Your Negative demand shock graph images are available in this site. Negative demand shock graph are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Negative demand shock graph files here. Get all free vectors.
If you’re searching for negative demand shock graph pictures information linked to the negative demand shock graph keyword, you have come to the ideal site. Our website frequently gives you hints for refferencing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly search and find more enlightening video content and images that fit your interests.
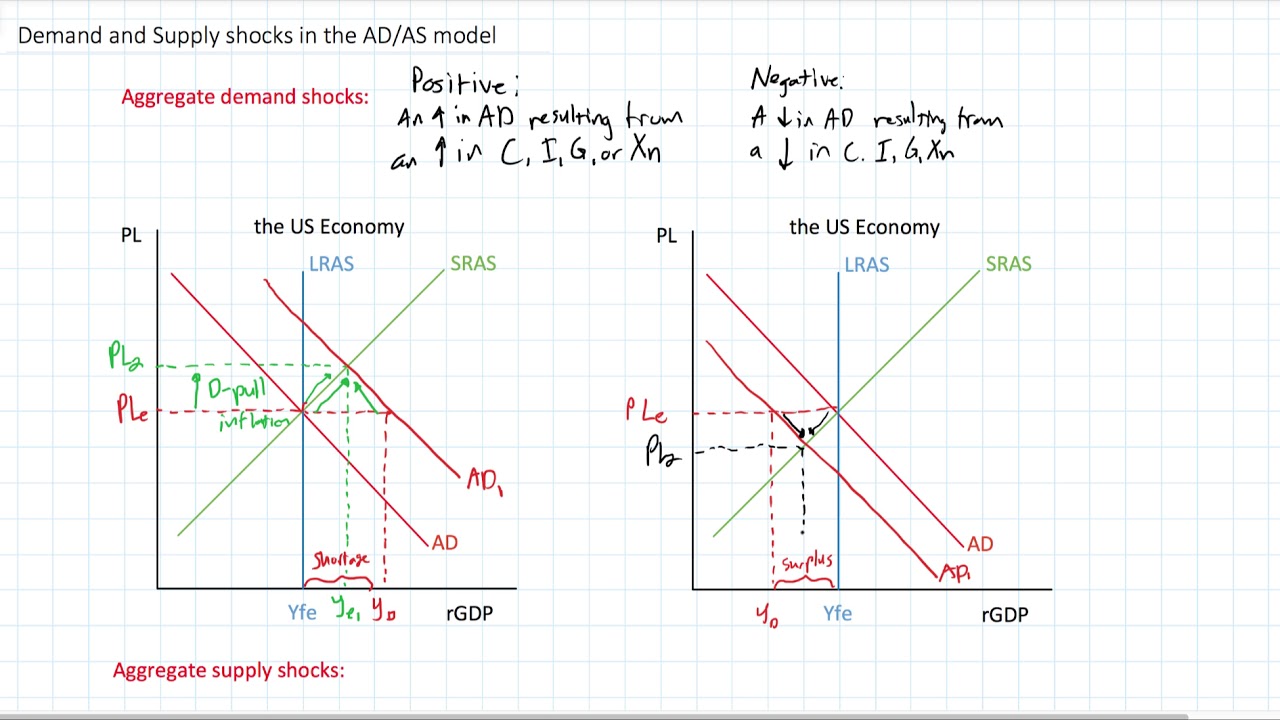
Negative Demand Shock Graph. These changes are called shocks to the economy. Too little production of an item may result in a positive demand shock while overproduction may result in a negative demand shock. Negative demand shock-a negative shift that leads to a lower aggregate price-AD curve shifts to the left Positive supply shock-a positive shift that leads to a lower aggregate price-SRAS curve shifts to the right Negative supply shock-stagflation-a negative shift that leads to a higher aggregate price-SRAS curve shifts to the left. Again supply played a slightly larger role than demand.
 A Larger Negative Demand Shock Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
A Larger Negative Demand Shock Download Scientific Diagram From researchgate.net
A demand shock on the other hand reduces consumers ability or willingness to purchase goods and services at given prices. Some of them include. When demand decreases its price decreases because of a shift. The elasticity of demand over a region of a demand curve is not really a well-defined object given that it is sensitive to how you construct it as. These changes are called shocks to the economy. Graph the short-run changes in the original equilibrium that will occur because of this demand shock.
