Your Negative demand shocks to the economy can come from images are ready. Negative demand shocks to the economy can come from are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Negative demand shocks to the economy can come from files here. Download all free images.
If you’re looking for negative demand shocks to the economy can come from images information related to the negative demand shocks to the economy can come from keyword, you have visit the ideal site. Our website always provides you with suggestions for viewing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more enlightening video articles and graphics that match your interests.
Negative Demand Shocks To The Economy Can Come From. We focus on the implications for aggregate demand of a change. An economic shock also known as a macroeconomic shock is any unexpected event that has a large-scale unexpected impact on the economy. Larger second-order negative impacts on demand and the potential for a self-reinforcing downward spiral in output employment income and demand. El Hadri et al.
 Demand Shock Definition From investopedia.com
Demand Shock Definition From investopedia.com
It is clear that output fluctuates less if the Fed follows a policy of keeping the money. For now the aim is simply to pin down the effects of different policies. Overall we find that the supply and demand shocks considered in this paper represent a reduction of around one quarter of the US economys value added one fifth of current employment and about 17. That could be another issue because it could put the economy in a situation where the inflation rate is close to zero and might even become negative. Namely a negative supply shock can trigger a demand shortage that leads to a contraction in output and employment larger than the supply shock itself. What happens to the aggregate output and price level.
Whether financial crises are negative demand or supply shocks is one of macroeconomics perennial and fundamental questions.
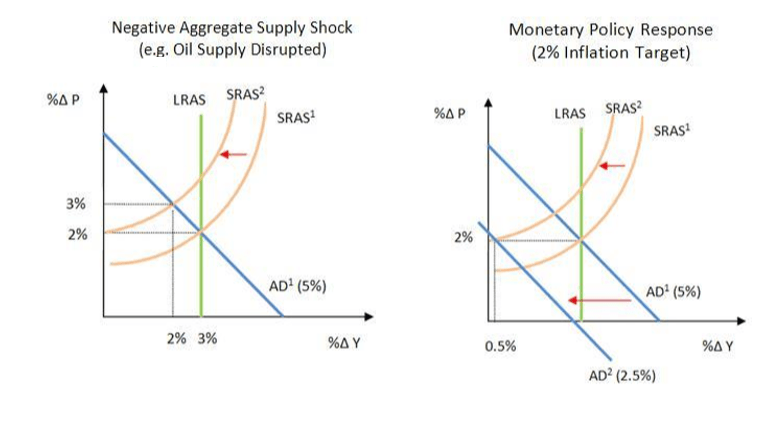
An alternative is to consider both the negative shock caused by non-essential. But a supply shock can lead to a demand shock according to Guerrieri Lorenzoni Straub and Werning. That could be another issue because it could put the economy in a situation where the inflation rate is close to zero and might even become negative. The figures below show what effect this has on output under the two policies. Negative demand shocks decrease aggregate demand in the economy because people are more inclined to save rather than consume. Supply creates its own excess demand.

One can endow the agents with noisy signals about the future and let them solve the associated signal-extraction problem. Naturally interest in this question spikes after major global downturns from the Great Depression in the 1930s to the recent. Rate policy or supply-side policy we come to that when we look at the different kinds of shocks that may affect the economy. A weak job market is the classic demand-side economic shock. Beyond intellectual curiosity views on this debate shape government policies in response to crises.
 Source: bookdown.org
Source: bookdown.org
Demand may indeed overreact to the supply shock and lead to a demand-deficient recession write the researchers. And slight negative shocks to the demand could drive prices down and then consumers are going to postpone their expenditures investment may go down and push the IS curve way to the left lowering the level of income. For example in development microeconomics the relationship between household income shocks and household levels of consumption is studied to understand a households ability to insure itself testing the full-insurance hypothesis. When a negative demand shock occurs governments try to counter this. In this paper we pose an economy where we.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Namely a negative supply shock can trigger a demand shortage that leads to a contraction in output and employment larger than the supply shock itself. El Hadri et al. This is easiest to understand if we begin in full equilibrium at the intersection of the - -and-curves. Negative external shocks such as the financial crisis and the pandemic create much instability and can lead to persistent periods of weaker economic growth higher unemployment falling real incomes and rising poverty. Namely a negative supply shock can trigger a demand shortage that leads to a contraction in output and employment larger than the supply shock itself.
