Your Population growth in developing countries images are ready in this website. Population growth in developing countries are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Population growth in developing countries files here. Find and Download all free images.
If you’re looking for population growth in developing countries images information related to the population growth in developing countries interest, you have come to the right site. Our site always provides you with hints for refferencing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video articles and images that match your interests.
Population Growth In Developing Countries. The greatest population growth rates were reached in Latin America and in Asia during the mid- to late 1960s. The highest population growth rates will continue to be in developing regions accounting for 97 of the increase to 2030. UN projects world population to reach 85 billion by 2030 driven by growth in developing countries. Fertility rates will remain high unless the educational health and social environment in which these families live is improved.
 1975 Present Urban Population In Developed And Less Developed Countries Developing Country Less Developed Countries Urban From pinterest.com
1975 Present Urban Population In Developed And Less Developed Countries Developing Country Less Developed Countries Urban From pinterest.com
John Bongaarts Population Policy Options in the Developing World Science Vol. The population in Sub-Saharan Africa will quadruple by 2100 according to current estimates by the United Nations Population Fund UNFPA. A slower rate of population growth together with the same rate of GDP increase would have left Kenya with more impressive gains in per capita income. As Chapter 4 showed in industrializing Europe it seldom exceeded 15 percent a year compared with the 2 to 4 percent that most developing coun-. The greatest population growth rates were reached in Latin America and in Asia during the mid- to late 1960s. Looking at the worlds low-income countries they see a population of more than 2 billion growing at a rate that suggests a doubling every 31 years.
Rapid population growth stretches both national and family budgets thin with the increasing numbers of children to be fed and educated and workers to be provided with jobs.
UN projects world population to reach 85 billion by 2030 driven by growth in developing countries. The population in Sub-Saharan Africa will quadruple by 2100 according to current estimates by the United Nations Population Fund UNFPA. For the last half-century we have lived in a world in which the population growth rate has been declining. On average developing countries tend to have faster growth rates than developed countries. Demographers have concluded that slower population growth would be beneficial for development in most developing countries and that the relationship between population and development is contextual The National Research Council 1986. Based on data from the World Bank and using a sample of forty-three developing economies we find that the growth rate of per capita GDP is linearly dependent upon population growth both the young and old dependency ratios the mortality rate and whether or not the rate of population growth is less than 12 percent per year.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Since then these regions have experienced. Slower per capita income growth lack of progress in reducing income inequality and more poverty are the probable consequences. Population Growth Problem In Developing Countries. Economic development and population. Its population growth rate during that period was 32 leaving it a growth rate of per capita GDP of just 01.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Population momentum is strong and will produce large population increases over the next 25 to 50 years. Looking at the worlds low-income countries they see a population of more than 2 billion growing at a rate that suggests a doubling every 31 years. Causes of Population Growth in developing Countries. John Bongaarts Population Policy Options in the Developing World Science Vol. The global population growth rate peaked long ago.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
