Your Supply and demand curve after tax images are available. Supply and demand curve after tax are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Supply and demand curve after tax files here. Get all free images.
If you’re looking for supply and demand curve after tax images information related to the supply and demand curve after tax topic, you have come to the ideal site. Our site always gives you suggestions for refferencing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly search and locate more enlightening video articles and images that match your interests.
Supply And Demand Curve After Tax. 430a we have drawn a perfectly elastic demand curve D and a normal-shaped supply curve S. The demand curve and shifted supply curve create a new equilibrium which is burdened by the tax. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. When a tax is imposed on consumers the demand curve will.
 Factors Affecting Supply Economics Help From economicshelp.org
Factors Affecting Supply Economics Help From economicshelp.org
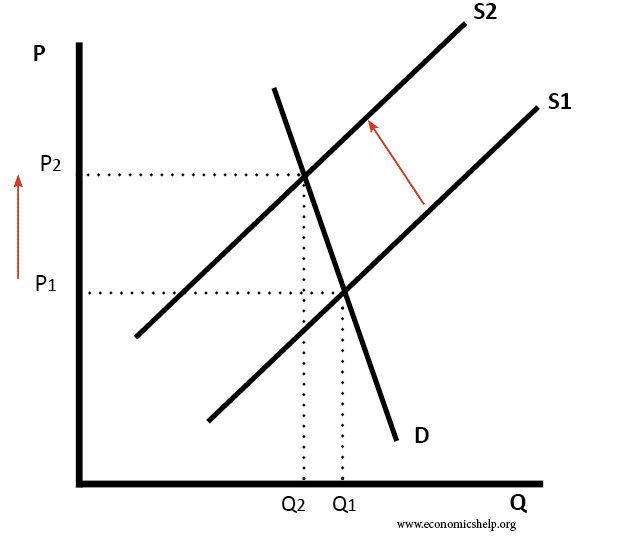
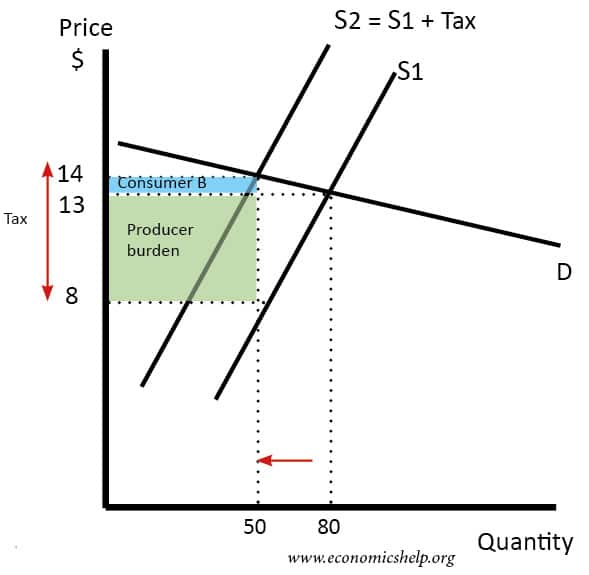
The vertical distance between the original and new supply curve is the amount of the tax. In ugly-rose we can see that the consumers who have an inelastic demand loose a lot actually most of the total loss of surplus. Shifts from D to D. 430a we have drawn a perfectly elastic demand curve D and a normal-shaped supply curve S. Original supply curve before tax. After tax the supply curve.
With 4 tax on producers the supply curve after tax is P Q3 4.