 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Supply creates its own excess demand. El Hadri et al. We call supply shocks with these properties Keynesian supply shocks. A weak job market is the classic demand-side economic shock. But a supply shock can lead to a demand shock according to Guerrieri Lorenzoni Straub and Werning.
 Source: bookdown.org
Source: bookdown.org
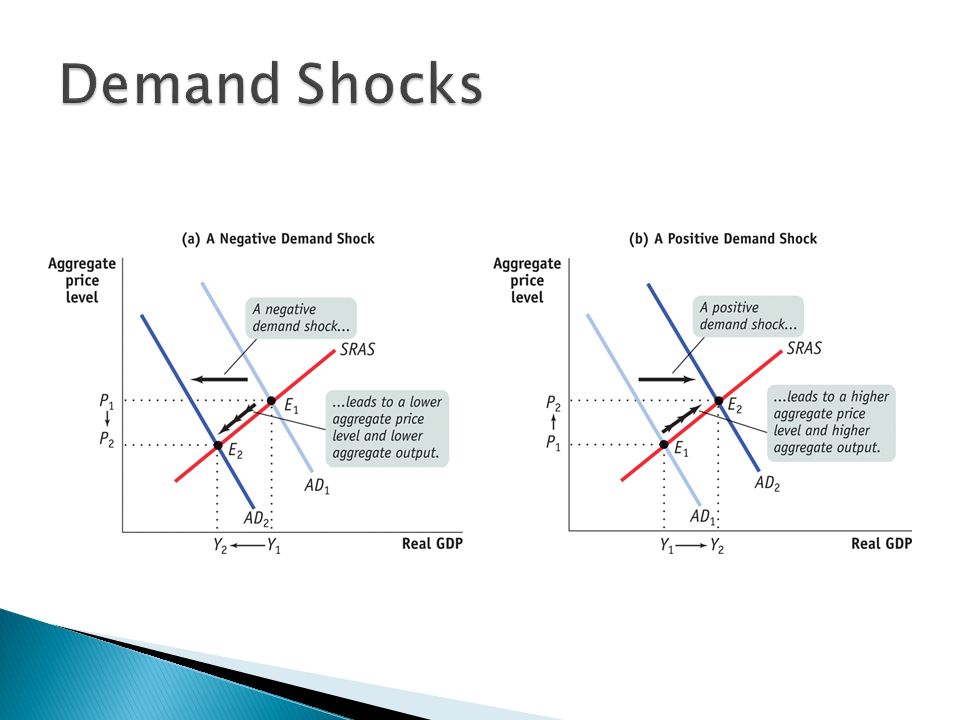
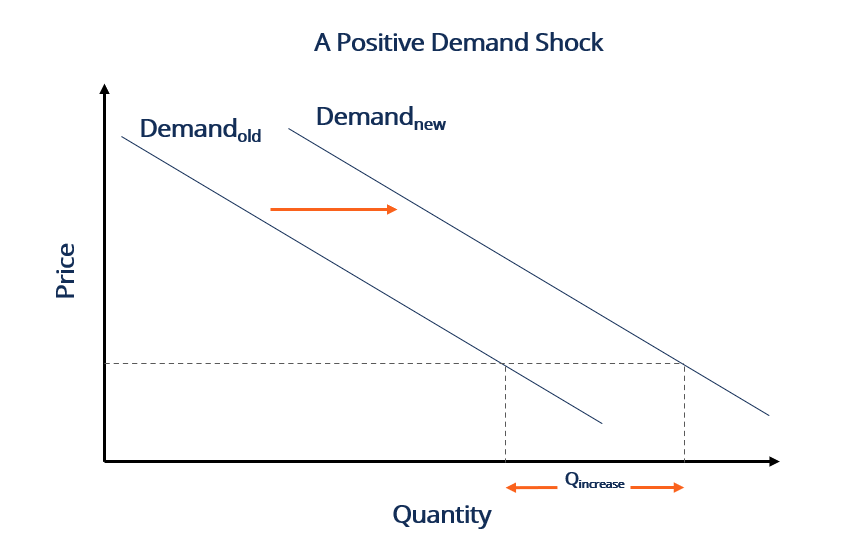
Negative demand shocks decrease aggregate demand in the economy because people are more inclined to save rather than consume. A negative demand shock such as a drop in consumer spending will lead to price decreases and the 2008 global financial crisis has been traced to such a demand shock in the US which led to a fall in house prices causing problems in the US subprime mortgage sector that then extended to the rest of the financial sector and wider economy. This is the so called Backus-Smith puzzle. 9 we consider that occupations only experience the negative shocks. But a supply shock can lead to a demand shock according to Guerrieri Lorenzoni Straub and Werning.
