Your Oligopoly curve economics images are available in this site. Oligopoly curve economics are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Oligopoly curve economics files here. Find and Download all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re looking for oligopoly curve economics images information connected with to the oligopoly curve economics topic, you have visit the right blog. Our website always gives you suggestions for refferencing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly search and locate more enlightening video content and images that fit your interests.
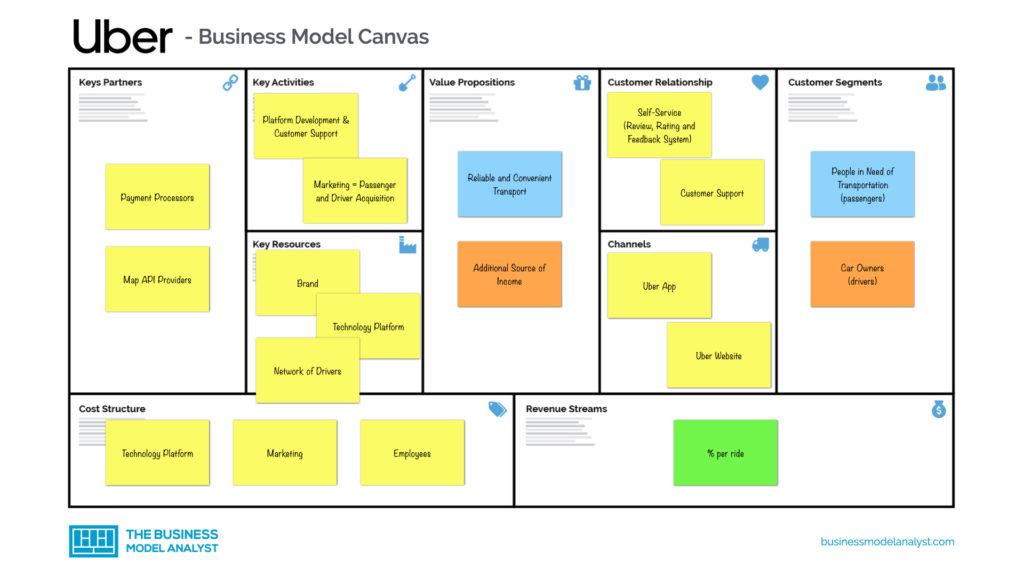
Oligopoly Curve Economics. When firms under oligopoly agree formally not to compete with each other about price or output profit it is called collusive oligopoly. Two models that are used to explain competitive behavior are the kinked demand curve and prisoners dilemma. There are different possible outcomes for oligopoly. The kinkeddemand theory however is considered an incomplete theory of oligopoly for several reasons.
 Pin On Economics From pinterest.com
Pin On Economics From pinterest.com
To illustrate consider Fig. The kink in the demand curve occurs because rival firms will behave differently to price cuts and price increases. Explain reasons for collusive and non-collusive behaviour. Production is not at the lowest point indicated by the AT Curve. The kinked demand curve model. Progressive oligopolies have high economic profits in spite of price decreases brought on by high-tech efficiencies.
Some behavior by firms in oligopoly can be described as cooperative rather than competitive.
The firms will expand output and cut price as long as there are profits remaining. In the first place as the demand curve or the average revenue AR curve of the firm has a kink its MR curve cannot be obtained as a continuous curve. Through kinked demand curve firms concentrate on non-price competition. Does oligopoly make economic or normal profit. Explain reasons for collusive and non-collusive behaviour. The kinked demand curve model.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
And on the other hand there is uncertainty regarding the reaction of the rivals. Explain reasons for collusive and non-collusive behaviour. This model of oligopoly suggests that prices are rigid and that firms will face different effects for both increasing price or decreasing price. Economic analysis of oligopoly A. If a cartel has absolute control over its members as is true of the OPEC it can operate as a monopoly.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
With the fierce price competitiveness created by this sticky-upward demand curve firms use non-price competition in order to accrue greater revenue and market share. Through kinked demand curve firms concentrate on non-price competition. Economic analysis of oligopoly A. Progressive oligopolies have high economic profits in spite of price decreases brought on by high-tech efficiencies. The kinkeddemand theory however is considered an incomplete theory of oligopoly for several reasons.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The kinked demand curve model. The kink in the demand curve occurs because rival firms will behave differently to price cuts and price increases. Oligopoly is a structural type of market consisting of and dominated by a small number of firms. What is the kinked demand curve model of oligopoly. Production is not at the lowest point indicated by the AT Curve.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The marginal cost curves of each firm are summed horizontally to derive an industry marginal cost curve. Explain reasons for collusive and non-collusive behaviour. Oligopoly - The Kinked Demand Curve. When firms under oligopoly agree formally not to compete with each other about price or output profit it is called collusive oligopoly. In the oligopoly model under discussion the properties of the kinked demand curve as well as its significance are especially discussed.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In other words a natural oligopoly would have a LRAC curve and a. P MR MC 2. There is no single economic model that explains all behavior in oligopoly. Two models that are used to explain competitive behavior are the kinked demand curve and prisoners dilemma. To illustrate consider Fig.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
This is because on one hand there is a huge interdependence among rivals. Does oligopoly make economic or normal profit. The firms will expand output and cut price as long as there are profits remaining. The marginal cost curves of each firm are summed horizontally to derive an industry marginal cost curve. Progressive oligopolies have high economic profits in spite of price decreases brought on by high-tech efficiencies.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
For example if each firm in an oligopoly sells an undifferentiated product like oil the demand curve that each firm faces will be horizontal at the market price. This collusive oligopoly resembles monopoly and extracts the maximum amount of profits from customers. The theory of oligopoly suggests that once a price has been determined will stick it at this price. Economic profits exist and quantity is restricted. The firms will expand output and cut price as long as there are profits remaining.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
