Your Negative demand shock meaning images are available in this site. Negative demand shock meaning are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Negative demand shock meaning files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos.
If you’re searching for negative demand shock meaning images information related to the negative demand shock meaning keyword, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our site frequently gives you suggestions for refferencing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more informative video content and images that fit your interests.
Negative Demand Shock Meaning. Propagation of Shocks over Economic Networks Production Networks Intuition for Demand-side Shocks dG 1 0 y 1 Upstream e ect. DEMAND SHOCK meaning - DEMAND SHOCK definition - DEMAND SHOCK expl. People avoiding restaurants for fear of contagion is an example of a demand shock. For example if transport faces a 67 per cent demand shock and no supply shock bus drivers working in this industry will experience an overall 67 per cent employment shock.
 Demand Shock Overview Duration Effects On Prices And Quantity From corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Demand Shock Overview Duration Effects On Prices And Quantity From corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Sector 1 gets hit by a negative demand shock dG 1 0. A demand shock is a sudden surprise event that temporarily increases or decreases demand for. Central bank rate increases. A negative demand shock caused by reduced world demand for domestic goods or decrease in investment will shift the AD curve downward from AD 0 to AD 2 which in conjunction with SRAS give a lower level of GDP Y 2 thus opening up the deflationary gap Y 2-Y 3The automatic stabilizers viz cost reductions due to low input demand and lower. Suppliers are adversely a ected y 1 x 12x 14. Which is a negative demand shock.
And slight negative shocks to the demand could drive prices down and then consumers are going to postpone their expenditures investment may go down and push the IS curve way to the left lowering the level of income and initiating a recession which could also lead to a liquidity trap that needs to be avoided.