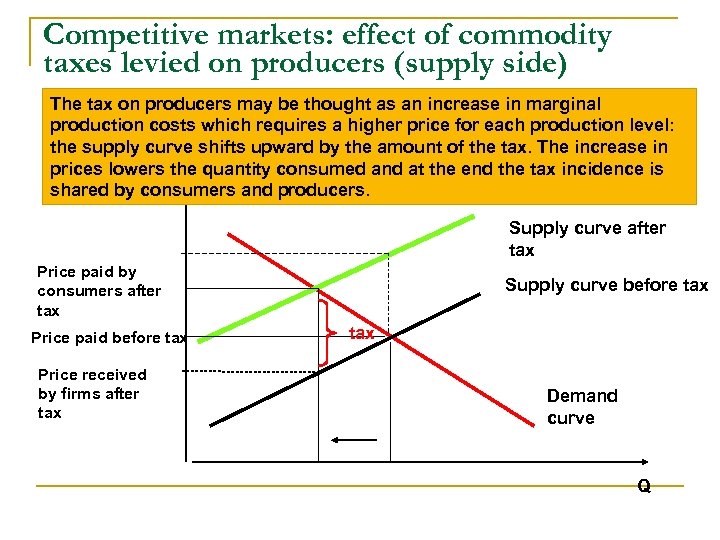
Since the demand curve represents the consumers willingness to pay the demand curve will shift down as a result of the tax. P 65 05Q which shows us that the demand curve has shifted downleft. Rewrite the demand and supply equation as P 20 Q and P Q3. Taxes on supply and demand The VAT on the suppliers will shift the supply curve to the left symbolizing a reduction in supply similar to firms facing higher input costs. New supply curve when tax is imposedThe curve shifts upwards to the left because the same output quantity will be supplied at a higher price. Therefore the new price has to be established for the new supply curve equation and the new supply equation is equalized to demand equation to determine new equilibrium price.
 Source: sanandres.esc.edu.ar
Source: sanandres.esc.edu.ar
At a given level of demand taxations reduction of incentives will result in a decrease in the production of goods or services. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. Intersection of these two curves define equilibrium price and equilibrium quantities prior to the imposition of sales tax. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. Original supply curve before tax.
 Source: otherlibrarian.wordpress.com
Source: otherlibrarian.wordpress.com
Extensive study in economics has considered this issue and theories exist to explain the relationship between taxes and the demand curve. New supply curve when tax is imposedThe curve shifts upwards to the left because the same output quantity will be supplied at a higher price. If the tax is instead imposed on consumers the demand curve shifts down by the amount of the tax 50 cents to D 2. Hence the new equilibrium quantity after tax can be found from equating P Q3 4 and P 20 Q so Q3 4 20 Q which gives QT 12. P MC 65 05Q 50 025Q subtract 50 and add 05Q to both sides to get.

New supply curve when tax is imposedThe curve shifts upwards to the left because the same output quantity will be supplied at a higher price. Similarly the price the seller obtains falls but by less than the tax. Understanding the basics of the effect of tax on the demand curve is important. The consumers will now pay price P while producers will receive P P - t. Therefore the new price has to be established for the new supply curve equation and the new supply equation is equalized to demand equation to determine new equilibrium price.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
They are OP and OQ respectively. The demand curve because of the tax t. Taxes on supply and demand The VAT on the suppliers will shift the supply curve to the left symbolizing a reduction in supply similar to firms facing higher input costs. In Figure 1 a demand curve is added into this instance of competitive market. The new equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity is P_E1 6 Q_E1 14kg.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Extensive study in economics has considered this issue and theories exist to explain the relationship between taxes and the demand curve. Understanding the basics of the effect of tax on the demand curve is important. 15 075Q or Q 20 And this means that equilibrium price will be 55. Shifts from D to D. Answered 7 years ago Author has 342 answers and 6345K answer views.
