Your Taxation supply and demand curve images are ready. Taxation supply and demand curve are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Taxation supply and demand curve files here. Download all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re searching for taxation supply and demand curve images information related to the taxation supply and demand curve topic, you have visit the ideal blog. Our website always gives you hints for refferencing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more enlightening video content and images that match your interests.
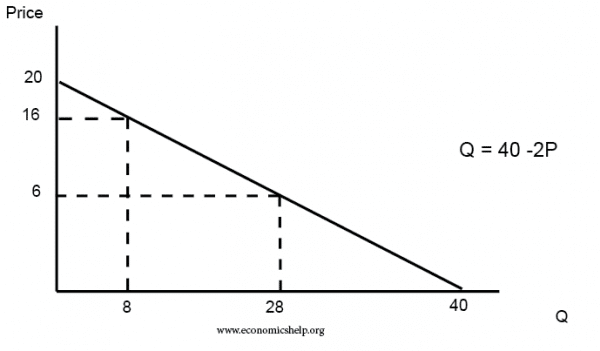
Taxation Supply And Demand Curve. Lets suppose that the function of demand of potatoes is given by Q_D 20 P QD 20P and the function of the supply of potatoes is given by Q_S 4P 5 QS 4P 5. It is clear that the taxation first will have t he highest impact on demand curve because at any level of the price the producer w ill have its supply amount to the market and it is n atural to. However demand being perfectly elastic price is not altered. At a given level of demand taxations reduction of incentives will result in a decrease in the production of goods or services.
 Taxation Influence On Supply And Demand From assignmentexpert.com
Taxation Influence On Supply And Demand From assignmentexpert.com
A relatively less elastic demand implies that consumers are not highly responsive to changes in price. Taxation has an enormous impact on. This implies that the equilibrium quantity after imposition. The loss of value for both buyers and sellers is called the deadweight loss of taxation. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. Taxes impact both the supply and demand curves.
The variation of the surplus of each agents is quite telling.
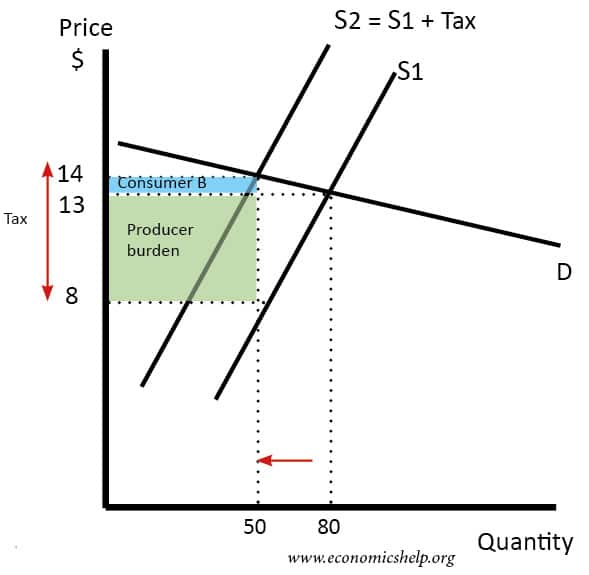
What is a subsidy example. The more elastic the supply curve the easier it is for sellers to reduce the quantity sold instead of taking lower prices. The loss of value for both buyers and sellers is called the deadweight loss of taxation. Supply curve can be given as Qs 5400 300Px new supply curve for tax implementation Therefore the new equilibrium price could be determined with equalising new supply curve and the demand curve as 5400 300 Px 12000 200 Px Px 6600500 1320 and the new equilibrium quantity Q 5400 300 132 9360 units. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. When the tax is introduced the consumer surplus orange and producer surplus blue shrink while deadweight loss purple the inefficiency caused by the tax increases.