These cause less quantity of goods to be consumed and those consumers still in the market pay a lower price for the good. Daron Acemoglu MIT Networks October 20 and 25 2016. Which is a negative demand shock. A positive demand shock is a sudden increase in demand while a negative demand shock is a decrease in demand. In this lesson summary review and remind yourself of the key terms and graphs related to changes in the AD-AS model. And slight negative shocks to the demand could drive prices down and then consumers are going to postpone their expenditures investment may go down and push the IS curve way to the left lowering the level of income and initiating a recession which could also lead to a liquidity trap that needs to be avoided.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Sector 1 gets hit by a negative demand shock dG 1 0. Prices of goods and services are affected in both cases. This assumption also implies that the demand shock that workers of an industry experience equals the industrys output demand shock in percentage terms. In economics a shock is an unexpected or unpredictable event that affects an economy either positively or negatively. Which is a negative demand shock.
 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Which of the following is an example of a negative aggregate demand shock. And slight negative shocks to the demand could drive prices down and then consumers are going to postpone their expenditures investment may go down and push the IS curve way to the left lowering the level of income and initiating a recession which could also lead to a liquidity trap that needs to be avoided. Sector 1 gets hit by a negative demand shock dG 1 0. A negative aggregate supply. A positive demand shock is a sudden increase in demand while a negative demand shock is a decrease in demand.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
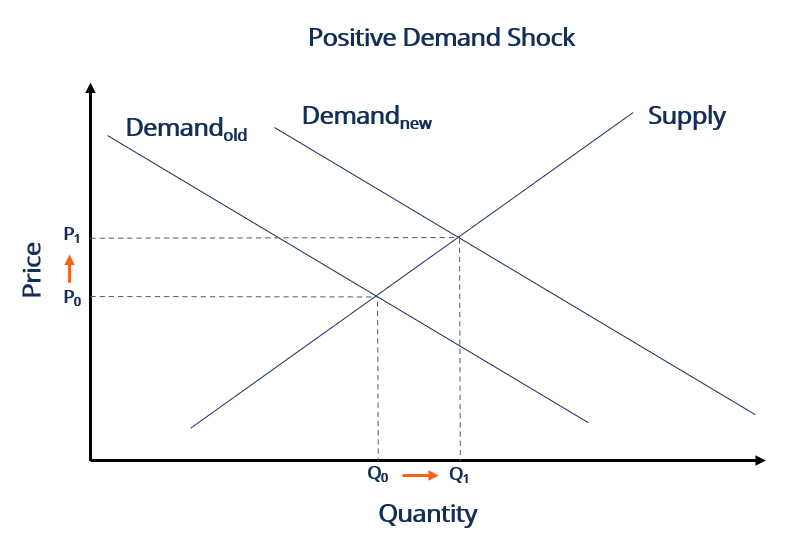
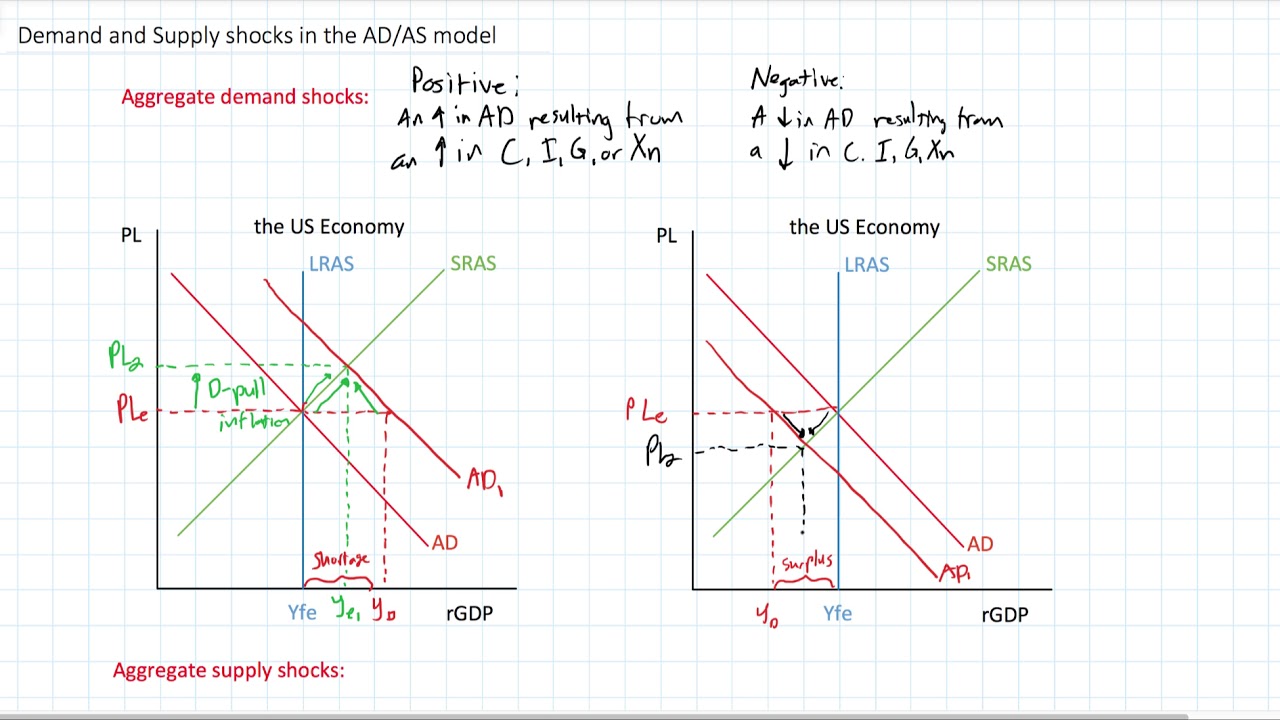
Some of them include. Topics include AD shocks such as changes in consumption investment government spending or net exports and supply shocks such as price surprises that impact SRAS and how changes in either of these impact output unemployment and the price. A faulty product may drive away the consumers which can trigger negative demand shock. For example the imposition of an embargo on trade in oil would cause an adverse supply shock since oil is a key factor of production for a wide variety of goods. A positive demand shock increases aggregate demand AD and a negative demand shock decreases aggregate demand.
 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
A demand shock is a sudden surprise event that temporarily increases or decreases demand for. A negative aggregate supply. In economics a demand shock is a sudden event that increases or decreases demand for goods or services temporarily. Leads to both higher. Negative Demand Shocks.
