Your Negative demand curve example images are ready in this website. Negative demand curve example are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Negative demand curve example files here. Get all free images.
If you’re searching for negative demand curve example images information linked to the negative demand curve example interest, you have visit the right site. Our website frequently gives you suggestions for refferencing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly hunt and locate more enlightening video articles and images that match your interests.
Negative Demand Curve Example. With a downward-sloping demand curve price and quantity demanded move in opposite directions so the price elasticity of demand is always negative. Click to see full answer. A social cost curve that is below the supply curve private cost curve for a good c. Some examples of negative externalities include.
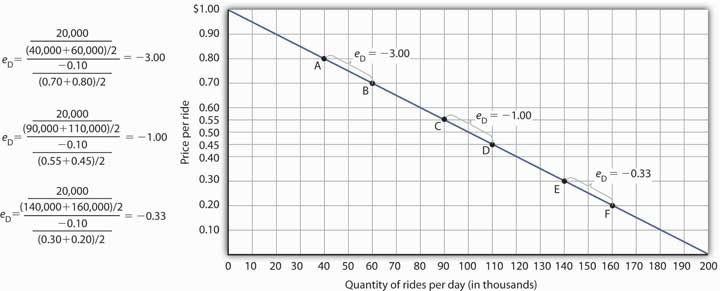 The Price Elasticity Of Demand From saylordotorg.github.io
The Price Elasticity Of Demand From saylordotorg.github.io
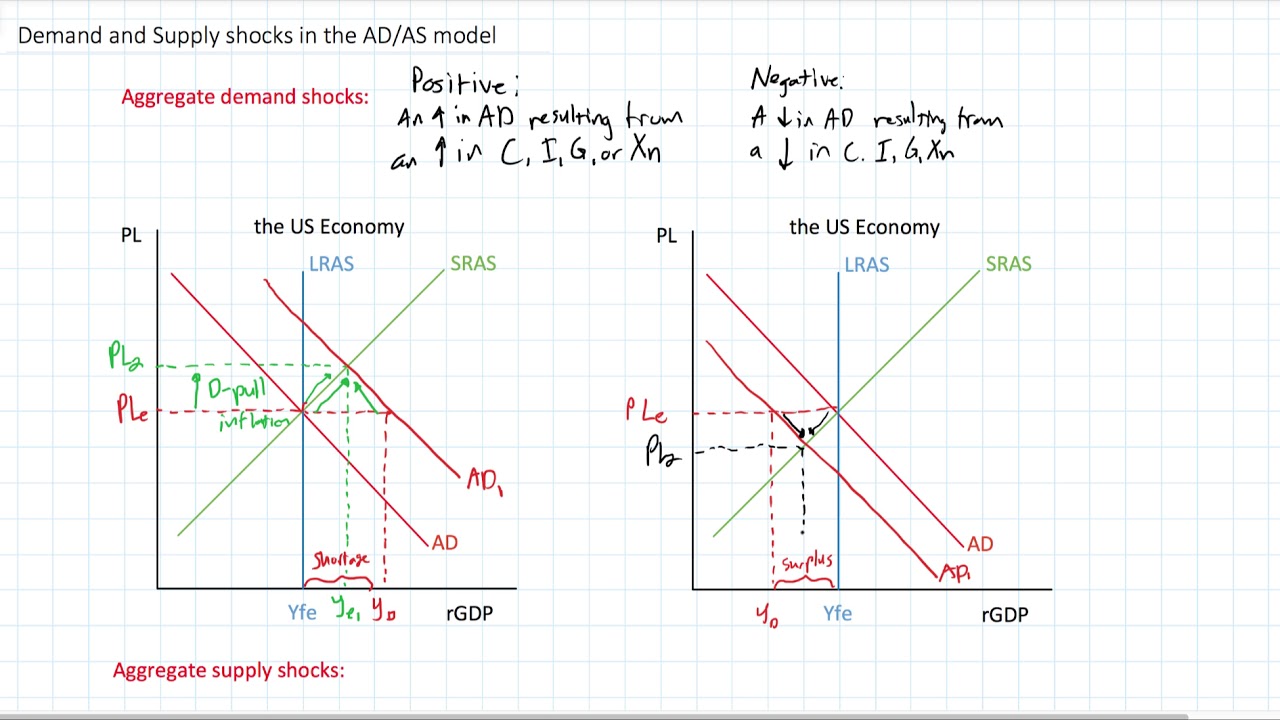
The aggregate demand curve and the short-run aggregate supply curve are identical. There can be many factors that can lead to a negative demand shock. This is called a negative demand shock. See Exercise 11 for an explanation of this important property of the power demand curve. If demand follows a power curve for any price the elasticity equals b. Some of them include.