Negative demand shock-a negative shift that leads to a lower aggregate price-AD curve shifts to the left Positive supply shock-a positive shift that leads to a lower aggregate price-SRAS curve shifts to the right Negative supply shock-stagflation-a negative shift that leads to a higher aggregate price-SRAS curve shifts to the left.
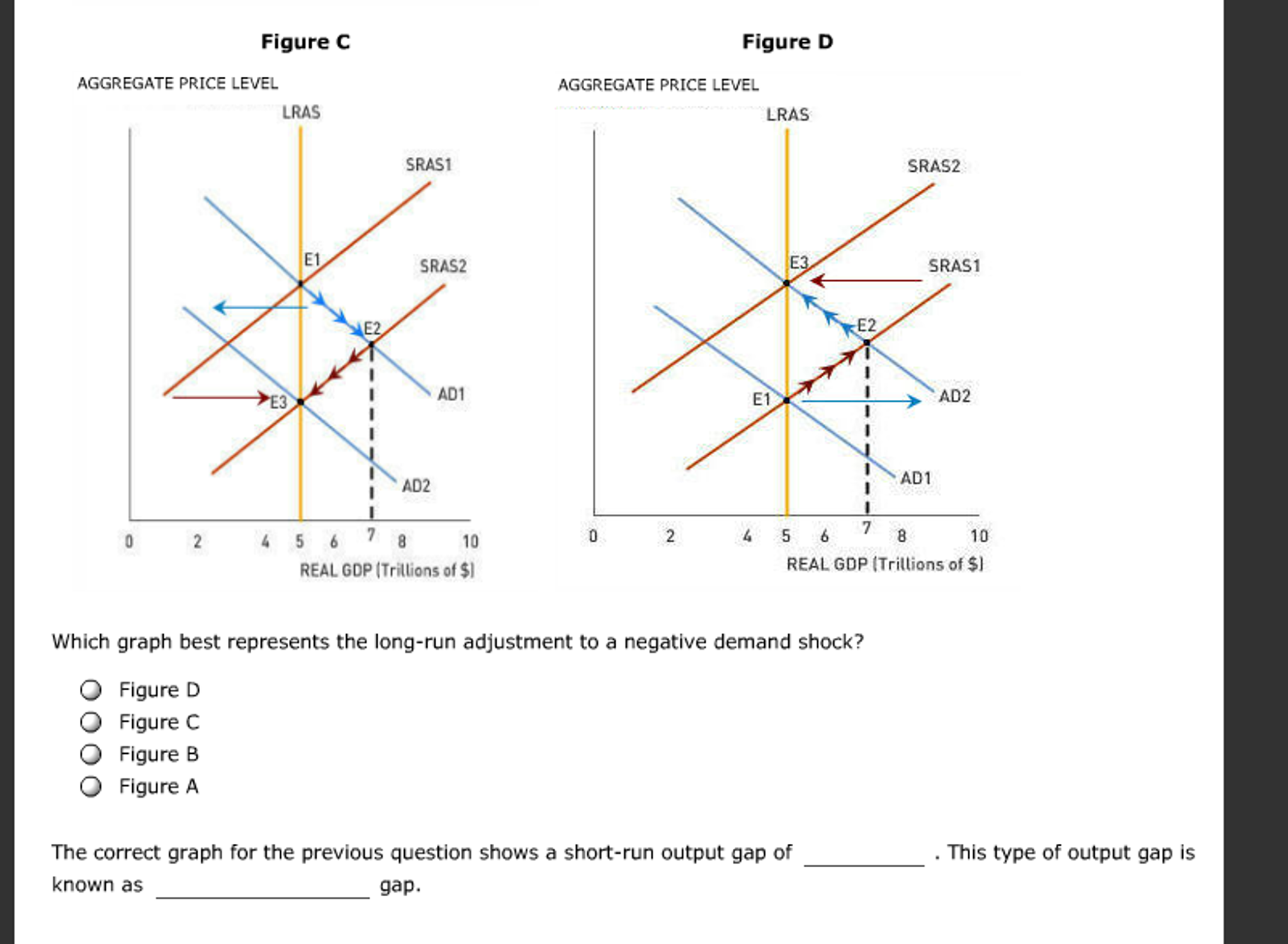
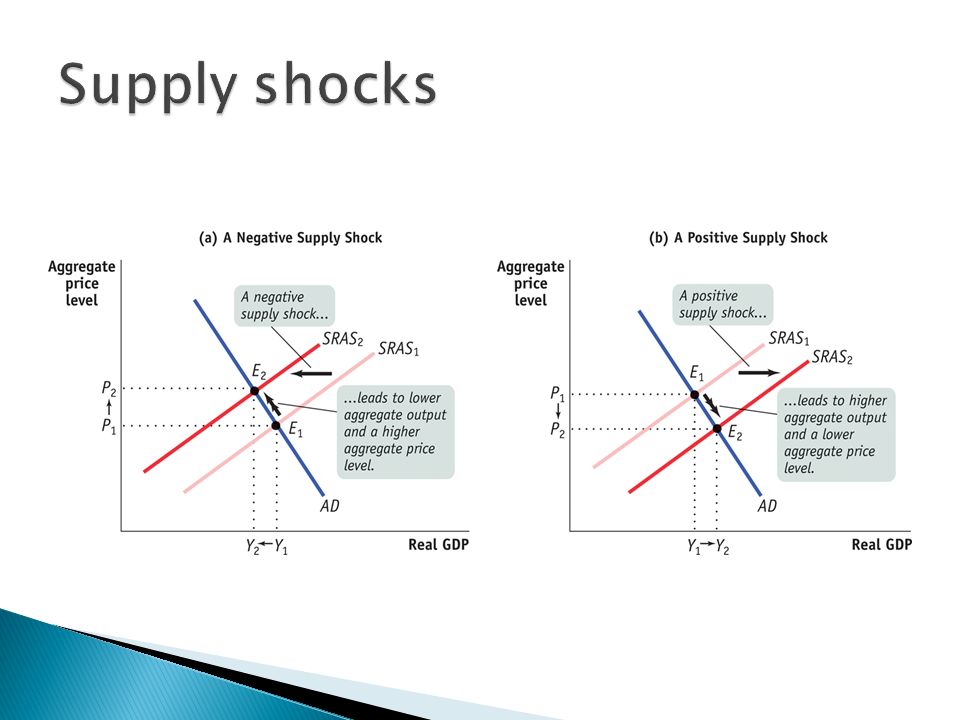
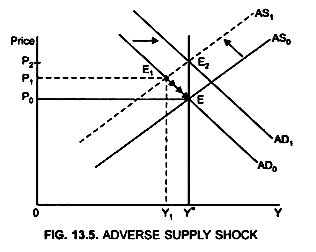
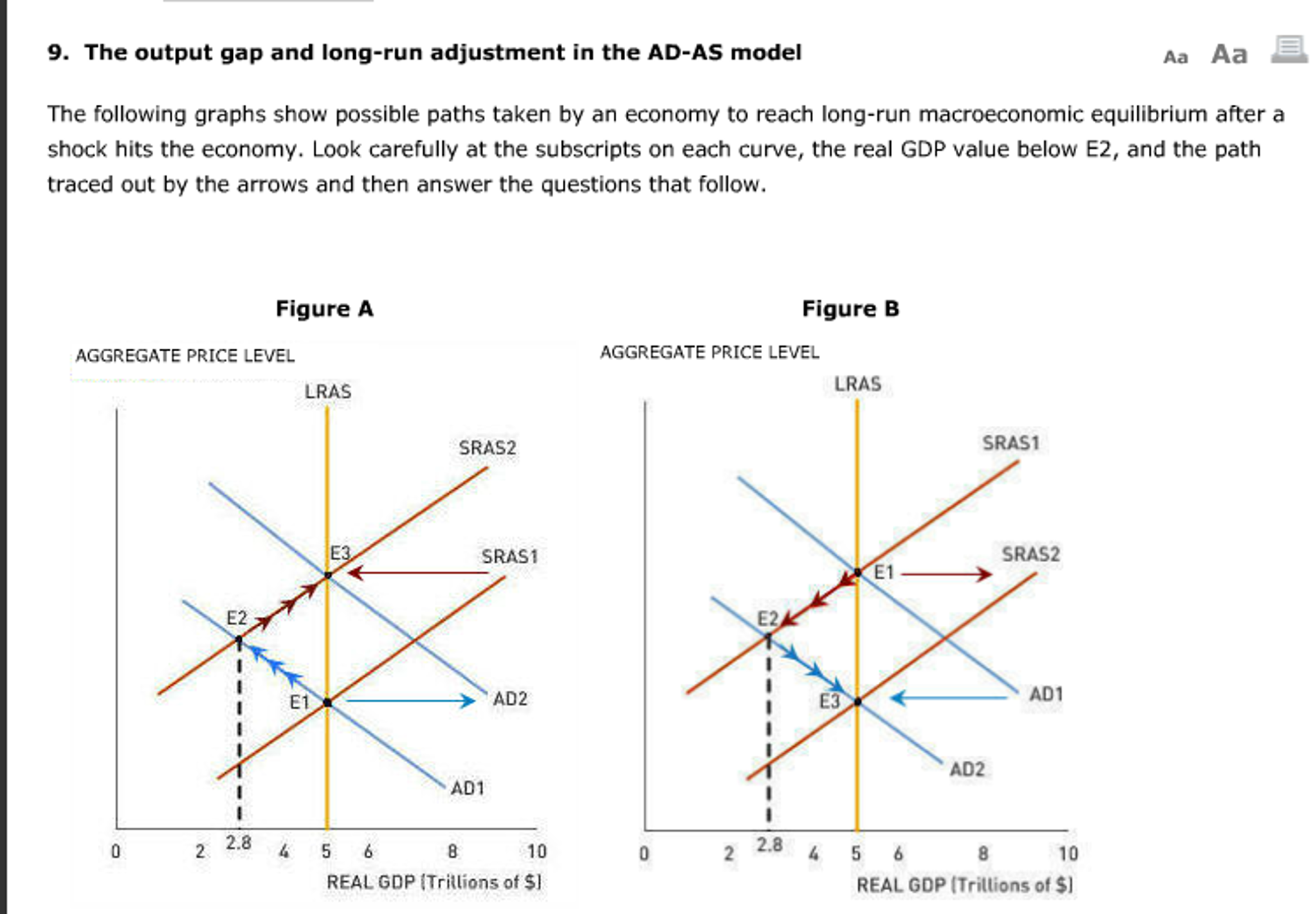
You should be able to graphically show the dynamics of both a positive and negative demand shock in constant and increasing cost competitive industries. A negative demand shock caused by reduced world demand for domestic goods or decrease in investment will shift the AD curve downward from AD 0 to AD 2 which in conjunction with SRAS give a lower level of GDP Y 2 thus opening up the deflationary gap Y 2 -Y 3. Move the appropriate curve or curves to illustrate the effect of the negative demand shock. For example if transport faces a 67 per cent demand shock and no supply shock bus drivers working in this industry will experience an overall 67 per cent employment shock. Refer to the graphs. The Supply Shocks With Diagram Any change in the AD and the AS will lead to fluctuations in the economy as a whole.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Central bank rate increases. Following the aggregate demand shock some of the shock appears in the form of a lower output gap and some is taken in the form of lower inflation. The elasticity of demand over a region of a demand curve is not really a well-defined object given that it is sensitive to how you construct it as. Topics include AD shocks such as changes in consumption investment government spending or net exports and supply shocks such as price surprises that impact SRAS and how changes in either of these impact output unemployment and the price. Move the appropriate curve or curves to illustrate the effect of the negative demand shock.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
