Your Substitution elasticity of demand formula images are available in this site. Substitution elasticity of demand formula are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Substitution elasticity of demand formula files here. Get all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re searching for substitution elasticity of demand formula pictures information connected with to the substitution elasticity of demand formula interest, you have come to the ideal blog. Our website always provides you with hints for refferencing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly search and locate more enlightening video content and images that match your interests.
Substitution Elasticity Of Demand Formula. Define x 1 and x 2 as Gross Substitutes if an increase in the price of x 2 leads to an increase in the demand for x 1. Where w and r are the point of the inputs. Own price elasticity of demand OPE Change in quantity demanded of Product X Change of price of Product X. These goods are substitutes because the Cross Price Elasticity of Demand is above 0 Positive.
 Cross Price Elasticity Of Demand I A Level And Ib Economics Youtube From m.youtube.com
Cross Price Elasticity Of Demand I A Level And Ib Economics Youtube From m.youtube.com
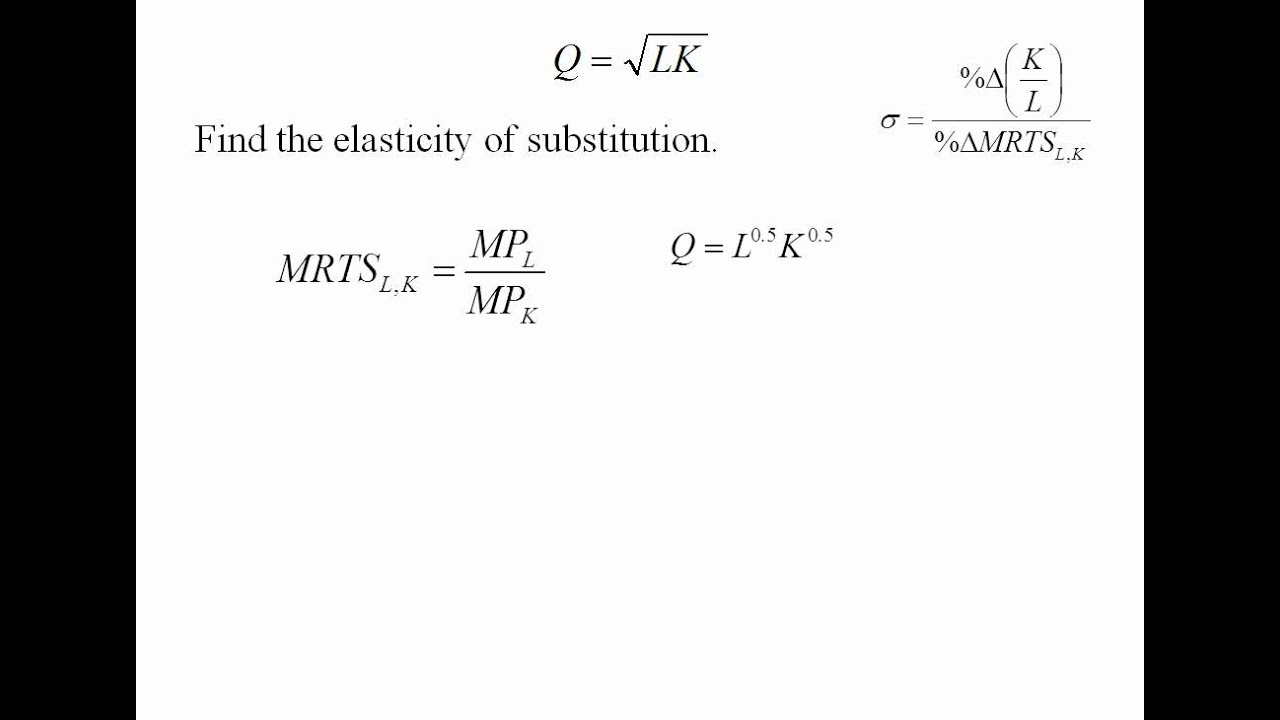
The elasticity of demand may be defined as the percentage change in the quantity demanded which would result from one percent change in price. The formula used here for computing elasticity. How responsive is demand when the price of a product changes that is what we call own-price elasticity of demand. This short paper notes that a. In other words for our canonical production function Y K L the elasticity of substitution between capital and labor is given by. Here MP K 0 along vertical stretch and MP L 0 along horizontal stretch of the isoquant.
