Your Taxes on supply and demand curve images are available. Taxes on supply and demand curve are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Taxes on supply and demand curve files here. Download all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re searching for taxes on supply and demand curve images information linked to the taxes on supply and demand curve keyword, you have visit the right blog. Our site frequently provides you with hints for viewing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more enlightening video articles and images that fit your interests.
Taxes On Supply And Demand Curve. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. How do subsidies generally affect the supply curve Why. AP is owned by the College Board which does not endorse this site or the above reviewStudy Questions1 Show supply demand with an equilibrium price and.
 Negative Externailty Consumption Sugar Tax Economics Sugar Tax Tax From in.pinterest.com
Negative Externailty Consumption Sugar Tax Economics Sugar Tax Tax From in.pinterest.com
Also does excise tax increase or decrease supply. From the firms perspective taxes or regulations are an additional cost of production that shifts supply to the left leading the firm to produce a lower quantity at every given price. A subsidy is an amount of money given directly to firms by the government to. Now now that weve understood everything or hopefully we have lets think about the various surpluses and the deadly weight losses and the tax revenues. Taxation shifts a supply curve to the left. While supply for the product has not changed all of the determinants of supply are the same producers incur higher cost which is why we will see a new equilibrium point further up the demand curve at a higher.
First let us calculate the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity that were before the imposed tax.
A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. When costs of production increase the business will decrease its supply of the item. And similarly that point of intersection also tells us our quantity with the taxes. Well think it through with our supply and our perfectly inelastic demand curve. Taxation shifts a supply curve to the left. The consumers will now pay price P while producers will receive P P - t.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
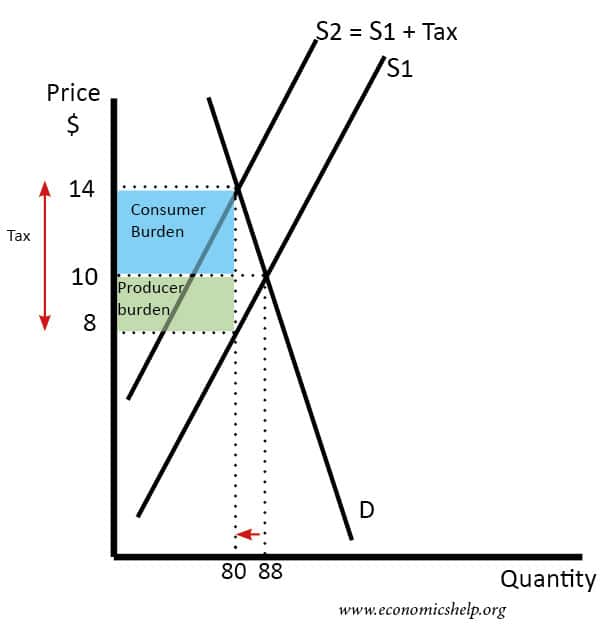
If excise tax is imposed on the producer the supplier will provide less quantity of Good A. And plot the demand and supply curves if the government has imposed an indirect tax at a rate of. First let us calculate the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity that were before the imposed tax. Hence the new equilibrium quantity after tax can be found from equating P Q3 4 and P 20 Q so Q3 4 20 Q which gives QT 12. Tax increases If the government increases the tax on a good that shifts the supply curve to the left consumer prices rise and sellers prices fall.