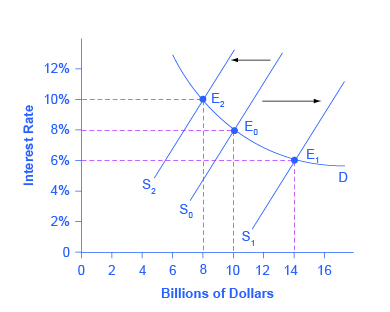
On the money market the supply of real money balance rises falls and interest rate rises falls. This is called a negative demand shock. In this lesson summary review and remind yourself of the key terms and graphs related to changes in the AD-AS model. These changes are called shocks to the economy. Negative demand shock-a negative shift that leads to a lower aggregate price-AD curve shifts to the left Positive supply shock-a positive shift that leads to a lower aggregate price-SRAS curve shifts to the right Negative supply shock-stagflation-a negative shift that leads to a higher aggregate price-SRAS curve shifts to the left.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Negative demand shock-a negative shift that leads to a lower aggregate price-AD curve shifts to the left Positive supply shock-a positive shift that leads to a lower aggregate price-SRAS curve shifts to the right Negative supply shock-stagflation-a negative shift that leads to a higher aggregate price-SRAS curve shifts to the left. The economy evolves over time after the initial impact of the shock as follows. Namely a negative supply shock can trigger a demand shortage that leads to a contraction in output and employment larger than the supply shock itself. These changes are called shocks to the economy. We call supply shocks with these properties Keynesian supply shocks.