Your Tax suppply and tax demand images are available. Tax suppply and tax demand are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Tax suppply and tax demand files here. Get all free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for tax suppply and tax demand pictures information connected with to the tax suppply and tax demand interest, you have pay a visit to the right site. Our site frequently provides you with hints for viewing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly surf and locate more enlightening video articles and images that fit your interests.
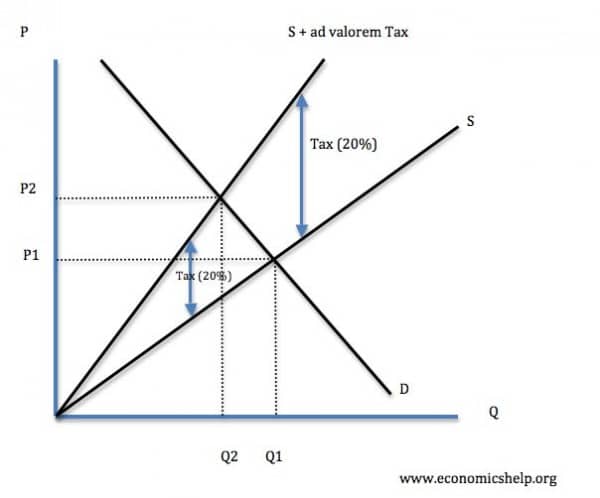
Tax Suppply And Tax Demand. A tax causes consumer surplus and producer surplus profit to fall. AP is owned by the College Board which does not endorse this site or the above reviewStudy Questions1 Show supply demand with an equilibrium price and. This is illustrated in Figure 53 Effect of a tax on equilibrium. Now we should express the price P without taxation through the new price level P_1 when the.
 Ad Valorem Tax Economics Help From economicshelp.org
Ad Valorem Tax Economics Help From economicshelp.org
A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. When the tax is imposed the price that the buyer pays must exceed. A tax causes consumer surplus and producer surplus profit to fall. Postdoctoral Researcher on Inclusive Governance for Resilient Indonesian Slums. Thats where the existing demand curve intersects with this new shifted supply with tax curve. Corporation tax was the fourth largest tax in 2018 raising 60 billion for the government.
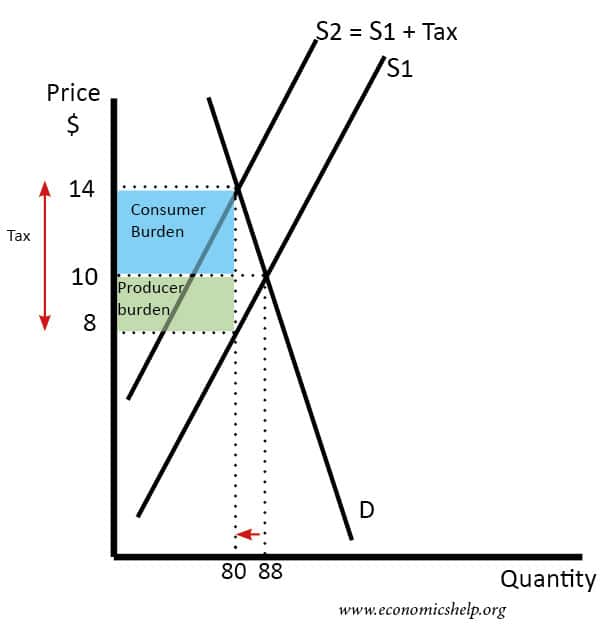
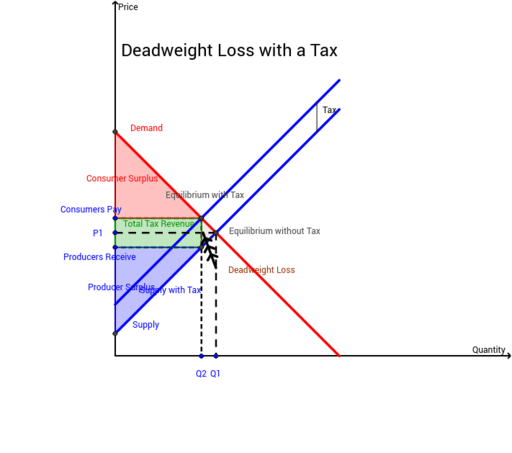
The consumers will still pay P and the suppliers will pay the tax thus receiving P.