 Source: sanandres.esc.edu.ar
Source: sanandres.esc.edu.ar
It is clear that the taxation first will have t he highest impact on demand curve because at any level of the price the producer w ill have its supply amount to the market and it is n atural to. Supply curve can be given as Qs 5400 300Px new supply curve for tax implementation Therefore the new equilibrium price could be determined with equalising new supply curve and the demand curve as 5400 300 Px 12000 200 Px Px 6600500 1320 and the new equilibrium quantity Q 5400 300 132 9360 units. Also how does tax affect supply and demand. As shown above the equilibrium price will rise and the equilibrium quantity will fall. The demand curve because of the tax t.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
A tax on the good does not lead to a large change in quantity demanded. In the model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply a tax rate increase will shift the aggregate demand curve to the left by an amount equal to the initial change in aggregate expenditures induced by the tax rate boost times the new value of the multiplier. Tax increases do not affect the demand curve nor do they increase supply or demand more or less. Tax increases If the government increases the tax on a good that shifts the supply curve to the left consumer prices rise and sellers prices fall. Calculate the elasticities of supply and demand at the original pre-tax equilibrium and verify that the relative elasticities of demand and supply are consistent with your answer to b ie.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
In a market where both the demand and supply are very elastic the imposition of an excise tax generates low revenue. A subsidy is an amount of money given directly to firms by the government to encourage production and consumption. What causes a decrease in aggregate demand. At a given level of demand taxations reduction of incentives will result in a decrease in the production of goods or services. Taxes impact both the supply and demand curves.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Supply curve can be given as Qs 5400 300Px new supply curve for tax implementation Therefore the new equilibrium price could be determined with equalising new supply curve and the demand curve as 5400 300 Px 12000 200 Px Px 6600500 1320 and the new equilibrium quantity Q 5400 300 132 9360 units. Here S T is the post-tax supply curve. Your instructor asks you to determine P_E P E and Q_E QE. The definition of a subsidy is money or grants given by the government to support a project. Tax increases If the government increases the tax on a good that shifts the supply curve to the left consumer prices rise and sellers prices fall.
 Source: tutorsonnet.com
Source: tutorsonnet.com
Taxes are among the market and regulatory conditions that define the demand curve. Lets suppose that the function of demand of potatoes is given by Q_D 20 P QD 20P and the function of the supply of potatoes is given by Q_S 4P 5 QS 4P 5. A tax increase does not affect the demand curve nor does it make supply or demand more or less elastic. Here S T is the post-tax supply curve. Also how does tax affect supply and demand.
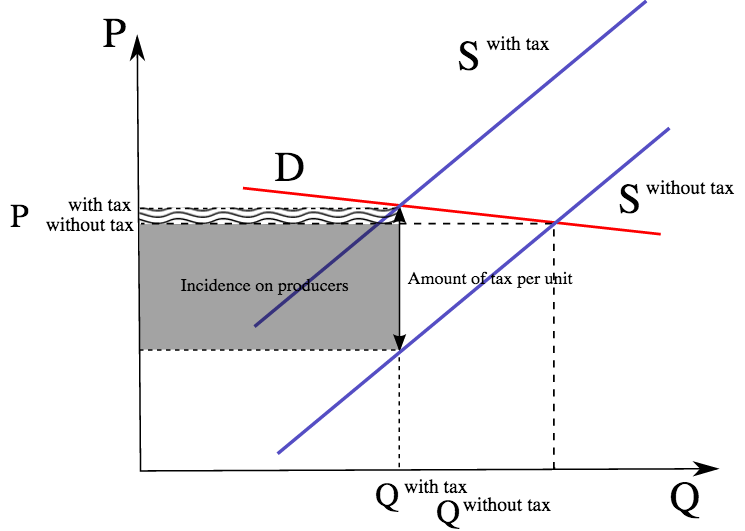
With 4 tax on producers the supply curve after tax is P Q3 4. Here S T is the post-tax supply curve. How do you calculate tax on supply and demand curve. If we have a completely unfettered market no intervention no taxes nothing like that then we see we have an equilibrium price and an equilibrium quantity. In the model of aggregate demand and aggregate supply a tax rate increase will shift the aggregate demand curve to the left by an amount equal to the initial change in aggregate expenditures induced by the tax rate boost times the new value of the multiplier.

After the imposition of sales tax supply curve shifts to the leftward direction. Your instructor asks you to determine P_E P E and Q_E QE. A subsidy is an amount of money given directly to firms by the government to encourage production and consumption. Excise taxes tend to be thought to hurt mainly the specific industries they target. This implies that the equilibrium quantity after imposition.
 Source: economics.stackexchange.com
Source: economics.stackexchange.com
The demand curve because of the tax t. Also how does tax affect supply and demand. Here S T is the post-tax supply curve. The difference between the two supply curves S and S T determines the volume of tax. What causes a decrease in aggregate demand.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
It is clear that the taxation first will have t he highest impact on demand curve because at any level of the price the producer w ill have its supply amount to the market and it is n atural to. The demand curve because of the tax t. Taxes impact both the supply and demand curves. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. If we have a completely unfettered market no intervention no taxes nothing like that then we see we have an equilibrium price and an equilibrium quantity.