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Often in response to a severe negative supply shock such as an oil shock inflation expectations rise quickly and the short-run Phillips curve shifts upward. On the money market the supply of real money balance rises falls and interest rate rises falls. Often in response to a severe negative supply shock such as an oil shock inflation expectations rise quickly and the short-run Phillips curve shifts upward. A demand shock on the other hand reduces consumers ability or willingness to purchase goods and services at given prices. This is called a negative demand shock.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
A negative demand shock caused by reduced world demand for domestic goods or decrease in investment will shift the AD curve downward from AD 0 to AD 2 which in conjunction with SRAS give a lower level of GDP Y 2 thus opening up the deflationary gap Y 2 -Y 3. While most sectors experienced negative supply shocks some sectors. Now suppose the economy experiences a negative demand shock. As shown below the entire demand curve shifts left. When we calculate the elasticity over a region it is essentially an average of the elasticity over that region.
 Source: wikiwand.com
Source: wikiwand.com
In this lesson summary review and remind yourself of the key terms and graphs related to changes in the AD-AS model. These changes are called shocks to the economy. This indicates that LM curve shits up down and the. Namely a negative supply shock can trigger a demand shortage that leads to a contraction in output and employment larger than the supply shock itself. Even after the economys move northeast on the Phillips curve policy makers are stuck with the short-run tradeoff between inflation and unemployment.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