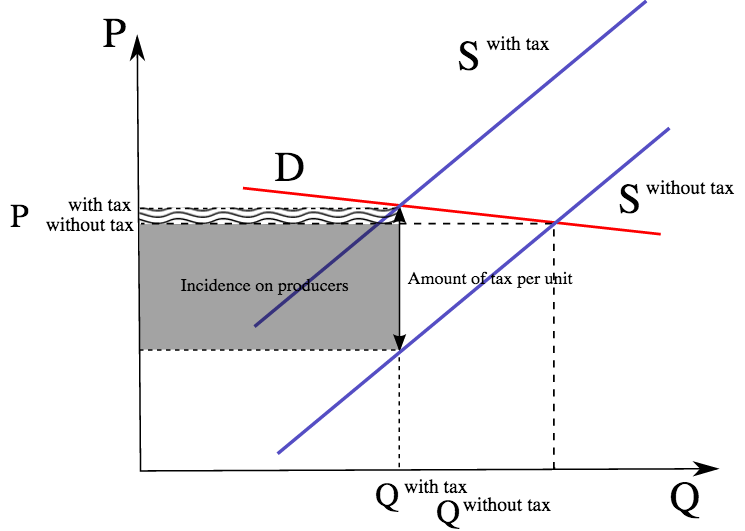
The following graph shows the annual supply and demand for this good as well as the supply curve shifted up by the amount of the proposed tax 100 per phone. In ugly-rose we can see that the consumers who have an inelastic demand loose a lot actually most of the total loss of surplus. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. The demand curve is the graphed curve demonstrating customers purchases. The consumers will now pay price P while producers will receive P P - t.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Well think it through with our supply and our perfectly inelastic demand curve. Since a tax can be viewed as raising the costs of production this could also be represented by a leftward shift of the supply curve where the new supply curve would intercept the demand at the new quantity Qt. While supply for the product has not changed all of the determinants of supply are the same producers incur higher cost which is why we will see a new equilibrium point further up the demand curve at a higher. Instead suppose the government taxes smartphones. First let us calculate the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity that were before the imposed tax.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
A subsidy is an amount of money given directly to firms by the government to. Similarly the price the seller obtains falls but by less than the tax. For simplicity Figure 510 omits the shift in the supply curve. Taxes increase the costs of producing and selling items which the business may pass on to the consumer in the form of higher prices. The pre-tax elasticity of demand and supply are calculated below.

AP is owned by the College Board which does not endorse this site or the above reviewStudy Questions1 Show supply demand with an equilibrium price and. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. Intersection of these two curves define equilibrium price and equilibrium quantities prior to the imposition of sales tax. On the following graph do for smartphones the same thing you did previously on the graph for leather jackets. Hence the new equilibrium quantity after tax can be found from equating P Q3 4 and P 20 Q so Q3 4 20 Q which gives QT 12.
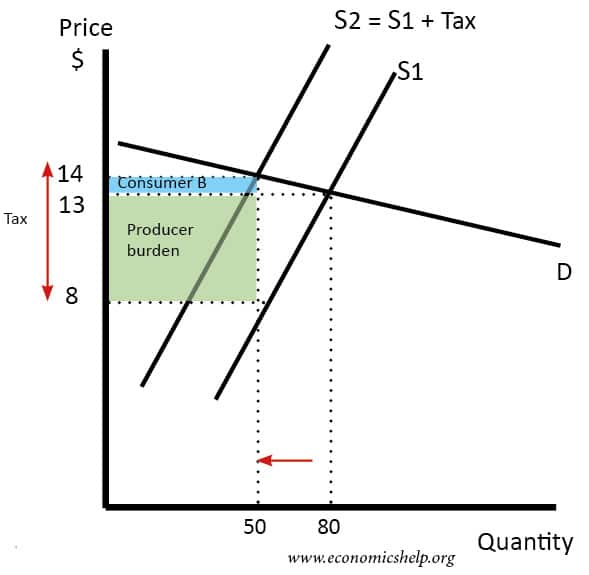 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. What ends up getting passed is a tax of 10 per vial. A tax causes consumer surplus and producer surplus profit to fall. Hence the new equilibrium quantity after tax can be found from equating P Q3 4 and P 20 Q so Q3 4 20 Q which gives QT 12. A tax increase does not affect the demand curve nor does it make supply or demand more or less elastic.