 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
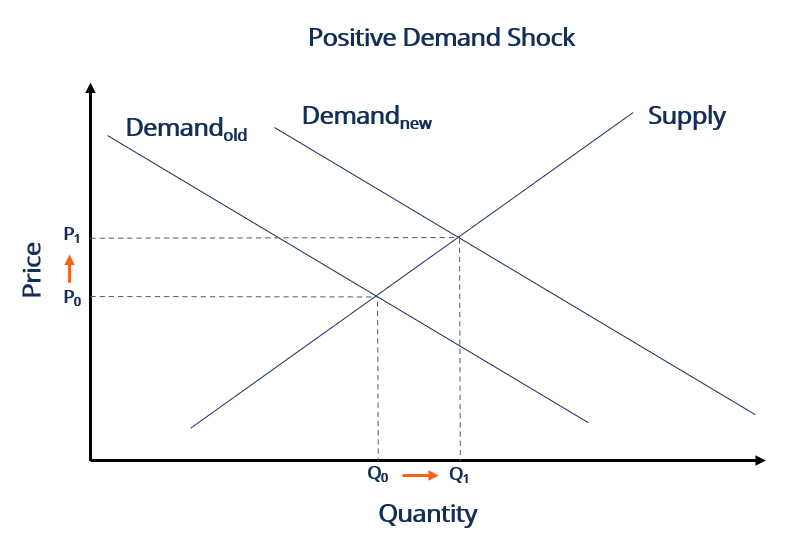
If an event causes massive layoffs or a downturn in the stock market consumers may slash spending triggering a negative feedback loop of businesses losing money leading to more layoffs and a further cut in consumption. Once one turns to general equilibrium however things get more complicated. An economic shock also known as a macroeconomic shock is any unexpected event that has a large-scale unexpected impact on the economy. For example in development microeconomics the relationship between household income shocks and household levels of consumption is studied to understand a households ability to insure itself testing the full-insurance hypothesis. Finally demand-side shocks can also be caused by transition to a low carbon economy.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Rate policy or supply-side policy we come to that when we look at the different kinds of shocks that may affect the economy. An economic shock also known as a macroeconomic shock is any unexpected event that has a large-scale unexpected impact on the economy. Positive external shocks might. A negative demand shock such as a drop in consumer spending will lead to price decreases and the 2008 global financial crisis has been traced to such a demand shock in the US which led to a fall in house prices causing problems in the US subprime mortgage sector that then extended to the rest of the financial sector and wider economy. An alternative is to consider both the negative shock caused by non-essential.