In this lesson summary review and remind yourself of the key terms and graphs related to changes in the AD-AS model. Temporary negative supply shocks such as those caused by a pandemic reduce output and employment. A negative demand shock caused by reduced world demand for domestic goods or decrease in investment will shift the AD curve downward from AD 0 to AD 2 which in conjunction with SRAS give a lower level of GDP Y 2 thus opening up the deflationary gap Y 2 -Y 3. This assumption also implies that the demand shock that workers of an industry experience equals the industrys output demand shock in percentage terms. Following the aggregate demand shock some of the shock appears in the form of a lower output gap and some is taken in the form of lower inflation.
 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
These changes are called shocks to the economy. Real demand drops causing economic stagnation. While most sectors experienced negative supply shocks some sectors. We call supply shocks with these properties Keynesian supply shocks. Now suppose the economy experiences a negative demand shock.

Often in response to a severe negative supply shock such as an oil shock inflation expectations rise quickly and the short-run Phillips curve shifts upward. While most sectors experienced negative supply shocks some sectors. Label both axes identify Y P and P 1 on your graph. Central bank rate increases. The automatic stabilizers viz cost reductions due to low input demand and lower.
 Source: khurak.net
Source: khurak.net
Suppose that Macroland experiences a negative demand shock. This is called a positive demand shock. Move the appropriate curve or curves to illustrate the effect of the negative demand shock. On the money market the supply of real money balance rises falls and interest rate rises falls. A temporary restriction placed on the trading of index futures because of substantial intraday decreases in the underlying indexes.