 Source: hifreqecon.com
Source: hifreqecon.com
With 4 tax on producers the supply curve after tax is P Q3 4. Supply curve can be given as Qs 5400 300Px new supply curve for tax implementation Therefore the new equilibrium price could be determined with equalising new supply curve and the demand curve as 5400 300 Px 12000 200 Px Px 6600500 1320 and the new equilibrium quantity Q 5400 300 132 9360 units. This implies that the equilibrium quantity after imposition. Shifts from D to D. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax.

Taxes cause a buyer to pay more for something and suppliers to receive less. Rewrite the demand and supply equation as P 20 Q and P Q3. With 4 tax on producers the supply curve after tax is P Q3 4. At a given level of demand taxations reduction of incentives will result in a decrease in the production of goods or services. The difference between the two supply curves S and S T determines the volume of tax.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
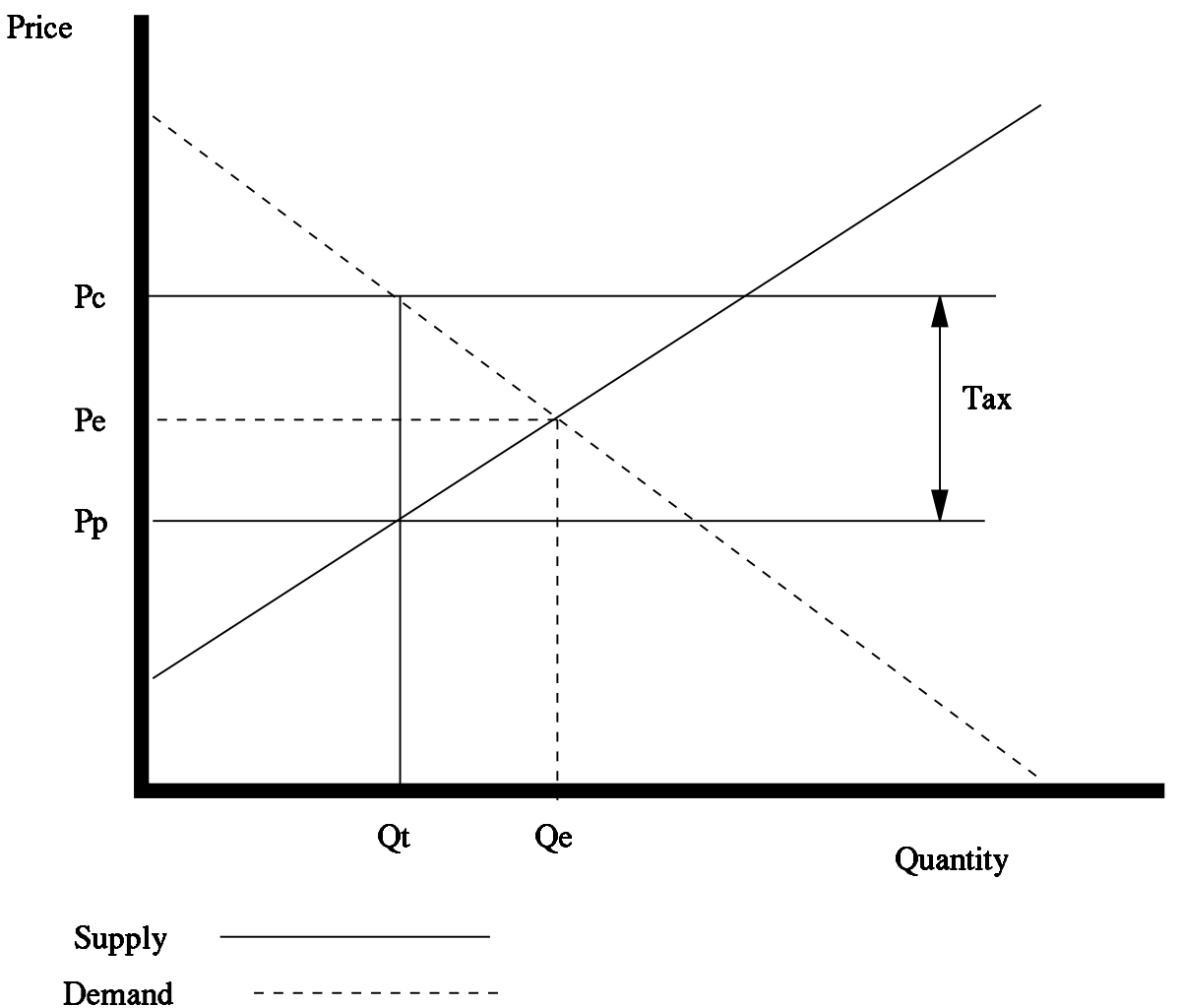
Your instructor asks you to determine P_E P E and Q_E QE. However demand being perfectly elastic price is not altered. Hence the new equilibrium quantity after tax can be found from equating P Q3 4 and P 20 Q so Q3 4 20 Q which gives QT 12. The consumers will now pay price P while producers will receive P P t. As sales tax causes the supply curve to shift inward it has a secondary effect on the equilibrium price for a product.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
Calculate the elasticities of supply and demand at the original pre-tax equilibrium and verify that the relative elasticities of demand and supply are consistent with your answer to b ie. Hence the new equilibrium quantity after tax can be found from equating P Q3 4 and P 20 Q so Q3 4 20 Q which gives QT 12. Lets suppose that the function of demand of potatoes is given by Q_D 20 P QD 20P and the function of the supply of potatoes is given by Q_S 4P 5 QS 4P 5. A subsidy is an amount of money given directly to firms by the government to encourage production and consumption. Rewrite the demand and supply equation as P 20 Q and P Q3.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
What causes a decrease in aggregate demand. How do subsidies generally affect the supply curve Why. Elastic Supply and Inelastic Demand This is the case of having an elastic supply and relatively inelastic demand. What causes a decrease in aggregate demand. In other words pre-tax and post-tax price P P T are the same.