Also Know does tax affect supply or demand. It is inadequate to address the projected consequences of a proposed tax cut utilizing demand-side logic when a supply. AP is owned by the College Board which does not endorse this site or the above reviewStudy Questions1 Show supply demand with an equilibrium price and. While supply for the product has not changed all of the determinants of supply are the same producers incur higher cost which is why we will see a new equilibrium point further up the demand curve at a higher. Qd 20-2125P 20-25P. Therefore what remains is an upwards shift that will lead to increased.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
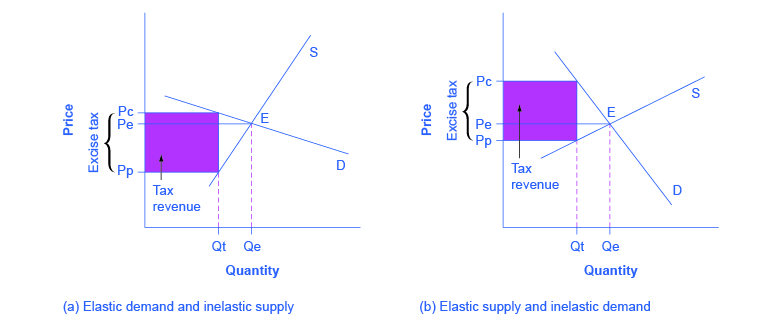
When supply is more elastic than demand buyers bear most of the tax burden. A tax causes consumer surplus and producer surplus profit to fall. Indonesian cities are facing both societal and ecological challenges especially in slum areas. If the supply curve is relatively flat the supply is price elastic. The tax revenue is given by the shaded area which is obtained by multiplying the tax per unit by the total quantity sold Qt.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
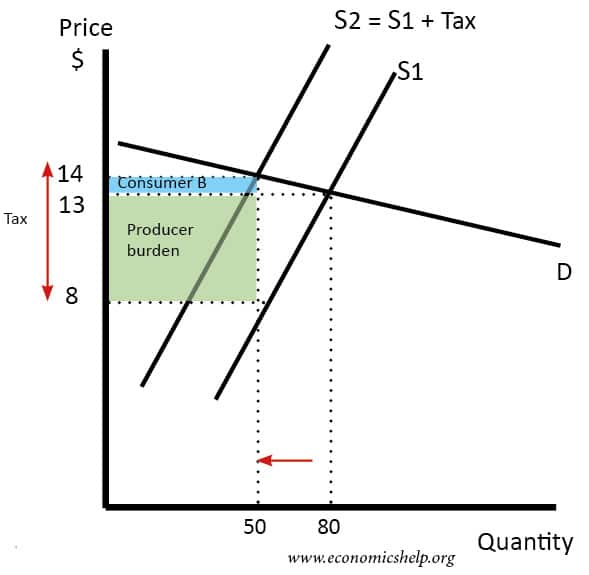
In both cases the effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. If the tax is imposed on the suppliers then the prices will be the same. As sales tax causes the supply curve to shift inward it has a secondary effect on the equilibrium price for a product. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. Thats where the existing demand curve intersects with this new shifted supply with tax curve.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. The main corporation tax rate is being lowered to 17 in April 2020. Tax revenue is larger the more inelastic the demand and supply are. When supply is more elastic than demand buyers bear most of the tax burden.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. Indonesian cities are facing both societal and ecological challenges especially in slum areas. - Proportional taxes work the same as per unit taxes except that you now multiply instead of addsubtract in relation to P - If the government imposed a 25 proportional tax on buyers what happens to demand. The main rate of corporation tax in the UK is 19. Assuming constant demand elasticity the greater the supply elasticity the greater is the burden on buyers.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The Effect of Tax on the Demand Curve. As a postdoc you will be part of an international Dutch-Indonesian team that will investigate practices of inclusive and collaborative governance in slum areas and work. The tax incidence depends on the relative price elasticity of supply and demand. If the supply is inelastic and the demand elastic than the roles are reverse the producers ending up bearing a heavier part of the tax. The relative effect on buyers and sellers is known as the incidence of the tax.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
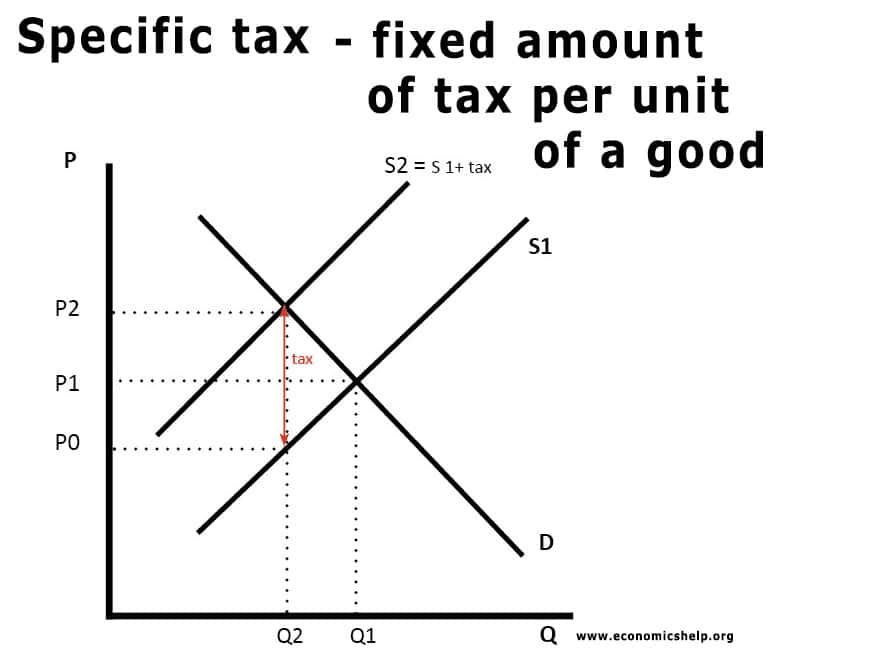
- Proportional taxes work the same as per unit taxes except that you now multiply instead of addsubtract in relation to P - If the government imposed a 25 proportional tax on buyers what happens to demand. The tax paid by the consumer is. Extensive study in economics has considered this issue and theories exist to explain the relationship between taxes and the demand curve. Since the tax is fixed per unit sold and not a percentage charge then the slope of the supply curve should not change. This is illustrated in Figure 53 Effect of a tax on equilibrium.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