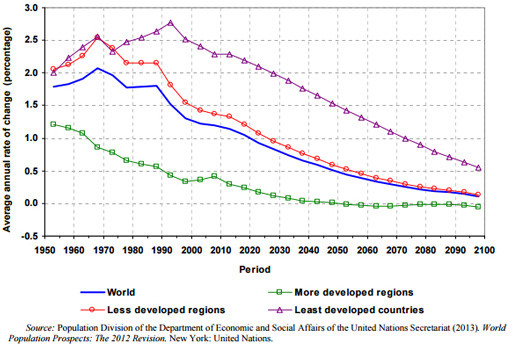
Population growth rates of 3 per cent or more and 70 countries had growth rates ranging between 2 per cent and 3 per cent the corresponding figures for 20102015 were 15 per cent and 41 per. Population and Growth Causality in Developing Countries 535 rate of population growth is affected by the level of per capita income22 Thus the model is not of a closed feedback but of a recursive relationship. By 1990 the world population was growing at almost 90 million a year. The greatest population growth rates were reached in Latin America and in Asia during the mid- to late 1960s. On average developing countries tend to have faster growth rates than developed countries.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
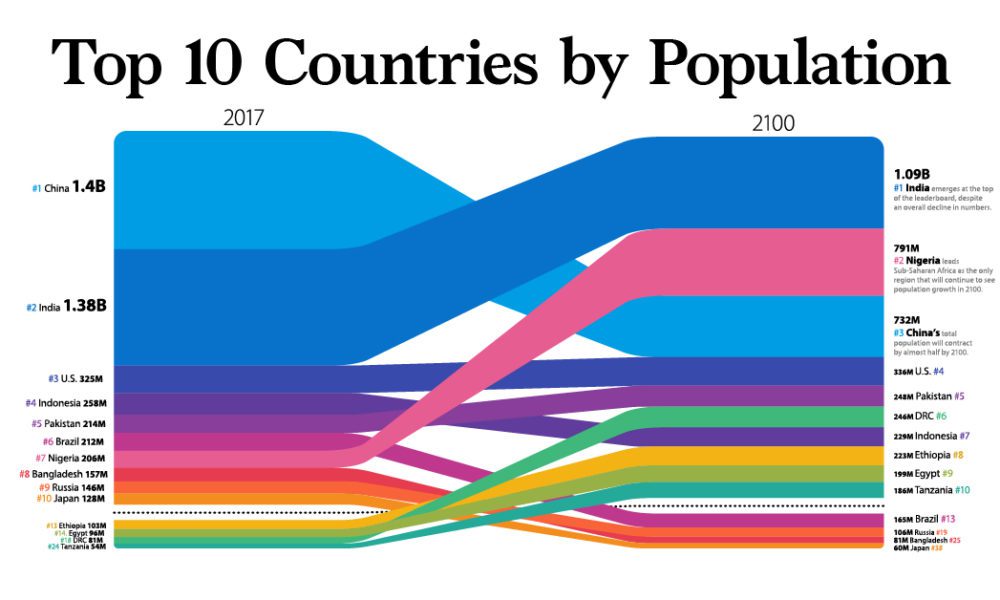
A slower rate of population growth together with the same rate of GDP increase would have left Kenya with more impressive gains in per capita income. The study by Kelly and Schmidt 1995 has also concluded. Looking at the worlds low-income countries they see a population of more than 2 billion growing at a rate that suggests a doubling every 31 years. A challenge to the realization. In the 25 years between 1950 and 1975 the population of Mexico increased from 27000000 to 60000000.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
And China from 554000000 to 933000000. For the last half-century we have lived in a world in which the population growth rate has been declining. Population momentum is strong and will produce large population increases over the next 25 to 50 years. Least keep up with population growth. The chart shows that global population growth reached a peak in 1962 and 1963 with an annual growth rate of 22.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Brazil from 53000000 to 108000000. While the population of developed countries will increase a mere 33 adding 41 million to the current 13 billion people. There are several reasons why population growth in developing countries is today a greater economic burden than it once was in todays developed countries. Fertility rates in developing countries remain high not as a result of irrational behavior on the part of the people living in these countries but as a result of their rational response to high infant mortality rates. Iran from 14000000 to 33000000.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Fertility rates in developing countries remain high not as a result of irrational behavior on the part of the people living in these countries but as a result of their rational response to high infant mortality rates. A slower rate of population growth together with the same rate of GDP increase would have left Kenya with more impressive gains in per capita income. There are several reasons why population growth in developing countries is today a greater economic burden than it once was in todays developed countries. The worlds population is projected to. The highest population growth rates will continue to be in developing regions accounting for 97 of the increase to 2030.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Comparing the Demographic Transition in Europe and in the currently developing countries the latter started 100 years later at a much lower economic level fell from much higher birth and death rates occurred much faster and with a much higher population growth rate and added vastly more people. There are several reasons why population growth in developing countries is today a greater economic burden than it once was in todays developed countries. In the 25 years between 1950 and 1975 the population of Mexico increased from 27000000 to 60000000. Fertility rates in developing countries remain high not as a result of irrational behavior on the part of the people living in these countries but as a result of their rational response to high infant mortality rates. Fertility rates will remain high unless the educational health and social environment in which these families live is improved.