 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
What It Means for Producers and Consumers. Negative demand shocks cause aggregate demand to decrease. A faulty product may drive away the consumers which can trigger negative demand shock. A positive demand shock increases aggregate demand AD and a negative demand shock decreases aggregate demand. DEMAND SHOCK meaning - DEMAND SHOCK definition - DEMAND SHOCK expl.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
And slight negative shocks to the demand could drive prices down and then consumers are going to postpone their expenditures investment may go down and push the IS curve way to the left lowering the level of income and initiating a recession which could also lead to a liquidity trap that needs to be avoided. Terms in this set 5 Negative demand shock. People avoiding restaurants for fear of contagion is an example of a demand shock. Either shock will have an. This paper assesses the impact of the September 11 terrorist attacks and its after-effects on US.
 Source: sciencedirect.com
Source: sciencedirect.com
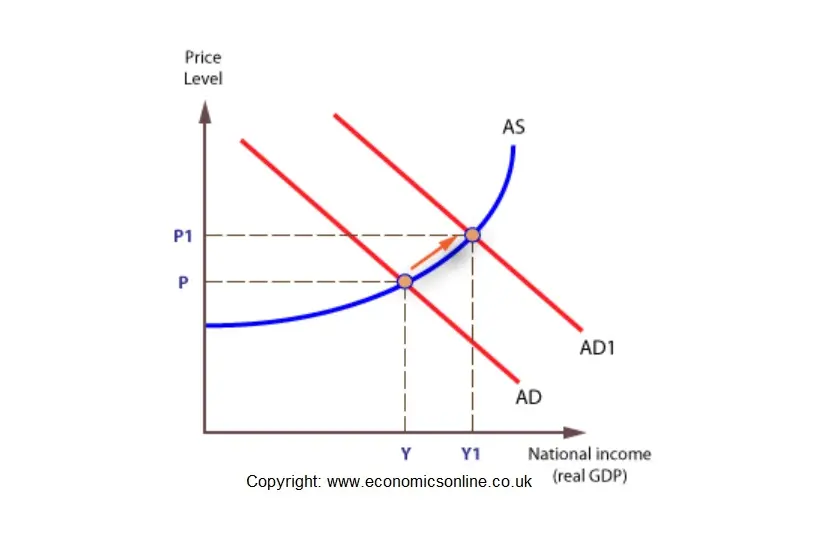
A negative demand shock caused by reduced world demand for domestic goods or decrease in investment will shift the AD curve downward from AD 0 to AD 2 which in conjunction with SRAS give a lower level of GDP Y 2 thus opening up the deflationary gap Y 2-Y 3The automatic stabilizers viz cost reductions due to low input demand and lower. Prices of goods and services are affected in both cases. In economics a shock is an unexpected or unpredictable event that affects an economy either positively or negatively. A negative demand shock is opposite to a positive demand shock. There can be many factors that can lead to a negative demand shock.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Both a positive demand shock and a negative demand shock will have an effect on the prices of goods and services. A negative aggregate supply. DEMAND SHOCK meaning - DEMAND SHOCK definition - DEMAND SHOCK expl. A negative demand shock caused by reduced world demand for domestic goods or decrease in investment will shift the AD curve downward from AD 0 to AD 2 which in conjunction with SRAS give a lower level of GDP Y 2 thus opening up the deflationary gap Y 2-Y 3The automatic stabilizers viz cost reductions due to low input demand and lower. In the short run the economy is self-correcting meaning the economy eventually moves back to potential output.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
A negative demand shock is opposite to a positive demand shock. A demand shock on the other hand reduces consumers ability or willingness to purchase goods and services at given prices. Both a positive demand shock and a negative demand shock will have an effect on the prices of goods and services. For example the imposition of an embargo on trade in oil would cause an adverse supply shock since oil is a key factor of production for a wide variety of goods. A faulty product may drive away the consumers which can trigger negative demand shock.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
Daron Acemoglu MIT Networks October 20 and 25 2016. A faulty product may drive away the consumers which can trigger negative demand shock. A positive demand shock is a sudden increase in demand while a negative demand shock is a decrease in demand. A positive demand shock is a sudden increase in demand while a negative demand shock is a decrease in demand. This assumption also implies that the demand shock that workers of an industry experience equals the industrys output demand shock in percentage terms.