Tax increases If the government increases the tax on a good that shifts the supply curve to the left consumer prices rise and sellers prices fall. Assuming constant demand elasticity the greater the supply elasticity the greater is the burden on buyers. Tax revenue is larger the more inelastic the demand and supply are. The tax incidence on the consumers is given by the difference between the price paid Pc and the initial equilibrium price Pe. If the supply is inelastic and the demand elastic than the roles are reverse the producers ending up bearing a heavier part of the tax.

AP is owned by the College Board which does not endorse this site or the above reviewStudy Questions1 Show supply demand with an equilibrium price and. As a postdoc you will be part of an international Dutch-Indonesian team that will investigate practices of inclusive and collaborative governance in slum areas and work. When demand is more elastic than supply producers bear most of the cost of the tax. When the tax is imposed the price that the buyer pays must exceed. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. Economists are often concerned with the effect of government policies like taxes or subsidies on the interaction of supply and demand. The tax incidence depends on the relative price elasticity of supply and demand. The relative effect on buyers and sellers is known as the incidence of the tax. When the tax is imposed the price that the buyer pays must exceed.
 Source: geogebra.org
Source: geogebra.org
Since the tax is fixed per unit sold and not a percentage charge then the slope of the supply curve should not change. Tax increases If the government increases the tax on a good that shifts the supply curve to the left consumer prices rise and sellers prices fall. This video goes over some brief examples showing how a tax on sellers and then a tax on consumers will affect the efficient equilibrium in a supply and deman. In both cases the effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. The distinction between demand-side and supply-side tax cuts is important.

Corporation tax was the fourth largest tax in 2018 raising 60 billion for the government. If the supply is inelastic and the demand elastic than the roles are reverse the producers ending up bearing a heavier part of the tax. The tax paid by the consumer is. Thats where the existing demand curve intersects with this new shifted supply with tax curve. This is illustrated in Figure 53 Effect of a tax on equilibrium.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
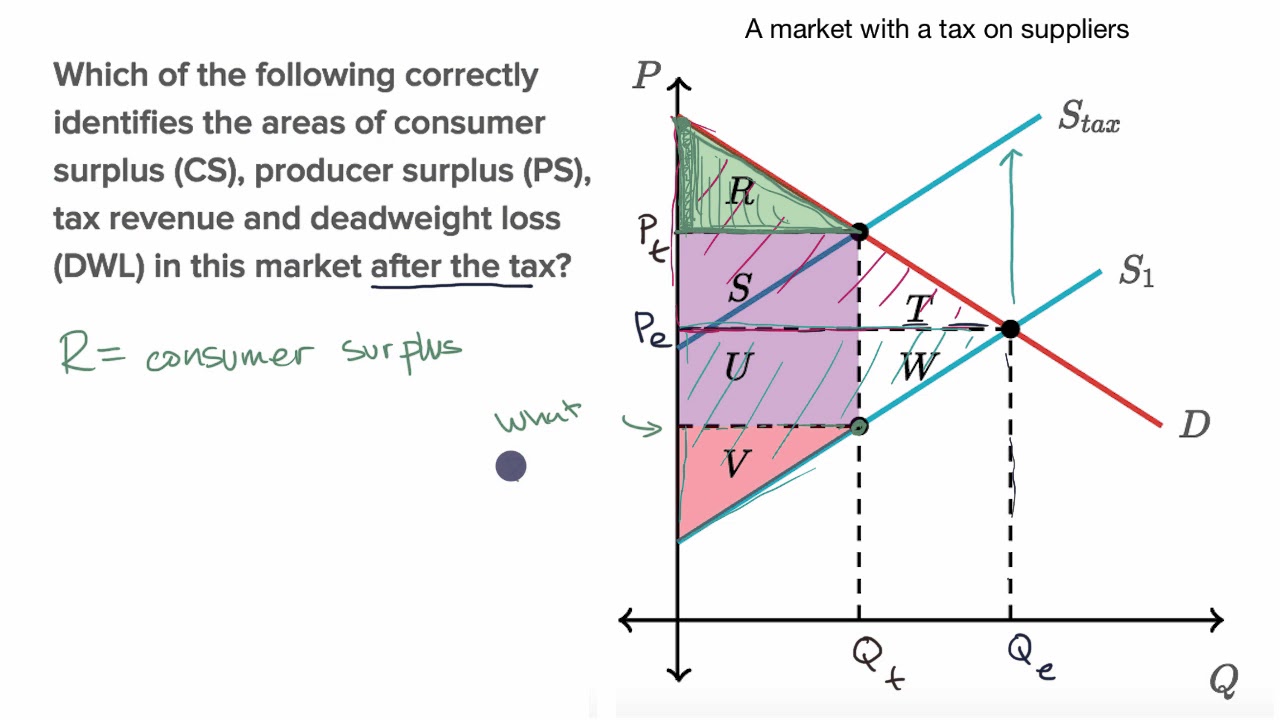
A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. It is inadequate to address the projected consequences of a proposed tax cut utilizing demand-side logic when a supply. The tax incidence depends on the relative price elasticity of supply and demand. In the graph above the total tax paid by the producer and the consumer is equal to P 0 P 2. And similarly that point of intersection also tells us our quantity with the taxes.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