 Source:
Source:
Since then these regions have experienced. Slower per capita income growth lack of progress in reducing income inequality and more poverty are the probable consequences. Based on data from the World Bank and using a sample of forty-three developing economies we find that the growth rate of per capita GDP is linearly dependent upon population growth both the young and old dependency ratios the mortality rate and whether or not the rate of population growth is less than 12 percent per year. Few problems in the world today can be solved without a population policy although the concentration on population problems to the neglect of positive measures to promote economic and social progress would be wrongheaded. Demographers have concluded that slower population growth would be beneficial for development in most developing countries and that the relationship between population and development is contextual The National Research Council 1986.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
Economic development and population. Demographers have concluded that slower population growth would be beneficial for development in most developing countries and that the relationship between population and development is contextual The National Research Council 1986. E if population is growing at 2. Or viewed the other way population growth is a major drag on raising per capita income. Coordinated Assistance Essential Rapid population growth in developing countries impedes efforts to improve the quality of life Many governmental inter- national and private and voluntary organ- iza tions provide population assistance to an ever.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Looking at the worlds low-income countries they see a population of more than 2 billion growing at a rate that suggests a doubling every 31 years. Population and Growth Causality in Developing Countries 535 rate of population growth is affected by the level of per capita income22 Thus the model is not of a closed feedback but of a recursive relationship. Iran from 14000000 to 33000000. The chart shows that global population growth reached a peak in 1962 and 1963 with an annual growth rate of 22. In particular these countries have seen an increase in the age-dependency ratio computed as the ratio of the young population under 15 and elderly population 65 and over to the working-age population 15 to 64.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The global population growth rate peaked long ago. As Chapter 4 showed in industrializing Europe it seldom exceeded 15 percent a year compared with the 2 to 4 percent that most developing coun-. And China from 554000000 to 933000000. Excess population in the developing countries and excess consumption in the developed world is seen as undermining. While the population of developed countries will increase a mere 33 adding 41 million to the current 13 billion people.
 Source: open.edu
Source: open.edu
Coordinated Assistance Essential Rapid population growth in developing countries impedes efforts to improve the quality of life Many governmental inter- national and private and voluntary organ- iza tions provide population assistance to an ever. UN projects world population to reach 85 billion by 2030 driven by growth in developing countries. For the last half-century we have lived in a world in which the population growth rate has been declining. Iran from 14000000 to 33000000. In particular these countries have seen an increase in the age-dependency ratio computed as the ratio of the young population under 15 and elderly population 65 and over to the working-age population 15 to 64.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Population growth rates of 3 per cent or more and 70 countries had growth rates ranging between 2 per cent and 3 per cent the corresponding figures for 20102015 were 15 per cent and 41 per. The worlds developing regions will see 12 billion people added a 207 increase. Coordinated Assistance Essential Rapid population growth in developing countries impedes efforts to improve the quality of life Many governmental inter- national and private and voluntary organ- iza tions provide population assistance to an ever. Since then these regions have experienced. The greatest population growth rates were reached in Latin America and in Asia during the mid- to late 1960s.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The chart shows that global population growth reached a peak in 1962 and 1963 with an annual growth rate of 22. Population growth is now much more rapid. Population Growth Problem In Developing Countries. Population growth rates of 3 per cent or more and 70 countries had growth rates ranging between 2 per cent and 3 per cent the corresponding figures for 20102015 were 15 per cent and 41 per. And China from 554000000 to 933000000.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Or viewed the other way population growth is a major drag on raising per capita income. The highest population growth occurs in poor countries. Population Growth Problem In Developing Countries. Comparing the Demographic Transition in Europe and in the currently developing countries the latter started 100 years later at a much lower economic level fell from much higher birth and death rates occurred much faster and with a much higher population growth rate and added vastly more people. Coordinated Assistance Essential Rapid population growth in developing countries impedes efforts to improve the quality of life Many governmental inter- national and private and voluntary organ- iza tions provide population assistance to an ever.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Looking at the worlds low-income countries they see a population of more than 2 billion growing at a rate that suggests a doubling every 31 years. Population and Growth Causality in Developing Countries 535 rate of population growth is affected by the level of per capita income22 Thus the model is not of a closed feedback but of a recursive relationship. E if population is growing at 2. The highest population growth occurs in poor countries. A challenge to the realization.
 Source: visualcapitalist.com
Source: visualcapitalist.com
Iran from 14000000 to 33000000. Comparing the Demographic Transition in Europe and in the currently developing countries the latter started 100 years later at a much lower economic level fell from much higher birth and death rates occurred much faster and with a much higher population growth rate and added vastly more people. Population Growth Problem In Developing Countries. There are several reasons why population growth in developing countries is today a greater economic burden than it once was in todays developed countries. Fertility rates in developing countries remain high not as a result of irrational behavior on the part of the people living in these countries but as a result of their rational response to high infant mortality rates.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title population growth in developing countries by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.