 Source: investopedia.com
Source: investopedia.com
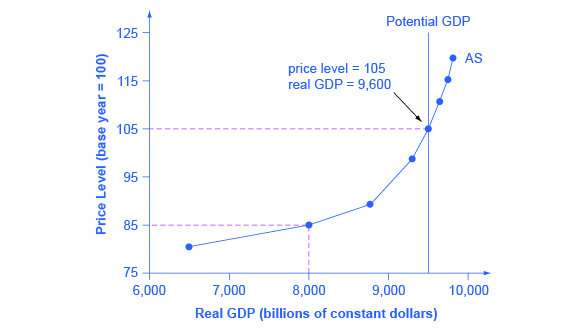
A demand shock on the other hand reduces consumers ability or willingness to purchase goods and services at given prices. For example if transport faces a 67 per cent demand shock and no supply shock bus drivers working in this industry will experience an overall 67 per cent employment shock. People avoiding restaurants for fear of contagion is an example of a demand shock. Leads to both higher. In the short run an economy-wide negative supply shock will shift the aggregate supply curve leftward decreasing the output and increasing the price level.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
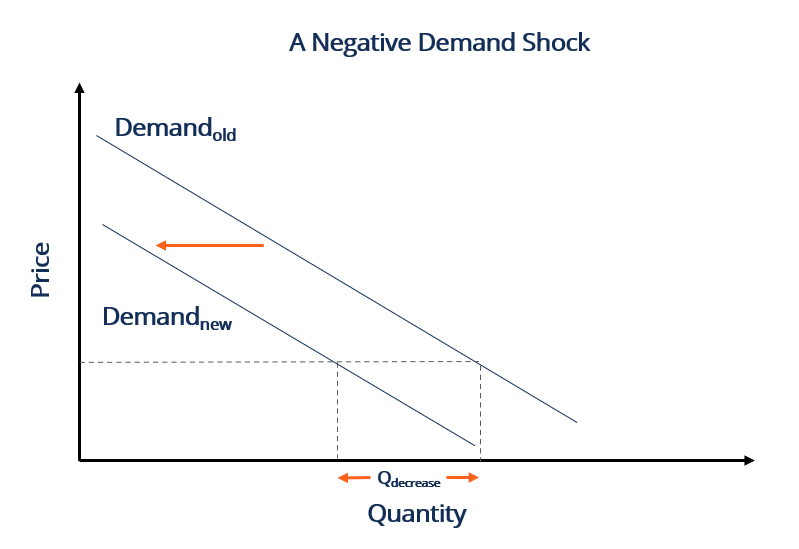
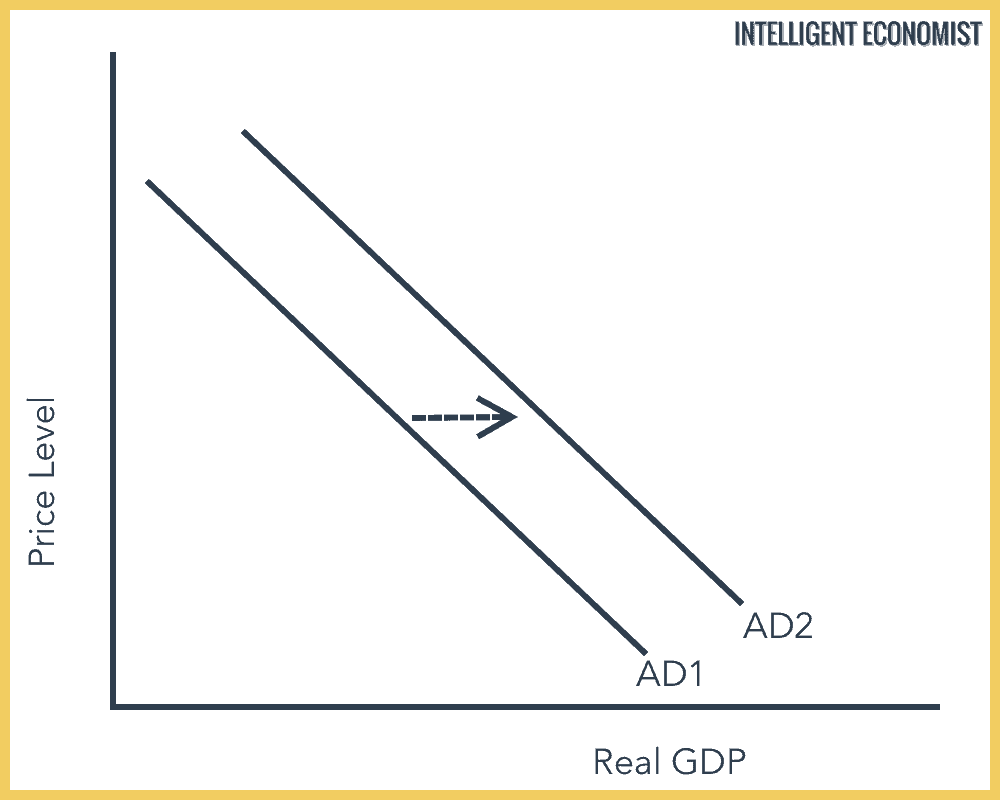
Negative Demand Shocks. A demand shock is a sudden surprise event that temporarily increases or decreases demand for. As shown below the entire demand curve shifts left. Central bank rate increases. Either shock will have an.
 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Both a positive demand shock and a negative demand shock will have an effect on the prices of goods and services. A demand shock is a sudden surprise event that temporarily increases or decreases demand for. Negative demand shocks cause aggregate demand to decrease. A productivity shock output adjusts gradually to its higher long-run level and there is a temporary negative effect on inflation and employment. DEMAND SHOCK meaning - DEMAND SHOCK definition - DEMAND SHOCK expl.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
In the short run the economy is self-correcting meaning the economy eventually moves back to potential output. A positive demand shock is a sudden increase in demand while a negative demand shock is a decrease in demand. A positive demand shock is a sudden increase in demand while a negative demand shock is a decrease in demand. We see that at any price the quantity demandeds decreased. A negative demand shock is opposite to a positive demand shock.
 Source: investopedia.com
Source: investopedia.com