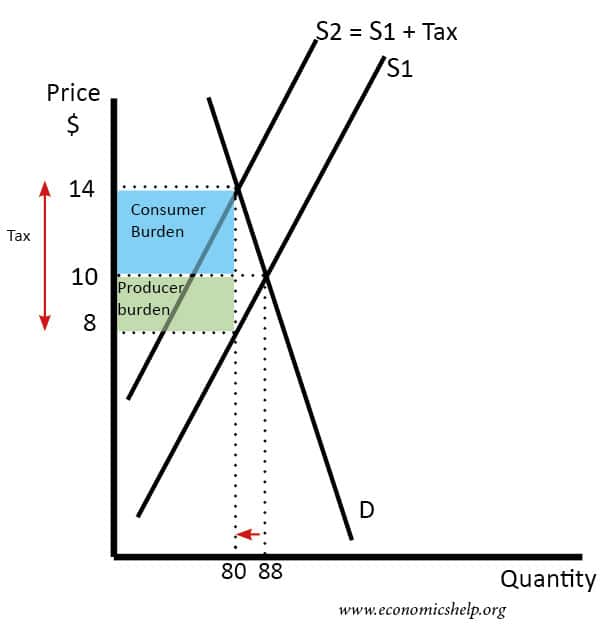 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
The consumers will now pay price P while producers will receive P P t. As sales tax causes the supply curve to shift inward it has a secondary effect on the equilibrium price for a product. The effect of a specific per unit subsidy is to shift the supply curve vertically. As shown above the equilibrium price will rise and the equilibrium quantity will fall. The new demandsupply curve is not drawn as which curve will be shifted depends on who is to be taxed and as we already know the effect of taxing either consumers or sellers will have an equivalent effect.
 Source: assignmentexpert.com
Source: assignmentexpert.com
The consumers will now pay price P while producers will receive P P t. What causes a decrease in aggregate demand. A tax increase does not affect the demand curve nor does it make supply or demand more or less elastic. Similarly the price the seller obtains falls but by less than the tax. As shown above the equilibrium price will rise and the equilibrium quantity will fall.
 Source: tutorsonnet.com
Source: tutorsonnet.com
Shifts from D to D. The difference between the two supply curves S and S T determines the volume of tax. As shown above the equilibrium price will rise and the equilibrium quantity will fall. For a given supply curve more inelastic demand results in higher tax revenues and lower deadweight loss associated with a tax increase. The effect of a specific per unit subsidy is to shift the supply curve vertically.
 Source: learneconomicsonline.com
Source: learneconomicsonline.com
When the tax is introduced the consumer surplus orange and producer surplus blue shrink while deadweight loss purple the inefficiency caused by the tax increases. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. Similarly the price the seller obtains falls but by less than the tax. If a new tax is enacted the demand curve may be expected to shift depending on the tax. If we have a completely unfettered market no intervention no taxes nothing like that then we see we have an equilibrium price and an equilibrium quantity.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title taxation supply and demand curve by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.