaugh.blogspot.com
Source: econowaugh.blogspot.com
A change in the demand for capital affects the demand for loanable funds and hence the interest rate in the loanable funds market. Crowding out in the loanable funds market. The change in the interest rate leads to a change in the quantity of capital demanded. Investment is expenditure of funds on the building up of new capital goods and inventories. The most important factor responsible for the demand for loanable funds is the demand for investment.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
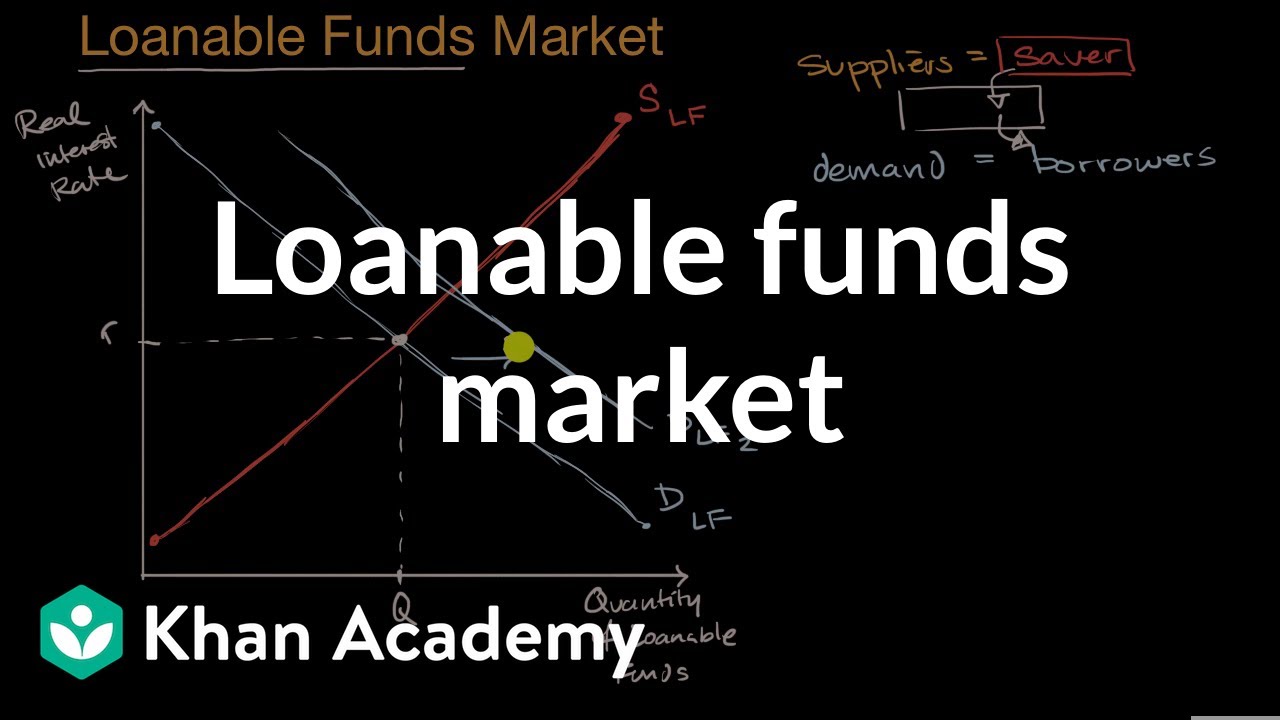
Individuals supply loanable funds through savings. The demand for loanable funds is based on borrowing. When worried consumers and businesses stop spending and increase their saving they may not put their saving into loanable funds markets and businesses may postpone investment spending even if interest rates are low. The price of loanable funds is the nominal interest rate. The supply curve is upward sloping because as the interest rate increases people will want to save more.