A numerical example can be easily translated into a graph.
An example would be solar panels when they were first introduced. This could be due to a rise in. As gas price goes up the quantity of gas demanded will go down. Thus for the demand curve q 100p-2 the price elasticity of demand always equals 2. Now we can use IS-LM model to derive AD curve in another way. An example of a positive demand shock would be government stimulus checks and relaxed monetary policy in response to the pandemic.
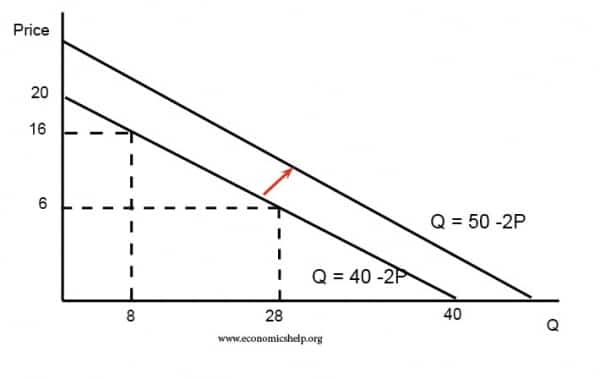 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
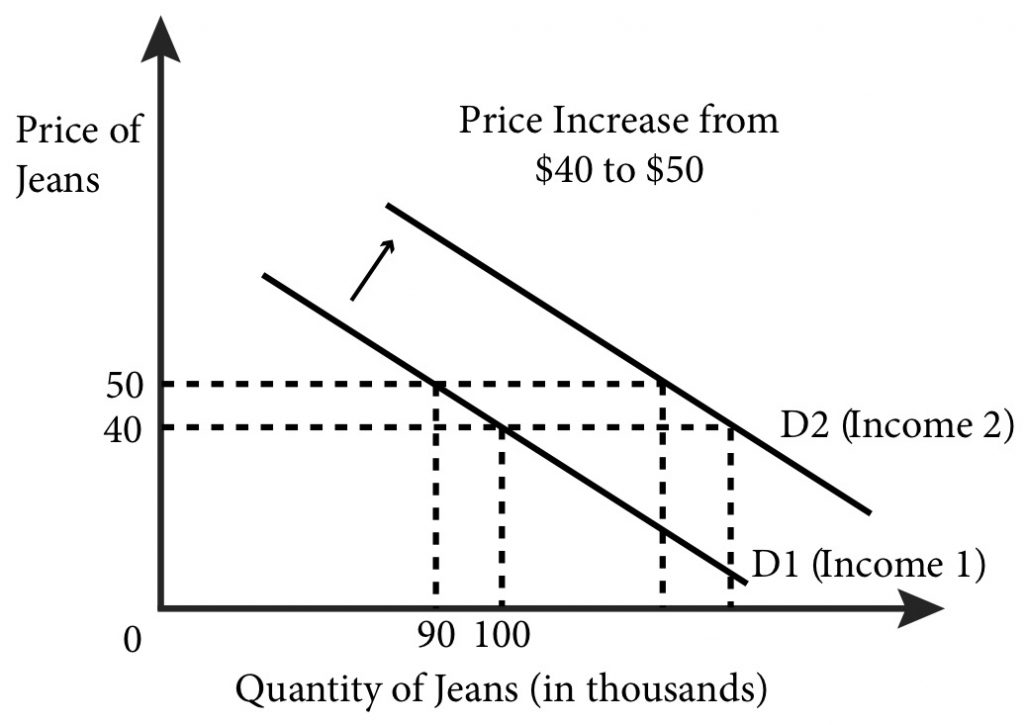
With a downward-sloping demand curve price and quantity demanded move in opposite directions so the price elasticity of demand is always negative. An example would be solar panels when they were first introduced. Estimating a Linear Demand Curve. Lastly examine multiple examples to understand its negative slope as well as using the market demand curve in both table and graph. In this case a has increased from 40 to 50.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
With a downward-sloping demand curve price and quantity demanded move in opposite directions so the price elasticity of demand is always negative. Often the elite of government will decide it is best if people would buy a certain product even though the public does not want it. Price elasticity is usually negative as shown in the above example. Plotting the curve P 800 - 3 Qd. As gas price goes up the quantity of gas demanded will go down.