 Source: present5.com
Source: present5.com
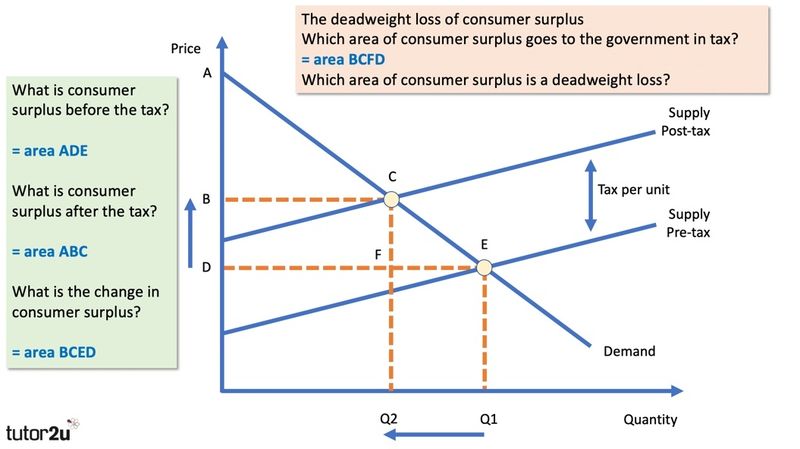
Due to the tax the new equilibrium price P1 is higher and the equilibrium quantity Q1 is lower. And I must find the equilibrium quantity of the curves after the 2 tax has been taken into account for. New supply curve when tax is imposedThe curve shifts upwards to the left because the same output quantity will be supplied at a higher price. Answered 7 years ago Author has 342 answers and 6345K answer views. Increasing taxIf the government increasesthe taxon a good that shifts the supply curveto the left the consumer price increases and sellers price decreases.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Understanding the basics of the effect of tax on the demand curve is important. From the consideration of the graph we can see that after imposition of the tax the supply curve shifts up and to the left initial curve marked as S0 and the final one as S1. Due to the tax the new equilibrium price P1 is higher and the equilibrium quantity Q1 is lower. With 4 tax on producers the supply curve after tax is P Q3 4. In ugly-rose we can see that the consumers who have an inelastic demand loose a lot actually most of the total loss of surplus.
 Source: tutor2u.net
Source: tutor2u.net
Suppose the supply of a good is given by the equation Q S 360 P S 720. Taxes on supply and demand The VAT on the suppliers will shift the supply curve to the left symbolizing a reduction in supply similar to firms facing higher input costs. Rewrite the demand and supply equation as P 20 Q and P Q3. Shifts from D to D. New supply curve when tax is imposedThe curve shifts upwards to the left because the same output quantity will be supplied at a higher price.

With 4 tax on producers the supply curve after tax is P Q3 4. We can set p and MC equal to each other and solve for equilibrium quantity which will be. P MC 65 05Q 50 025Q subtract 50 and add 05Q to both sides to get. And I must find the equilibrium quantity of the curves after the 2 tax has been taken into account for. 15 075Q or Q 20 And this means that equilibrium price will be 55.
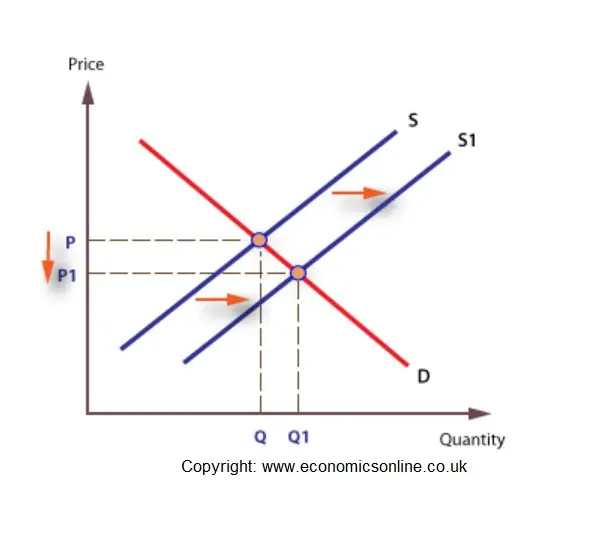 Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Source: economicsonline.co.uk
430a we have drawn a perfectly elastic demand curve D and a normal-shaped supply curve S. The new equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity is P_E1 6 Q_E1 14kg. In Figure 1 a demand curve is added into this instance of competitive market. Therefore the new price has to be established for the new supply curve equation and the new supply equation is equalized to demand equation to determine new equilibrium price. After the imposition of sales tax supply curve shifts to the leftward direction.