10 As we remarked in our earlier discussion the elasticity of an inverse func-tion is just the inverse of the elasticity of a function.
In other words quantity changes slower than price. If the value is less than 1 demand is inelastic. The formula for the price elasticity itself of demand is as follows. Once they raise prices above market prices consumers will switch and ask for substitute products. How responsive is demand when the price of a product changes that is what we call own-price elasticity of demand. Here MP K 0 along vertical stretch and MP L 0 along horizontal stretch of the isoquant.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
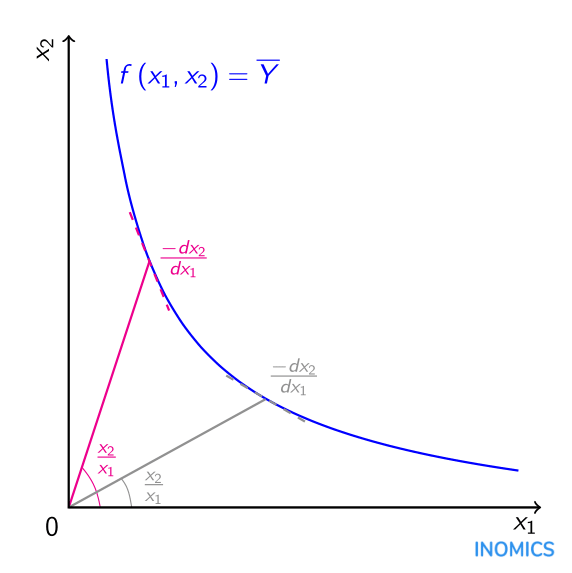
That is p 1 p 2 p 1 p 2 h0 p p h p 1 p 2 dlnh p p 2 dln p 1 p 2. S d ln LKd ln K L. If the price of a complement rises our demand will fall if the price of a substitute rises our demand will rise. This video shows how to calculate the elasticity of substitution using two examples. MODEL CESCALIB ELAST TDEF SDEF OBJDEF.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
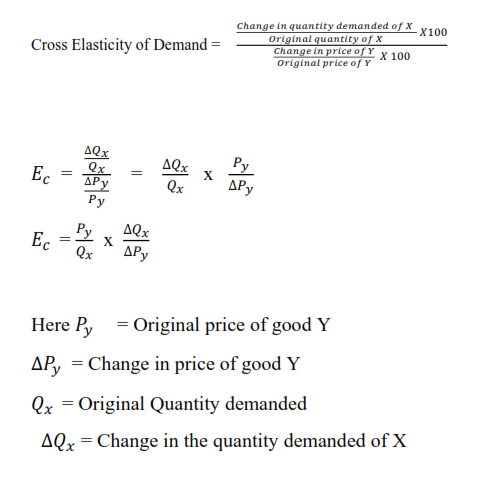