A calibrated version of the model is able to generate realistic amounts of short-run volatility due to demand shocks in line with existing time-series evidence. A demand shock is a sudden surprise event that temporarily increases or decreases demand for. In this lesson summary review and remind yourself of the key terms and graphs related to changes in the AD-AS model. Propagation of Shocks over Economic Networks Production Networks Intuition for Demand-side Shocks dG 1 0 y 1 Upstream e ect. A productivity shock output adjusts gradually to its higher long-run level and there is a temporary negative effect on inflation and employment.
 Source: economicsonline.co.uk
Source: economicsonline.co.uk
There can be many factors that can lead to a negative demand shock. There can be many factors that can lead to a negative demand shock. Using monthly time-series data from 1986 to 2003 we find that September 11 resulted in both a negative transitory shock of over 30 and an ongoing negative demand shock amounting to roughly 74 of pre-September 11 demand. What does DEMAND SHOCK mean. People avoiding restaurants for fear of contagion is an example of a demand shock.
 Source: ig.com
Source: ig.com
A calibrated version of the model is able to generate realistic amounts of short-run volatility due to demand shocks in line with existing time-series evidence. Shocks affecting household or corporate spending such as changes in unemployment savings confidence wages and profits. In economics a demand shock is a sudden event that increases or decreases demand for goods or services temporarily. In economics a shock is an unexpected or unpredictable event that affects an economy either positively or negatively. A calibrated version of the model is able to generate realistic amounts of short-run volatility due to demand shocks in line with existing time-series evidence.

This assumption also implies that the demand shock that workers of an industry experience equals the industrys output demand shock in percentage terms. Sector 1 gets hit by a negative demand shock dG 1 0. A decrease in consumer confidence. A negative demand shock is opposite to a positive demand shock. For example if transport faces a 67 per cent demand shock and no supply shock bus drivers working in this industry will experience an overall 67 per cent employment shock.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title negative demand shock meaning by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.