The higher the interest rate the greater the cost of paying it back. When the real interest rate decreases investment spending increases. Households act as suppliers of money though saving and they will supply a large quantity of money that is they will save more as the interest rate increases. First it will increase the demand for loanable funds in order to increase the purchase of assets overseas shifting the demand curve D LF to the right increasing the real interest rate. A change in the interest rate in turn affects the quantity of capital demanded on any demand curve.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
The supply of loanable funds is based on savings. The higher the interest rate the greater the cost of paying it back. There is one very important addition to the group of those who supply credit in the loanable funds model. Investment is expenditure of funds on the building up of new capital goods and inventories. The logic of this point of view is that if the government runs a deficit it has to borrow money just like everyone else.
 Source: freeeconhelp.com
Source: freeeconhelp.com
The most important factor responsible for the demand for loanable funds is the demand for investment. The most important factor responsible for the demand for loanable funds is the demand for investment. These actions would be aimed at the money market and would simultaneously impact the market for loanable funds. Crowding out in the loanable funds market. Deficits increase the demand for loanable funds.
 Source: opentextbooks.org.hk
Source: opentextbooks.org.hk
If decrease in tax the gdp will go up and increase will decrease gdp. When a change in the supply of money leads to a change in the interest rate the resulting change in real GDP causes the supply of loanable funds to change as well. Money makes the biggest difference for the loanable funds market. When a fall in the interest rate leads to higher investment spending the resulting increase in real GDP generates exactly enough additional savings to match the rise in investment spending. If a change in the tax laws encouraged greater investment the result would be.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
In the loanable funds market the price is the interest rate and the thing being exchanged is money. If decrease in tax the gdp will go up and increase will decrease gdp. Increases the equilibrium interest rate and increases the equilibrium quantity of loanable funds. When the real interest rate decreases investment spending increases. The demand schedule for loanable funds is drawn with respect to their price.

Government budget deficits can raise the interest rate and can lead to crowding out of investment spending. The demand for loanable funds is based on borrowing. What affects the loanable funds market. Economy the nations monetary and credit system is regulated and strongly influenced by the central bank the Federal Reserve. The most important factor responsible for the demand for loanable funds is the demand for investment.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
AWhat would you expect to happen to the new equilibrium interest rate and quantity of loanable funds. Changes in perceived business opportunities and in government borrowing shift the demand curve for loanable funds. When the government borrows money this results in an increase in the demand for loanable funds as shown in this graph. The loanable funds market shows the relationship between the real interest rate and quantity of loanable funds. The supply of loanable funds is based on savings.

Households act as suppliers of money though saving and they will supply a large quantity of money that is they will save more as the interest rate increases. Investment is expenditure of funds on the building up of new capital goods and inventories. Rate of interest is obviously the cost of borrowing of funds for investment. The Loanable Funds Market. These actions would be aimed at the money market and would simultaneously impact the market for loanable funds.
 Source: opentextbooks.org.hk
Source: opentextbooks.org.hk
Just so what affects the loanable funds market. There is one very important addition to the group of those who supply credit in the loanable funds model. When the real interest rate decreases investment spending increases. This rise in savings shifts the supply curve for loanable funds rightward and reducing the equilibrium interest rate in the loanable funds market. As the interest rate falls the quantity of loanable funds demanded decreasesincreases.
 Source: econ101help.com
Source: econ101help.com
The price of loanable funds is the nominal interest rate. The most important factor responsible for the demand for loanable funds is the demand for investment. Use the model for the market for loanable funds to assess the effect if the government implemented a new government policy that incentivized SAVINGS while at the same time also instituting a new policy that disincetivized INVESTMENTS. The demand schedule for loanable funds is drawn with respect to their price. Equilibrium in the loanable fund market.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Households act as suppliers of money though saving and they will supply a large quantity of money that is they will save more as the interest rate increases. An equilibrium in the loanable fund market occurs when demand equals supply for loanable funds. The gdp deflator is negatively correlated with tax. Rate of interest is obviously the cost of borrowing of funds for investment. A change in the interest rate in turn affects the quantity of capital demanded on any demand curve.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The supply curve is upward sloping because as the interest rate increases people will want to save more. An equilibrium in the loanable fund market occurs when demand equals supply for loanable funds. Households act as suppliers of money though saving and they will supply a large quantity of money that is they will save more as the interest rate increases. With a decrease in government spending your demand curve for the loan-able funds market will shift inward and push the interest rate lower. In the loanable funds market the price is the interest rate and the thing being exchanged is money.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title what affects the loanable funds market by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.