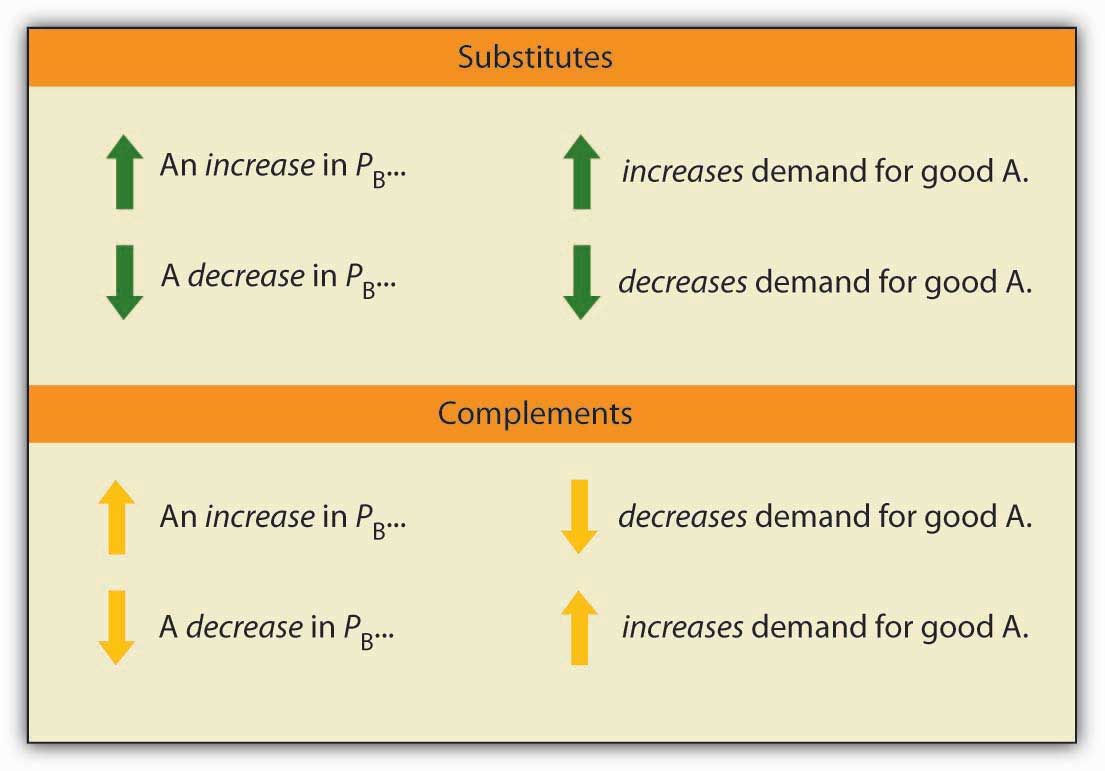
But current consumption may also increase as the household decides to consume more. A complement will have a negative cross-price elasticity since if the change in price is positive the change in quantity will be negative and vice-versa. Ec is the cross elasticity of demand Q X Original quantity demanded of product X ΔQ X Change in quantity demanded of product X P y Original price of product Y ΔP y Change in the price of product Y Cross Elasticity of Demand Example Let us understand the concept of cross elasticity of demand with the help of an example. A substitute will have a positive cross. In other words quantity changes faster than price.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The formula for the price elasticity itself of demand is as follows. S d ln LKd ln K L. This short paper notes that a. Own price elasticity of demand OPE Change in quantity demanded of Product X Change of price of Product X. A complement will have a negative cross-price elasticity since if the change in price is positive the change in quantity will be negative and vice-versa.