 Source: economics.fundamentalfinance.com
Source: economics.fundamentalfinance.com
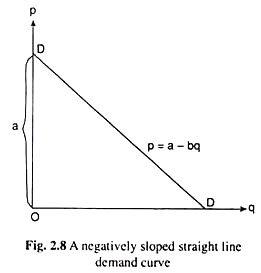
If the demand equation is linear it will be of the form. This means that for the same price demand is greater. There can be many factors that can lead to a negative demand shock. Some examples of negative externalities include. Some of them include.
 Source: open.oregonstate.education
Source: open.oregonstate.education
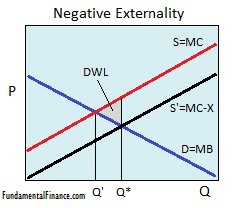
The short-run aggregate supply curve is vertical. The next module on the Keynesian Perspective will discuss the components of aggregate demand and the factors that affect them in more detail. On a supply and demand graph demand curves usually have a negative slope running from the top left of the graph to the bottom right. A negative externality on production occurs when the production of a good or service imposes a cost on third parties who are not involved in the production or consumption of the product. Lastly examine multiple examples to understand its negative slope as well as using the market demand curve in both table and graph.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
This indicates that LM curve shits up down and the. An example of a positive demand shock would be government stimulus checks and relaxed monetary policy in response to the pandemic. On the money market the supply of real money balance rises falls and interest rate rises falls. The next module on the Keynesian Perspective will discuss the components of aggregate demand and the factors that affect them in more detail. Negative demand occurs when under free-market conditions no one would be interested in the product.

The aggregate demand curve and the short-run aggregate supply curve are identical. Total revenue for each quantity equals the quantity times the price at which that quantity is demanded. It is extremely rare for there to be negative demand. It must slope downwards. Negative demand occurs when under free-market conditions no one would be interested in the product.
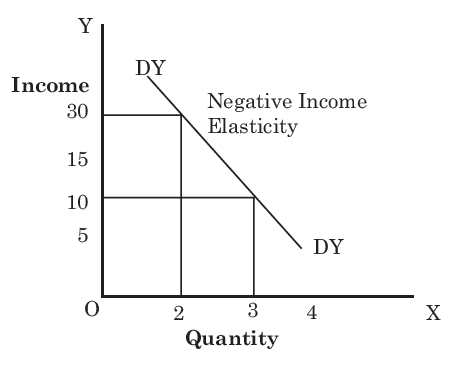 Source: geektonight.com
Source: geektonight.com
A social value that is above the demand curve for a good d. Price elasticity is usually negative as shown in the above example. The economy reaches its potential output. The monopoly firms total revenue curve is. Mathematically the variable representing the price of the complementary good would have a negative coefficient in the demand function.
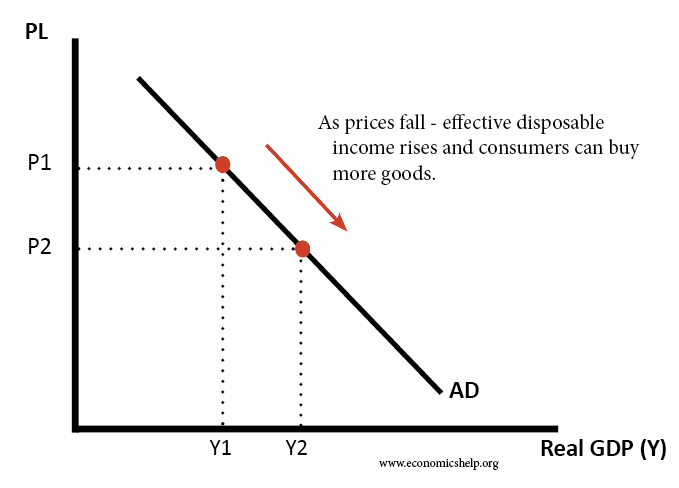 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Negative sloping demand curve is often explained in terms of utility analysis. P a - b Qd where a is the intercept along the Y-axis the highest price anyone would pay and b is the slope of the equation. The short-run aggregate supply curve is vertical. According to Marshall utility derived from a commodity can be measured in cardinal numbers like 1 2 3 etc just as we can measure the temperature of human body. An example of a negative demand shock would be a global pandemic.