The Supply Shocks With Diagram Any change in the AD and the AS will lead to fluctuations in the economy as a whole. People avoiding restaurants for fear of contagion is an example of a demand shock. Negative Demand Shocks. Draw an equilibrium with the firm on the left graph and the market on the right graph. Too little production of an item may result in a positive demand shock while overproduction may result in a negative demand shock.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
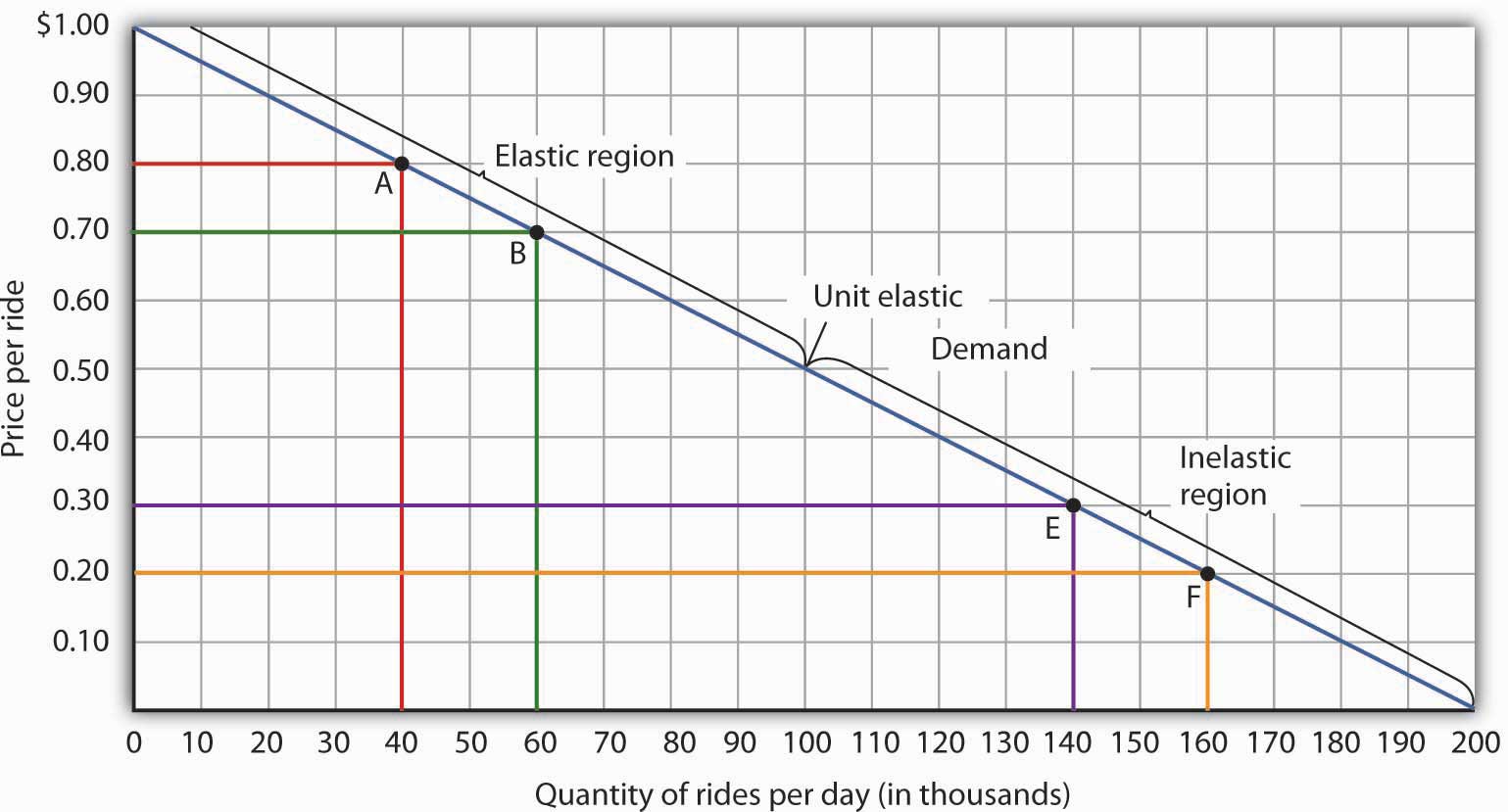
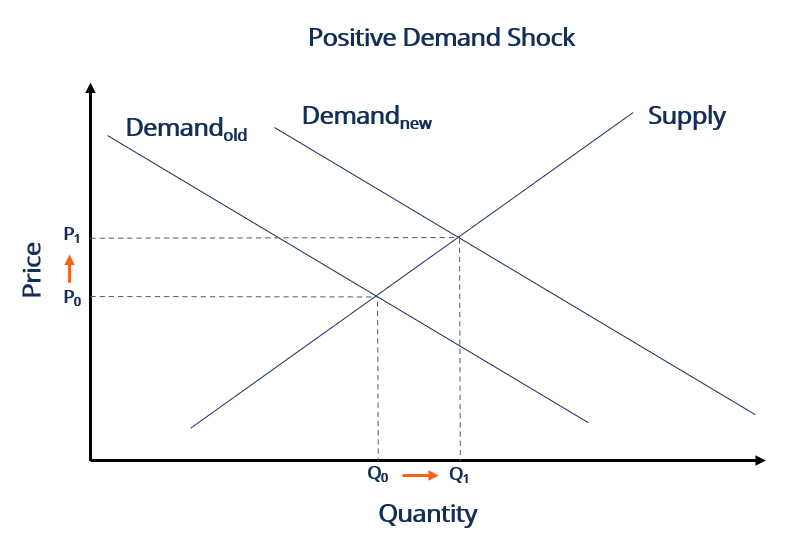
Negative supply shocks have many potential causes. This indicates that LM curve shits up down and the. Im not sure I would push it as hard as I once did. When demand for goods or services increases its price or price levels increases because of a shift in the demand curve to the right. Now suppose that there is a negative demand.

A negative demand shock caused by reduced world demand for domestic goods or decrease in investment will shift the AD curve downward from AD 0 to AD 2 which in conjunction with SRAS give a lower level of GDP Y 2 thus opening up the deflationary gap Y 2 -Y 3. People avoiding restaurants for fear of contagion is an example of a demand shock. Namely a negative supply shock can trigger a demand shortage that leads to a contraction in output and employment larger than the supply shock itself. Given the temporary nature of the shock the short run AS SRAS curve would shift left. For example if transport faces a 67 per cent demand shock and no supply shock bus drivers working in this industry will experience an overall 67 per cent employment shock.
 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Some of them include. As dire as they may be. A negative demand shock caused by reduced world demand for domestic goods or decrease in investment will shift the AD curve downward from AD 0 to AD 2 which in conjunction with SRAS give a lower level of GDP Y 2 thus opening up the deflationary gap Y 2 -Y 3. A potential trigger of demand shock is media coverage that stimulates a desire in the public for an item. Graph the short-run changes in the original equilibrium that will occur because of this demand shock.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