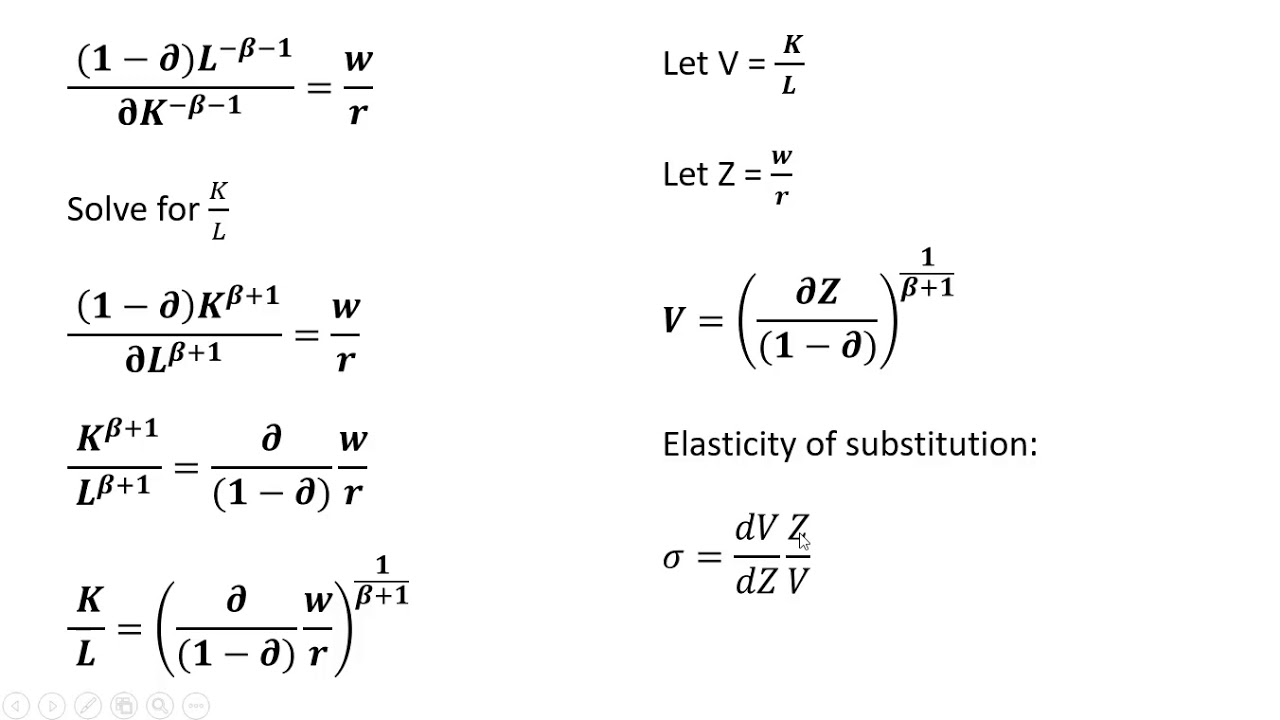 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
We ignore the negative or positive signs of the elasticity calculation results when classifying goods. In other words quantity changes faster than price. The formula used here for computing elasticity. The function gde ned. Our formula for elasticity.
 Source: simplynotes.in
Source: simplynotes.in
S d ln LKd ln K L. The function gde ned. Greater than 1 the demand is elastic. OBJ E SUMIKSIKSIK - SQRGAMMA - SUMK SQRSIGMAK. Formally the elasticity of substitution measures the percentage change in factor proportions due to a change in marginal rate of technical substitution.
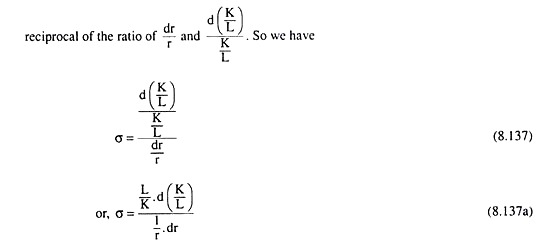 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
The elasticity of demand is the proportionate change of amount purchased in response to a small change in price divided by the proportionate change in price. Formally the elasticity of substitution measures the percentage change in factor proportions due to a change in marginal rate of technical substitution. The elasticity of substitution is just the negative of the elasticity of the function hwith respect to its argument p 1p 2. If the production function of a firm be Q f K L then the formula for the elasticity of substitution σ is given as Now at the point of cost-minimising equilibrium subject to an output constraint we have ADVERTISEMENTS. The elasticity of demand may be defined as the percentage change in the quantity demanded which would result from one percent change in price.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
10 As we remarked in our earlier discussion the elasticity of an inverse func-tion is just the inverse of the elasticity of a function. Here MP K 0 along vertical stretch and MP L 0 along horizontal stretch of the isoquant. Where w and r are the point of the inputs. Cross Price Elasticity of Demand 015 025 06 2. If the production function of a firm be Q f K L then the formula for the elasticity of substitution σ is given as Now at the point of cost-minimising equilibrium subject to an output constraint we have ADVERTISEMENTS.