If the government increases the tax on a good that shifts the supply curve to the left the consumer price increases and sellers price decreasesA tax increase does not affect the demand curve nor does it make supply or demand more or less elastic. If the tax is imposed on the suppliers then the prices will be the same. Since the tax is fixed per unit sold and not a percentage charge then the slope of the supply curve should not change. Assuming constant demand elasticity the greater the supply elasticity the greater is the burden on buyers. Economists are often concerned with the effect of government policies like taxes or subsidies on the interaction of supply and demand.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. - Proportional taxes work the same as per unit taxes except that you now multiply instead of addsubtract in relation to P - If the government imposed a 25 proportional tax on buyers what happens to demand. As a postdoc you will be part of an international Dutch-Indonesian team that will investigate practices of inclusive and collaborative governance in slum areas and work. Tax increases do not affect the demand curve nor do they increase supply or demand more or less. Tax increases If the government increases the tax on a good that shifts the supply curve to the left consumer prices rise and sellers prices fall.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Extensive study in economics has considered this issue and theories exist to explain the relationship between taxes and the demand curve. Thats where the existing demand curve intersects with this new shifted supply with tax curve. If the supply is inelastic and the demand elastic than the roles are reverse the producers ending up bearing a heavier part of the tax. And similarly that point of intersection also tells us our quantity with the taxes. In the case of an indirect tax we need to modify our function of supply since the tax is collected from the sellers the demand function will not change.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In the case of an indirect tax we need to modify our function of supply since the tax is collected from the sellers the demand function will not change. If the supply curve is relatively flat the supply is price elastic. Therefore what remains is an upwards shift that will lead to increased. Taxes on supply and demand The VAT on the suppliers will shift the supply curve to the left symbolizing a reduction in supply similar to firms facing higher input costs. AP is owned by the College Board which does not endorse this site or the above reviewStudy Questions1 Show supply demand with an equilibrium price and.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
The main corporation tax rate is being lowered to 17 in April 2020. If the supply curve is relatively flat the supply is price elastic. In the case of an indirect tax we need to modify our function of supply since the tax is collected from the sellers the demand function will not change. Tax increases If the government increases the tax on a good that shifts the supply curve to the left consumer prices rise and sellers prices fall. This is illustrated in Figure 53 Effect of a tax on equilibrium.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In both cases the effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. Implementing dismalscience comment suggestion the unit tax burdens the suppliers. In both cases the effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. Figure 316 Elastic Demand and Inelastic Supply. The tax incidence on the consumers is given by the difference between the price paid Pc and the initial equilibrium price Pe.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title tax suppply and tax demand by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.