A temporary restriction placed on the trading of index futures because of substantial intraday decreases in the underlying indexes. This assumption also implies that the demand shock that workers of an industry experience equals the industrys output demand shock in percentage terms. Negative demand shock-a negative shift that leads to a lower aggregate price-AD curve shifts to the left Positive supply shock-a positive shift that leads to a lower aggregate price-SRAS curve shifts to the right Negative supply shock-stagflation-a negative shift that leads to a higher aggregate price-SRAS curve shifts to the left. These changes are called shocks to the economy. Negative demand shocks cause aggregate demand to decrease.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Again supply played a slightly larger role than demand. Consider the accompanying graph of aggregate demand AD and short run aggregate supply SRAS for a hypothetical economy. We call supply shocks with these properties Keynesian supply shocks. Im not sure I would push it as hard as I once did. Aggregate Demand Curve In chapter 10 we derive AD curve based on the quantity theory of money.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Temporary negative supply shocks such as those caused by a pandemic reduce output and employment. Elasticity of demand in a graph P Q P 0 Q 0 A D P 1 Q 1 The elasticity of demand usually changes everywhere along a demand curve. What happens to the firms inventory of computers if there is a negative demand shock and prices are flexible. These changes are called shocks to the economy. For example if transport faces a 67 per cent demand shock and no supply shock bus drivers working in this industry will experience an overall 67 per cent employment shock.

This is called a negative demand shock. In this lesson summary review and remind yourself of the key terms and graphs related to changes in the AD-AS model. This is called a negative demand shock. This assumption also implies that the demand shock that workers of an industry experience equals the industrys output demand shock in percentage terms. Temporary negative supply shocks such as those caused by a pandemic reduce output.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title negative demand shock graph by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.