 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
The elasticity of demand is the proportionate change of amount purchased in response to a small change in price divided by the proportionate change in price. Our formula for elasticity. If the real interest rate rises current consumption may decrease due to increased return on savings. Using the above-mentioned formula the calculation of price elasticity of demand can be done as. We ignore the negative or positive signs of the elasticity calculation results when classifying goods.
 Source: inomics.com
Source: inomics.com
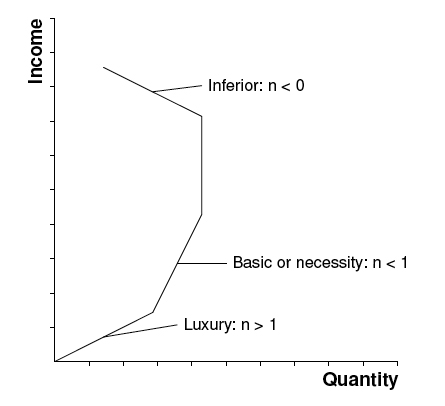
If the real interest rate rises current consumption may decrease due to increased return on savings. Goods whose income elasticity of demand is positive are said to be NORMAL GOODS meaning that demand for them will rise when household income rises. In other words quantity changes slower than price. Our formula for elasticity. If the value is less than 1 demand is inelastic.
 Source: saylordotorg.github.io
Source: saylordotorg.github.io
Where w and r are the point of the inputs. Goods whose income elasticity of demand is positive are said to be NORMAL GOODS meaning that demand for them will rise when household income rises. In other words for our canonical production function Y K L the elasticity of substitution between capital and labor is given by. We measure it by dividing the percentage change in the quantity of demand for an item by the percentage change in its price. 10 As we remarked in our earlier discussion the elasticity of an inverse func-tion is just the inverse of the elasticity of a function.
 Source: boycewire.com
Source: boycewire.com
In other words quantity changes slower than price. Here MP K 0 along vertical stretch and MP L 0 along horizontal stretch of the isoquant. The function gde ned. Product A butter has a 10. A complement will have a negative cross-price elasticity since if the change in price is positive the change in quantity will be negative and vice-versa.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Goods whose income elasticity of demand is positive are said to be NORMAL GOODS meaning that demand for them will rise when household income rises. The elasticity of demand may be defined as the percentage change in the quantity demanded which would result from one percent change in price. Define x 1 and x 2 as Gross Substitutes if an increase in the price of x 2 leads to an increase in the demand for x 1. If the price of a complement rises our demand will fall if the price of a substitute rises our demand will rise. That is p 1 p 2 p 1 p 2 h0 p p h p 1 p 2 dlnh p p 2 dln p 1 p 2.
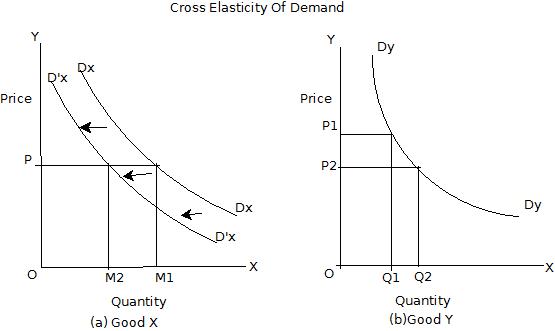 Source: wikieducator.org
Source: wikieducator.org
Category of goods based on their own price elasticity of demand. Goods whose income elasticity of demand is positive are said to be NORMAL GOODS meaning that demand for them will rise when household income rises. Apply some bounds to avoid divide by zero. The elasticity of substitution is just the negative of the elasticity of the function hwith respect to its argument p 1p 2. But current consumption may also increase as the household decides to consume more.