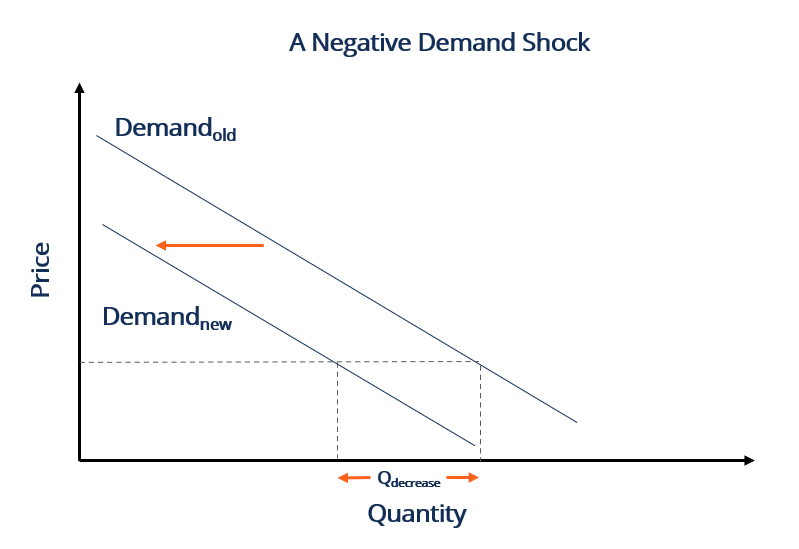
A negative externality on production occurs when the production of a good or service imposes a cost on third parties who are not involved in the production or consumption of the product. A social value that is above the demand curve for a good d. As shown below the entire demand curve shifts left. Negative demand shocks cause aggregate demand to decrease. This means that for the same price demand is greater.
 Source: businesstopia.net
Source: businesstopia.net
Click to see full answer. Estimating a Linear Demand Curve. It reflects a shift in the demand curve to the right. Price elasticity is usually negative as shown in the above example. With a downward-sloping demand curve price and quantity demanded move in opposite directions so the price elasticity of demand is always negative.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
According to Marshall utility derived from a commodity can be measured in cardinal numbers like 1 2 3 etc just as we can measure the temperature of human body. Price elasticity is usually negative as shown in the above example. See Exercise 11 for an explanation of this important property of the power demand curve. A social demand that is below the demand curve for a good. In this case a has increased from 40 to 50.
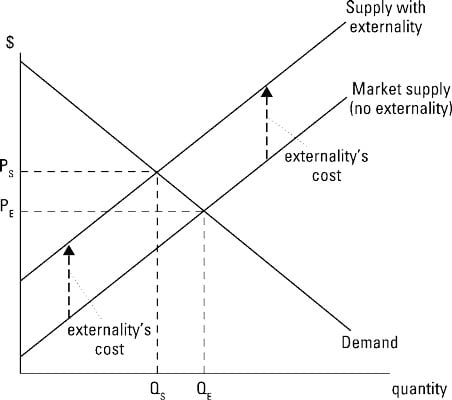 Source: dummies.com
Source: dummies.com
The quantity of aggregate output supplied is equal to the quantity demanded. A numerical example can be easily translated into a graph. B slope of demand curve. Qd 20 2P. Negative demand shocks cause aggregate demand to decrease.