 Source: economics.stackexchange.com
Source: economics.stackexchange.com
AP is owned by the College Board which does not endorse this site or the above reviewStudy Questions1 Show supply demand with an equilibrium price and. If a new tax is enacted the demand curve may be expected to shift depending on the tax. Similarly the price the seller obtains falls but by less than the tax. Hence the new equilibrium quantity after tax can be found from equating P Q3 4 and P 20 Q so Q3 4 20 Q which gives QT 12. Also does excise tax increase or decrease supply.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
How do subsidies generally affect the supply curve Why. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. The variation of the surplus of each agents is quite telling. Quantity shifts from Q 0 to Q 1 after the excise tax is imposed on the production of Good A. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
You should also verify that these demand and supply curves imply a market price of 1 and quantity of 100 bgyr. First let us calculate the equilibrium price and equilibrium quantity that were before the imposed tax. The pre-tax elasticity of demand and supply are calculated below. Intersection of these two curves define equilibrium price and equilibrium quantities prior to the imposition of sales tax. Government subsidies reduce the cost of production and increase supply at.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. And similarly that point of intersection also tells us our quantity with the taxes. How do you calculate tax on supply and demand curve. Tax increases do not affect the demand curve nor do they increase supply or demand more or less. The pre-tax elasticity of demand and supply are calculated below.
 Source: tr.pinterest.com
Source: tr.pinterest.com
How do subsidies generally affect the supply curve Why. 430a we have drawn a perfectly elastic demand curve D and a normal-shaped supply curve S. A tax causes consumer surplus and producer surplus profit to fall. 125 125 from each sold kilogram of potatoes. Hence the new equilibrium quantity after tax can be found from equating P Q3 4 and P 20 Q so Q3 4 20 Q which gives QT 12.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
A tax increase does not affect the demand curve nor does it make supply or demand more or less elastic. A tax on buyers is thought to shift the demand curve to the leftreduce consumer demandbecause the price of goods relative to their value to consumers has gone up. Im just making it instead of a percentage Im just doing it as a fixed amount so that we get kind of a fixed shift in terms of the perceived supply price. Taxes increase the costs of producing and selling items which the business may pass on to the consumer in the form of higher prices. Thats where the existing demand curve intersects with this new shifted supply with tax curve.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
First we write the four conditions that must hold as given by equations 91a-d. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. Thats where the existing demand curve intersects with this new shifted supply with tax curve. Since a tax can be viewed as raising the costs of production this could also be represented by a leftward shift of the supply curve where the new supply curve would intercept the demand at the new quantity Qt. Im just making it instead of a percentage Im just doing it as a fixed amount so that we get kind of a fixed shift in terms of the perceived supply price.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
A tax on buyers is thought to shift the demand curve to the leftreduce consumer demandbecause the price of goods relative to their value to consumers has gone up. Similarly the price the seller obtains falls but by less than the tax. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. From the firms perspective taxes or regulations are an additional cost of production that shifts supply to the left leading the firm to produce a lower quantity at every given price. Intersection of these two curves define equilibrium price and equilibrium quantities prior to the imposition of sales tax.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
We can use these linear demand and supply curves to calculate the effect of a 50 cents per gallon tax. Taxation shifts a supply curve to the left. And plot the demand and supply curves if the government has imposed an indirect tax at a rate of. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. While supply for the product has not changed all of the determinants of supply are the same producers incur higher cost which is why we will see a new equilibrium point further up the demand curve at a higher.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The demand curve is the graphed curve demonstrating customers purchases. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. While supply for the product has not changed all of the determinants of supply are the same producers incur higher cost which is why we will see a new equilibrium point further up the demand curve at a higher. When costs of production increase the business will decrease its supply of the item.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The consumers will now pay price P while producers will receive P P - t. We can use these linear demand and supply curves to calculate the effect of a 50 cents per gallon tax. The pre-tax elasticity of demand and supply are calculated below. 430a we have drawn a perfectly elastic demand curve D and a normal-shaped supply curve S. With 4 tax on producers the supply curve after tax is P Q3 4.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The demand curve because of the tax t. QD 150 - 50Pb Demand QS 60 40Ps. The demand curve because of the tax t. A tax increase does not affect the demand curve nor does it make supply or demand more or less elastic. How do you calculate tax on supply and demand curve.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title taxes on supply and demand curve by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.