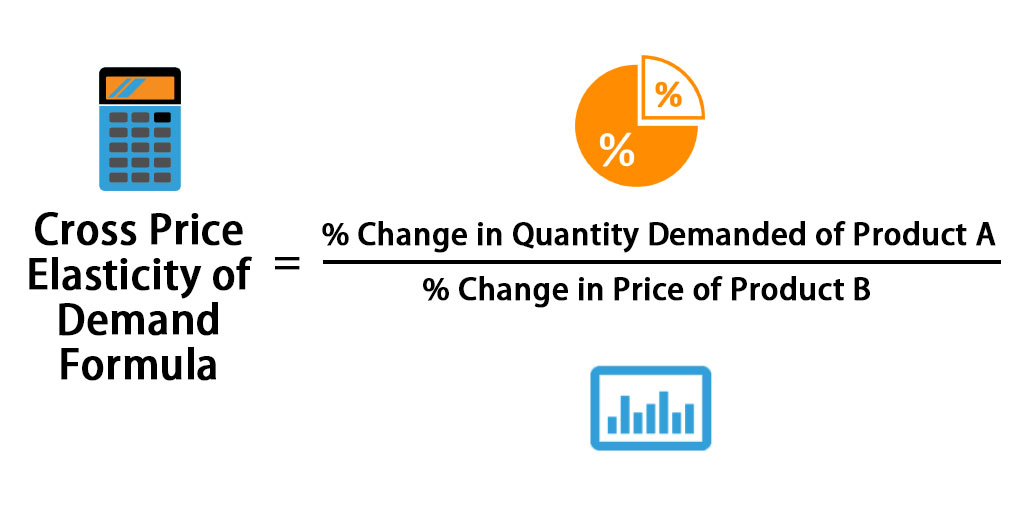 Source: educba.com
Source: educba.com
Product A butter has a 10. Register to view this lesson Are you a student. Apply some bounds to avoid divide by zero. These goods are substitutes because the Cross Price Elasticity of Demand is above 0 Positive. Price Elasticity of Demand Percentage change in quantity Percentage change in price.
 Source: educba.com
Source: educba.com
Greater than 1 the demand is elastic. The resulting formula has proven very useful in understanding the derived demand for productive factors the distribution of factor incomes and Marshalls Four Rules. A substitute will have a positive cross. Cross Price Elasticity of Demand 015 025 06 2. Here MP K 0 along vertical stretch and MP L 0 along horizontal stretch of the isoquant.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
If the value is less than 1 demand is inelastic. The formula for the price elasticity itself of demand is as follows. Where w and r are the point of the inputs. Price Elasticity of Demand Percentage change in quantity Percentage change in price. The elasticity of demand may be defined as the percentage change in the quantity demanded which would result from one percent change in price.
 Source: businesstopia.net
Source: businesstopia.net
10 As we remarked in our earlier discussion the elasticity of an inverse func-tion is just the inverse of the elasticity of a function. Here MP K 0 along vertical stretch and MP L 0 along horizontal stretch of the isoquant. Substitution and Income Effects Slutsky Equation Giffen Goods Price Elasticity of Demand Spring 2001 Econ 11–Lecture 7 2 Substitutes and Complements We will now examine the effect of a change in the price of another good on demand. The resulting formula has proven very useful in understanding the derived demand for productive factors the distribution of factor incomes and Marshalls Four Rules. For cross-price elasticity this means.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
But current consumption may also increase as the household decides to consume more. Cross Price Elasticity of Demand 015 025 06 2. In other words for our canonical production function Y K L the elasticity of substitution between capital and labor is given by. Apply some bounds to avoid divide by zero. Greater than 1 the demand is elastic.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title substitution elasticity of demand formula by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.