If all shocks to the economy arise from the exogenous changes in the demand for goods and services this means that all shocks are to the IS curve. Whether financial crises are negative demand or supply shocks is one of macroeconomics perennial and fundamental questions. Its also possible that the deterioration of demand will have larger economic effects than the supply shock that caused it and the researchers dub. One can endow the agents with noisy signals about the future and let them solve the associated signal-extraction problem. Rate policy or supply-side policy we come to that when we look at the different kinds of shocks that may affect the economy.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
One can endow the agents with noisy signals about the future and let them solve the associated signal-extraction problem. Finally demand-side shocks can also be caused by transition to a low carbon economy. We focus on the implications for aggregate demand of a change. And slight negative shocks to the demand could drive prices down and then consumers are going to postpone their expenditures investment may go down and push the IS curve way to the left lowering the level of income. Naturally interest in this question spikes after major global downturns from the Great Depression in the 1930s to the recent.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Moderate inflation gives monetary policymakers more room to stimulate the economy when needed reducing the risk of falling into a liquidity trap. This is easiest to understand if we begin in full equilibrium at the intersection of the - -and-curves. In this paper we pose an economy where we. What would happen in the long run to the aggregate price and output levels. During the global financial crisis of 2008 a negative demand shock in the United States economy was caused by several factors that included falling house prices the subprime mortgage crisis and lost household wealth which led to a drop in consumer spending.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Since occupations are employed by different industries the total shock to an occupation can be influenced by positive demand shocks from the healthcare sector and negative demand shocks from non-essential industries. Whether financial crises are negative demand or supply shocks is one of macroeconomics perennial and fundamental questions. For now the aim is simply to pin down the effects of different policies. 9 we consider that occupations only experience the negative shocks. But a supply shock can lead to a demand shock according to Guerrieri Lorenzoni Straub and Werning.