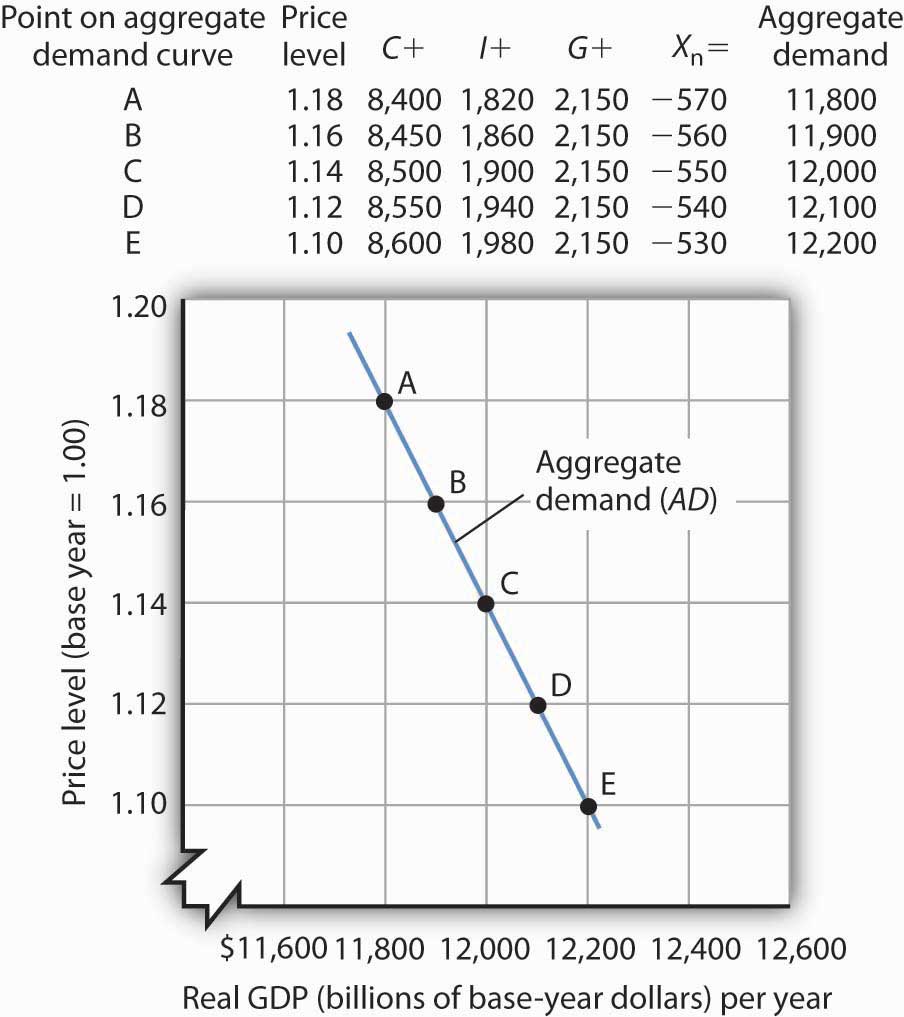 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Price elasticity that is positive is uncommon. Marshall intended to measure utility by an imaginary unit called util. We see that at any price the quantity demandeds decreased. It is extremely rare for there to be negative demand. Now we can use IS-LM model to derive AD curve in another way.
 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
The aggregate demand curve and the short-run aggregate supply curve are identical. Estimating a Linear Demand Curve. Marshall intended to measure utility by an imaginary unit called util. Negative demand occurs when under free-market conditions no one would be interested in the product. Because the price elasticity of demand shows the responsiveness of quantity demanded to a price change assuming that other factors that influence demand are unchanged it reflects movements along a demand curve.
 Source: faculty.icc.edu
Source: faculty.icc.edu
Check your understanding by. If the demand equation is linear it will be of the form. For example Q d a - P - P g where Q is the quantity of automobiles demanded P is the price of automobiles and P g is the price of gasoline. Q 10 P Q 10 P. The quantity of aggregate output supplied is equal to the quantity demanded.
 Source: saylordotorg.github.io
Source: saylordotorg.github.io
Some of them include. Central bank rate increases. This means that for the same price demand is greater. Some examples of negative externalities include. Plotting the curve P 800 - 3 Qd.
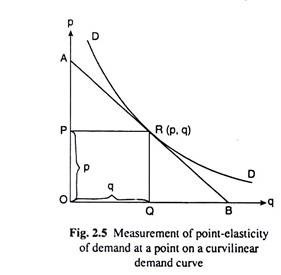 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
The short-run aggregate supply curve is vertical. Q 10 P Q 10 P. Lastly examine multiple examples to understand its negative slope as well as using the market demand curve in both table and graph. This could be due to a rise in. Example of linear demand curve.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Marshall intended to measure utility by an imaginary unit called util. These are all costs that fall on people other than the producer and consumer of that product. As shown below the entire demand curve shifts left. The economy reaches its potential output. Total revenue for each quantity equals the quantity times the price at which that quantity is demanded.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title negative demand curve example by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.