To illustrate consider Fig. For example if each firm in an oligopoly sells an undifferentiated product like oil the demand curve that each firm faces will be horizontal at the market price. Oligopoly - The Kinked Demand Curve. In the oligopoly model under discussion the properties of the kinked demand curve as well as its significance are especially discussed. It can be described as a form of imperfect competition where the actions of a firm significantly influence the other firms in the market.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Oligopoly - The Kinked Demand Curve. The theory of oligopoly suggests that once a price has been determined will stick it at this price. Economic profits exist and quantity is restricted. Oligopoly - The Kinked Demand Curve. This is because on one hand there is a huge interdependence among rivals.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
And on the other hand there is uncertainty regarding the reaction of the rivals. And on the other hand there is uncertainty regarding the reaction of the rivals. It happens so because his own output adjustment will induce significant effects on his rival firms prices or. It can be described as a form of imperfect competition where the actions of a firm significantly influence the other firms in the market. Economic analysis of oligopoly A.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
If a cartel has absolute control over its members as is true of the OPEC it can operate as a monopoly. This model of oligopoly suggests that prices are rigid and that firms will face different effects for both increasing price or decreasing price. This is the major contribution of the kinkeddemand theory. Oligopoly - The Kinked Demand Curve. Unlike other market structures under Oligopoly it is not possible to determine the demand curve of a firm.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
In the first place as the demand curve or the average revenue AR curve of the firm has a kink its MR curve cannot be obtained as a continuous curve. The firms will expand output and cut price as long as there are profits remaining. The marginal cost curves of each firm are summed horizontally to derive an industry marginal cost curve. P MR MC 2. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Progressive oligopolies have high economic profits in spite of price decreases brought on by high-tech efficiencies. Progressive oligopolies have high economic profits in spite of price decreases brought on by high-tech efficiencies. The firms may agree on setting output quota or fix prices or limit product promotion or agree not to poach in each others market. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. This is the major contribution of the kinkeddemand theory.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Oligopoly there must again be substantial economies of scale but enough to support more than just one firm. This is the major contribution of the kinkeddemand theory. The firms may agree on setting output quota or fix prices or limit product promotion or agree not to poach in each others market. If however the oilproducing firms form a cartel like OPEC to determine their output and price they will jointly face a downwardsloping market demand curve just like a. In an oligopoly no single firm enjoys a large amount of market power.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
This model of oligopoly suggests that prices are rigid and that firms will face different effects for both increasing price or decreasing price. Economies of Scope Economies of scope is an economic concept that refers to the decrease in the total cost of production when a range of products are produced together. Oligopoly is a structural type of market consisting of and dominated by a small number of firms. The kinked demand curve model assumes that a business might face a dual demand curve for its product based on the likely reactions of other firms to a change in its price or another variable. It happens so because his own output adjustment will induce significant effects on his rival firms prices or.
 Source: gr.pinterest.com
Source: gr.pinterest.com
There are different possible outcomes for oligopoly. If however the oilproducing firms form a cartel like OPEC to determine their output and price they will jointly face a downwardsloping market demand curve just like a. The marginal cost curves of each firm are summed horizontally to derive an industry marginal cost curve. The theory of oligopoly suggests that once a price has been determined will stick it at this price. If a cartel has absolute control over its members as is true of the OPEC it can operate as a monopoly.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
Oligopoly is a structural type of market consisting of and dominated by a small number of firms. The firms will expand output and cut price as long as there are profits remaining. In the oligopoly model under discussion the properties of the kinked demand curve as well as its significance are especially discussed. When firms under oligopoly agree formally not to compete with each other about price or output profit it is called collusive oligopoly. The market demand curve that each oligopolist faces is determined by the output and price decisions of the other firms in the oligopoly.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
This is the major contribution of the kinkeddemand theory. What is the kinked demand curve model of oligopoly. Understand the characteristics of this market structure with particular reference to the interdependence of firms. Production is not at the lowest point indicated by the AT Curve. Two models that are used to explain competitive behavior are the kinked demand curve and prisoners dilemma.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title oligopoly curve economics by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.