 Source: investopedia.com
Source: investopedia.com
An economic shock also known as a macroeconomic shock is any unexpected event that has a large-scale unexpected impact on the economy. We focus on the implications for aggregate demand of a change. An economic shock also known as a macroeconomic shock is any unexpected event that has a large-scale unexpected impact on the economy. El Hadri et al. A weak job market is the classic demand-side economic shock.
 Source: seekingalpha.com
Source: seekingalpha.com
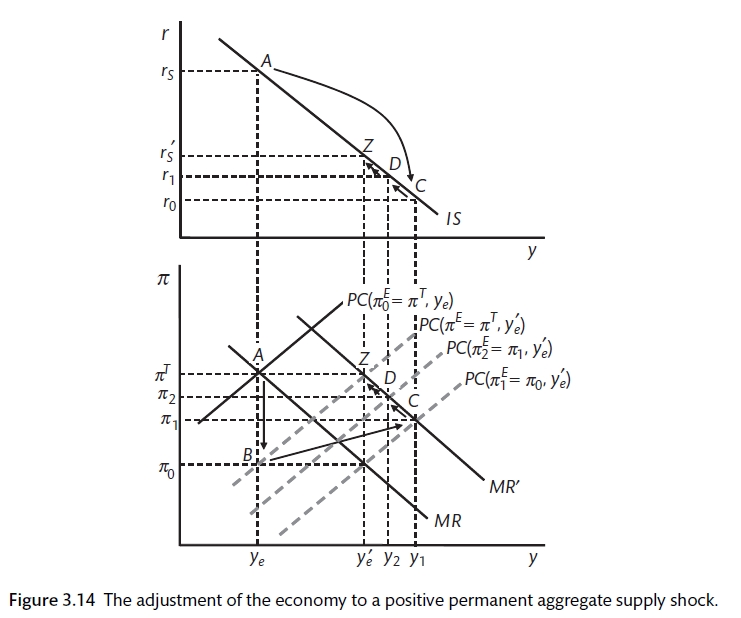
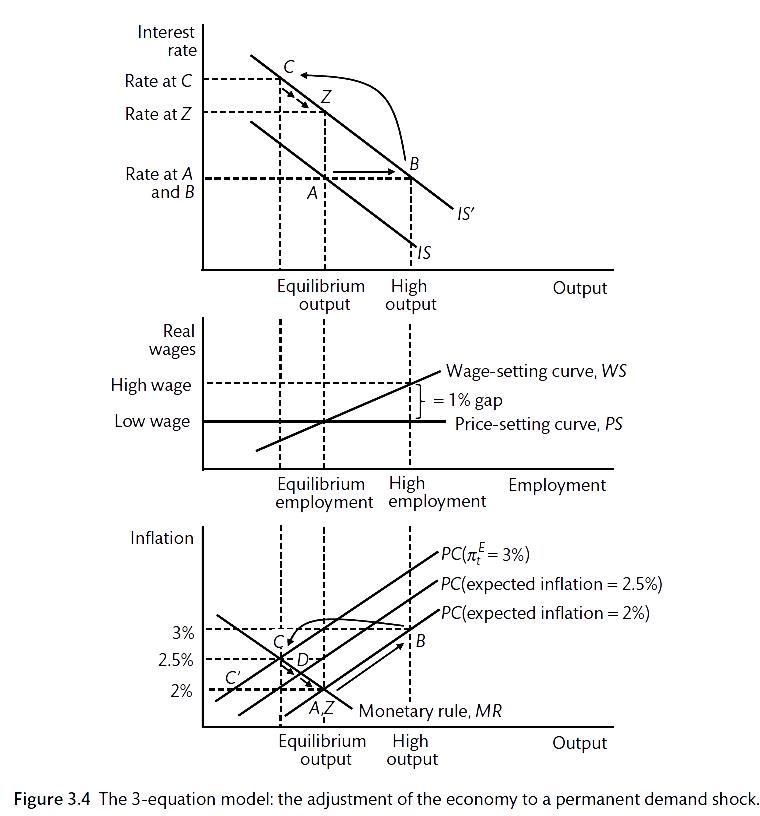
And slight negative shocks to the demand could drive prices down and then consumers are going to postpone their expenditures investment may go down and push the IS curve way to the left lowering the level of income. Rate policy or supply-side policy we come to that when we look at the different kinds of shocks that may affect the economy. We call supply shocks with these properties Keynesian supply shocks. Suppose a shock causes the IS curve to shift from IS1 to IS2. 9 we consider that occupations only experience the negative shocks.
 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
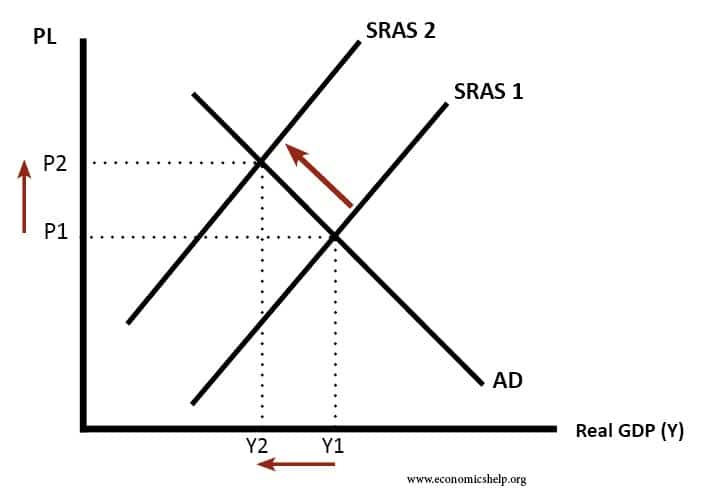
What happens to the aggregate output and price level. Positive external shocks might. An alternative is to consider both the negative shock caused by non-essential. Does this economy face a short-run recessionary gap or an inflationary gap. We focus on the implications for aggregate demand of a change.

An economic shock also known as a macroeconomic shock is any unexpected event that has a large-scale unexpected impact on the economy. Its also possible that the deterioration of demand will have larger economic effects than the supply shock that caused it and the researchers dub. For now the aim is simply to pin down the effects of different policies. Expansionary monetary or fiscal policy iv. Namely a negative supply shock can trigger a demand shortage that leads to a contraction in output and employment larger than the supply shock itself.

