Your Population growth curve of yeast is images are ready. Population growth curve of yeast is are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Population growth curve of yeast is files here. Find and Download all free photos.
If you’re looking for population growth curve of yeast is images information related to the population growth curve of yeast is topic, you have pay a visit to the ideal site. Our site always gives you suggestions for refferencing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and locate more enlightening video content and images that match your interests.
Population Growth Curve Of Yeast Is. The abbreviations used for yeast cell cycle stand for the. Its growth levels off as the population depletes the nutrients that are necessary for its growth. The budding yeast showed a higher growth rate of 21 doublings per minute compared with the fission yeast which had a growth rate of 13 doublings per minute. What Factors Limit the Size of a Population of Yeast.
 Growth Curves Of Investigated Yeast Strains In 7 P Wort With 50 Ibu Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
Growth Curves Of Investigated Yeast Strains In 7 P Wort With 50 Ibu Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
This paper describes a high-throughput method based on exponential yeast growth to estimate the effects of concentration changes and nature of the carbon source on respiratory and fermentative metabolism. The yeast species used in both bread baking and the brewing of ales Saccharomyces cerevisiae thrives at temperatures between about 5. As the consumption of sugar is analogous to yeast growth the use of a common biological growth curve should work well for this application. Classic example is yeast in a champagne bottle. What Factors Limit the Size of a Population of Yeast. The growth of S.
Set it to zero.
Examples of Logistic Growth. 23 log 758 185k. Shake the flask containing the yeast culture gently to distribute the cells evenly. Thus the population rate is largely determined by the biotic potentials and size of the populationHowever exponential growth produces J-shaped curve. In the real world however there are variations to this idealized curve. Set it to zero.
 Source: studylib.net
Source: studylib.net
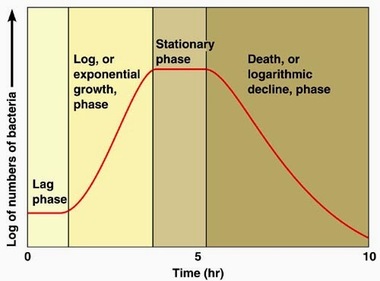
Yeast a microscopic fungus used to make bread and alcoholic beverages exhibits the classical S-shaped curve when grown in a test tube a. In biology growth curves represent the change in cell population over a period of time. Disregarding the irregularities of the growth rate curve is the general trend downward. Its growth levels off as the population depletes the nutrients that are necessary for its growth. Examples of Logistic Growth Yeast a unicellular fungus used to make bread and alcoholic beverages exhibits the classical S-shaped curve when grown in a test tube Figure 2a.
 Source: biology-igcse.weebly.com
Source: biology-igcse.weebly.com
Yeast cell size in this condition pH4 and DO 5 was estimated to be about 2 3 μ by light microscopy software Figure 4. This increase in population is continued till large amount of food materials exist in the habitat. Disregarding the irregularities of the growth rate curve is the general trend downward. A population is a group of individuals that belong to the same species and. The rate has started to decrease by 9 and 10 because the yeast is starting to be killed off by the alcohol.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
This is a fairly large drop in the expansion of the population of yeast. In this condition the longest time of the growth phase 78 hours was obtained. As the consumption of sugar is analogous to yeast growth the use of a common biological growth curve should work well for this application. As resources become less available the growth of a population slows or stops. The Gomertz model GM is an empirical model named after Benjamin Gompertz 1825 that is widely used in the field of microbiology to predict the growth curves of bacteria Buchanan Whiting Damert.
 Source: emilyspiersbiology.weebly.com
Source: emilyspiersbiology.weebly.com
This is a fairly large drop in the expansion of the population of yeast. The rate has started to decrease by 9 and 10 because the yeast is starting to be killed off by the alcohol. List several factors that have enabled the human population growth to inc rate. Figure 28 Population growth as a function of N based on the logistic equation. Which growth curve does the United States population resemble the theore growth curve of the yeast population.

The rate of increase from day 10 to 11 is half that of the increase from day 3 to 4. That is the number of cells in the population increases by 1094 per hour. We propose a method to standardize the growth of yeast with respect to an initial OD fitting two observed growth curves at the same time by the modified. Using sterile medium as the reference calibrate the colorimeter ie. In biology growth curves represent the change in cell population over a period of time.
 Source: maquah.net
Source: maquah.net
The population is still growing but at a much slower rate. Yeast cultures growing on. The population is still growing but at a much slower rate. Among many factors that affect the growth of yeast some are manipulative through various mechanisms. 113 Lab 9 Population A population is a group of.
 Source: maquah.net
Source: maquah.net
In biology growth curves represent the change in cell population over a period of time. That is the number of cells in the population increases by 1094 per hour. As resources become less available the growth of a population slows or stops. This is a fairly large drop in the expansion of the population of yeast. This increase in population is continued till large amount of food materials exist in the habitat.