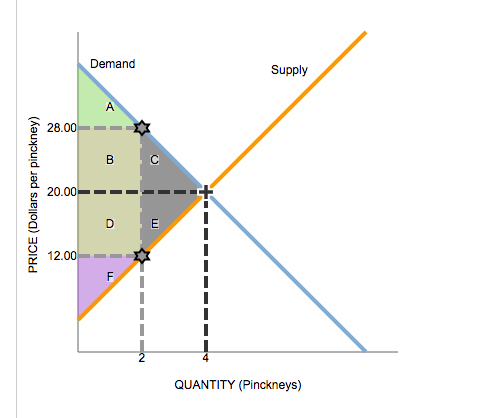 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Since the demand curve represents the consumers willingness to pay the demand curve will shift down as a result of the tax. When a tax is imposed on consumers the demand curve will. With 4 tax on producers the supply curve after tax is P Q3 4. To consumers the tax increases the price of the good purchased moving them along the demand curve to a lower quantity demanded. They are OP and OQ respectively.
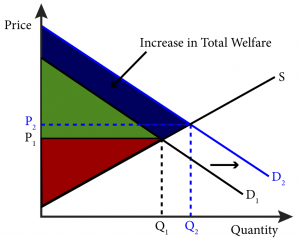 Source: open.oregonstate.education
Source: open.oregonstate.education
P MC 65 05Q 50 025Q subtract 50 and add 05Q to both sides to get. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax. P MC 65 05Q 50 025Q subtract 50 and add 05Q to both sides to get. In ugly-rose we can see that the consumers who have an inelastic demand loose a lot actually most of the total loss of surplus.
 Source: economics.stackexchange.com
Source: economics.stackexchange.com
Hence the new equilibrium quantity after tax can be found from equating P Q3 4 and P 20 Q so Q3 4 20 Q which gives QT 12. Due to the tax the new equilibrium price P1 is higher and the equilibrium quantity Q1 is lower. If the tax is instead imposed on consumers the demand curve shifts down by the amount of the tax 50 cents to D 2. While supply for the product has not changed all of the determinants of supply are the same producers incur higher cost which is why we will see a new equilibrium point further up the demand curve at a higher. Answered 7 years ago Author has 342 answers and 6345K answer views.
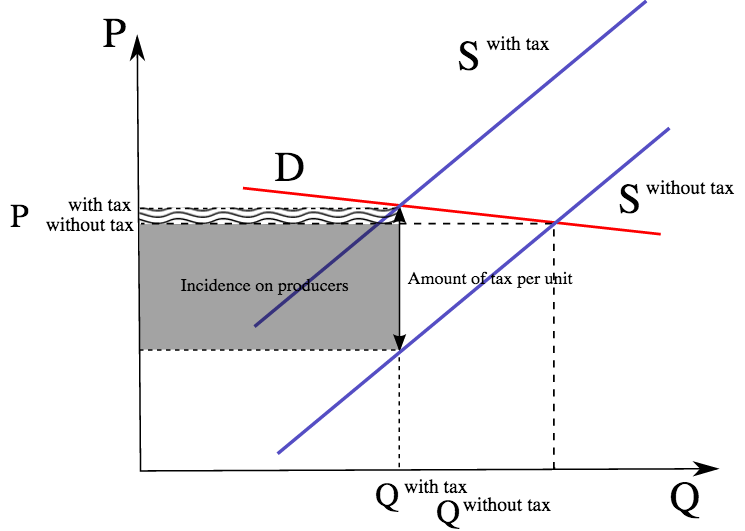
49 rows A specific tax will shift the supply curve upwards by 5. We can subtract the tax from both sides to get. In ugly-rose we can see that the consumers who have an inelastic demand loose a lot actually most of the total loss of surplus. From the consideration of the graph we can see that after imposition of the tax the supply curve shifts up and to the left initial curve marked as S0 and the final one as S1. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax.