We focus on the implications for aggregate demand of a change. Demand may indeed overreact to the supply shock and lead to a demand-deficient recession write the researchers. What happens to the aggregate output and price level. But a supply shock can lead to a demand shock according to Guerrieri Lorenzoni Straub and Werning. The figures below show what effect this has on output under the two policies.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
So real interest rate can become negative even though nominal interest rate is fixed at zero. One can endow the agents with noisy signals about the future and let them solve the associated signal-extraction problem. This is the so called Backus-Smith puzzle. El Hadri et al. Beyond intellectual curiosity views on this debate shape government policies in response to crises.
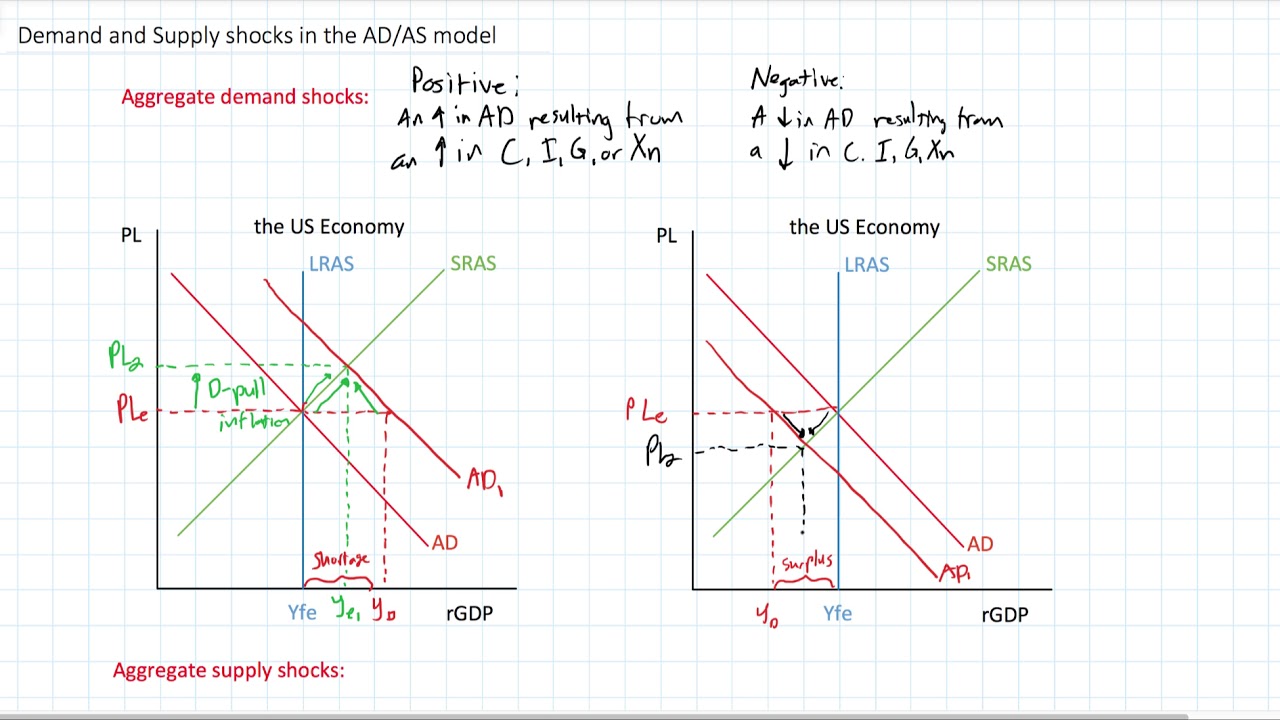 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Moderate inflation gives monetary policymakers more room to stimulate the economy when needed reducing the risk of falling into a liquidity trap. We focus on the implications for aggregate demand of a change. Latterly the covid-19 pandemic has created one of the worst economic shocks to impact the whole world economy. If an event causes massive layoffs or a downturn in the stock market consumers may slash spending triggering a negative feedback loop of businesses losing money leading to more layoffs and a further cut in consumption. And slight negative shocks to the demand could drive prices down and then consumers are going to postpone their expenditures investment may go down and push the IS curve way to the left lowering the level of income.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title negative demand shocks to the economy can come from by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.