 Source: theory.labster.com
Source: theory.labster.com
List several factors that have enabled the human population growth to inc rate. All populations of living things change in size over time. In yeast the growth curve is generated by plotting the optical density or OD of cell culture at 600 nm in the y axis and time on the x axis. The human population is no different. Now from equation 2-6 T069301094 hr-1 633 hr.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In the real world however there are variations to this idealized curve. Examples of Logistic Growth. Examples of Logistic Growth Yeast a unicellular fungus used to make bread and alcoholic beverages exhibits the classical S-shaped curve when grown in a test tube Figure 2a. The Gomertz model GM is an empirical model named after Benjamin Gompertz 1825 that is widely used in the field of microbiology to predict the growth curves of bacteria Buchanan Whiting Damert. J Shaped Curve.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Which growth curve does the United States population resemble the theore growth curve of the yeast population. The population is still growing but at a much slower rate. Laboratory studies on growth of protozoan populations such as Paramecium caudatum yeast Drosophila grain beetles and diatoms Gause 1932 1934 Vandermeer 1969 Pearl 1927 Crombie 1945 Park et al. The yeast cells reached the highest growth rate 3309 in pH4 and DO 5 condition. What Factors Limit the Size of a Population of Yeast.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
That is the number of cells in the population increases by 1094 per hour. Factors affecting yeast growth. Cerevisiae is measured in a microplate or shaken conical flask by determining the optical density OD at 600 nm. S Shaped or Sigmoid Curve. Among many factors that affect the growth of yeast some are manipulative through various mechanisms.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
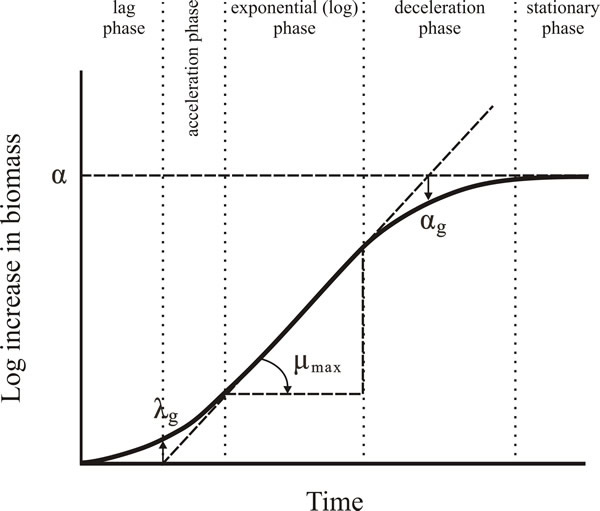
99 wild-type yeast strains growth data observed for 24 hours and the other consists of 200 wild-type yeast strains observed for 44 hours cultured in normal environment. As the consumption of sugar is analogous to yeast growth the use of a common biological growth curve should work well for this application. B The yeast cell cycle diagram shows the phases of the cell cycle. Yeast cultures growing on. What Factors Limit the Size of a Population of Yeast.
 Source: davidmoore.org.uk
Source: davidmoore.org.uk
This should give a starting concentration of 00025 gl for your growth curve. The human population is no different. That is the number of cells in the population increases by 1094 per hour. Yeast cultures growing on. Yeast a microscopic fungus used to make bread and alcoholic beverages exhibits the classical S-shaped curve when grown in a test tube a.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Laboratory studies on growth of protozoan populations such as Paramecium caudatum yeast Drosophila grain beetles and diatoms Gause 1932 1934 Vandermeer 1969 Pearl 1927 Crombie 1945 Park et al. Among many factors that affect the growth of yeast some are manipulative through various mechanisms. Yeast a microscopic fungus used to make bread and alcoholic beverages exhibits the classical S-shaped curve when grown in a test tube a. The abbreviations used for yeast cell cycle stand for the. The population is still growing but at a much slower rate.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
This should give a starting concentration of 00025 gl for your growth curve. The budding yeast showed a higher growth rate of 21 doublings per minute compared with the fission yeast which had a growth rate of 13 doublings per minute. In this condition the longest time of the growth phase 78 hours was obtained. Factors affecting yeast growth. 23 log 758 185k.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
1964 Tilman 1977 do consistently show a logistic growth. The growth of S. Disregarding the irregularities of the growth rate curve is the general trend downward. The yeast cells reached the highest growth rate 3309 in pH4 and DO 5 condition. The general S-shaped curve of this growth pattern called logistic growth is shown below in the graph of a yeast population.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Set it to zero. J-shape curve is a curve that shows the population density of an organisms as they increase rapidly in a logarithmic or exponential form but abruptly stops due to environmental resistance. 113 Lab 9 Population A population is a group of. Using aseptic technique dilute 100 times by adding 1 cm3 to 99 cm3 sterile broth in a flask. All populations of living things change in size over time.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
We propose a method to standardize the growth of yeast with respect to an initial OD fitting two observed growth curves at the same time by the modified. This should give a starting concentration of 00025 gl for your growth curve. Figure 28 Population growth as a function of N based on the logistic equation. Which growth curve does the United States population resemble the theore growth curve of the yeast population. This increase in population is continued till large amount of food materials exist in the habitat.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title population growth curve of yeast is by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.