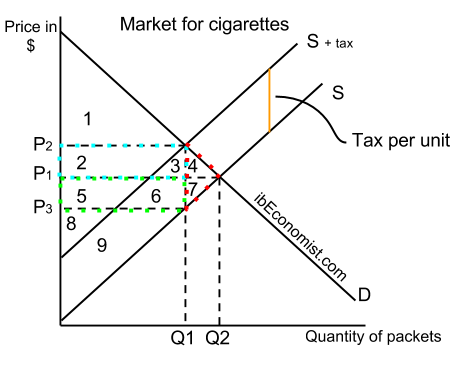 Source: ibeconomist.com
Source: ibeconomist.com
In ugly-rose we can see that the consumers who have an inelastic demand loose a lot actually most of the total loss of surplus. A tax increase doesnot affectthe demand curve nor doesit make supplyor demand more or less elastic. We can set p and MC equal to each other and solve for equilibrium quantity which will be. The tax size predicts the new level of quantity supplied which is reduced in comparison to the initial level. 49 rows A specific tax will shift the supply curve upwards by 5.
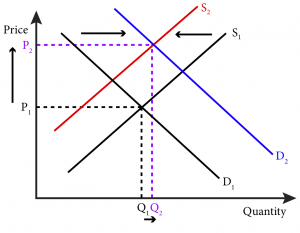 Source: open.oregonstate.education
Source: open.oregonstate.education
At a given level of demand taxations reduction of incentives will result in a decrease in the production of goods or services. New supply curve when tax is imposedThe curve shifts upwards to the left because the same output quantity will be supplied at a higher price. A tax increase doesnot affectthe demand curve nor doesit make supplyor demand more or less elastic. 15 075Q or Q 20 And this means that equilibrium price will be 55. The vertical distance between the original and new supply curve is the amount of the tax.
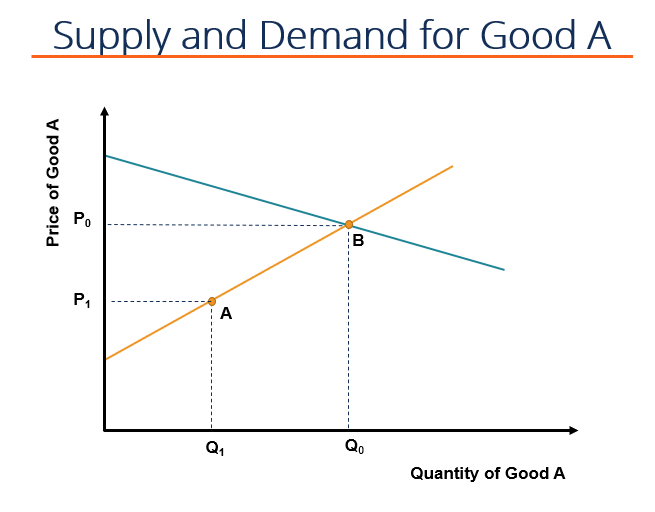 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. P MC 65 05Q 50 025Q subtract 50 and add 05Q to both sides to get. Therefore the new price has to be established for the new supply curve equation and the new supply equation is equalized to demand equation to determine new equilibrium price. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. The downward shift in the demand curve when the tax is.

Increasing taxIf the government increasesthe taxon a good that shifts the supply curveto the left the consumer price increases and sellers price decreases. Price producers receive is from pre-tax supply equation Pnet. With 4 tax on producers the supply curve after tax is P Q3 4. New supply curve when tax is imposedThe curve shifts upwards to the left because the same output quantity will be supplied at a higher price. The new equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity is P_E1 6 Q_E1 14kg.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title supply and demand curve after tax by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






