Your Logistic population growth theory images are ready in this website. Logistic population growth theory are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Logistic population growth theory files here. Find and Download all free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for logistic population growth theory pictures information linked to the logistic population growth theory topic, you have visit the right site. Our site frequently provides you with hints for seeing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly search and find more enlightening video articles and images that match your interests.
Logistic Population Growth Theory. From which you can see that the differential equation of population growth takes on a. Moving beyond that one-dimensional model we now consider the growth of two interde-pendent populations. In fact given an initial population with growth and reproductivity capacity the theoretical expectation would be that the population size will approach infinity as the time increases indefinitely. Logistic growth–spread of a disease–population of a species in a limited habitat fish in a lake fruit flies in a jar–sales of a new technological product Logistic Function For real numbers a b and c the function.
 Exponential Growth Logistic Growth Article Khan Academy From khanacademy.org
Exponential Growth Logistic Growth Article Khan Academy From khanacademy.org
Bifurcation diagram rendered with 1D Chaos Explorer. We can use in developing this theory the carrying capacity. As seen in Figure 21 the world population is approaching the capacity of carrying K in the formula of logistic differential equation rather than increasing exponentially. Population growth in the United States in 1920. In fact given an initial population with growth and reproductivity capacity the theoretical expectation would be that the population size will approach infinity as the time increases indefinitely. Next there is the Logistic Population Growth.
If the present population is 62500 then the population after 2 years can be denoted by.
The population of a town has a constant growth rate of 4 percent per annum. From which you can see that the differential equation of population growth takes on a. Obviously this is a roughly approximation of the reality since the real process of reproduction is not instantaneous in time and is strictly dependent on the previous instants of time. Logistic growth–spread of a disease–population of a species in a limited habitat fish in a lake fruit flies in a jar–sales of a new technological product Logistic Function For real numbers a b and c the function. Logistic differential equation model gives more realistic data with K carrying capacity compared to the exponential model in population growth modeling of a single species. I lim N t K t the population will ultimately reach its carrying capacity.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
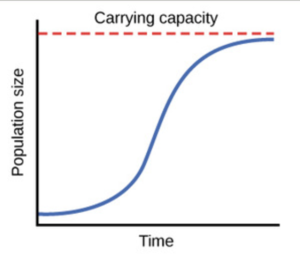
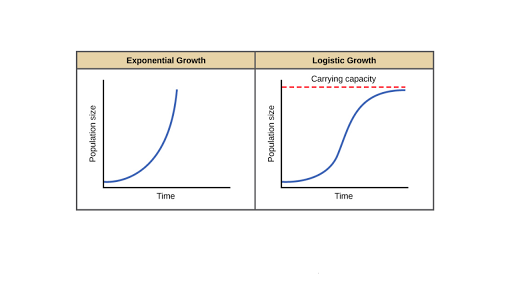
In logistic growth a population will continue to grow until it reaches carrying capacity which is the maximum number of individuals the environment can support. Logistic growth–spread of a disease–population of a species in a limited habitat fish in a lake fruit flies in a jar–sales of a new technological product Logistic Function For real numbers a b and c the function. If growth is limited by resources such as food the exponential growth of the population begins to slow as competition for those resources increases. We can use in developing this theory the carrying capacity. As seen in Figure 21 the world population is approaching the capacity of carrying K in the formula of logistic differential equation rather than increasing exponentially.
 Source: projectrhea.org
Source: projectrhea.org
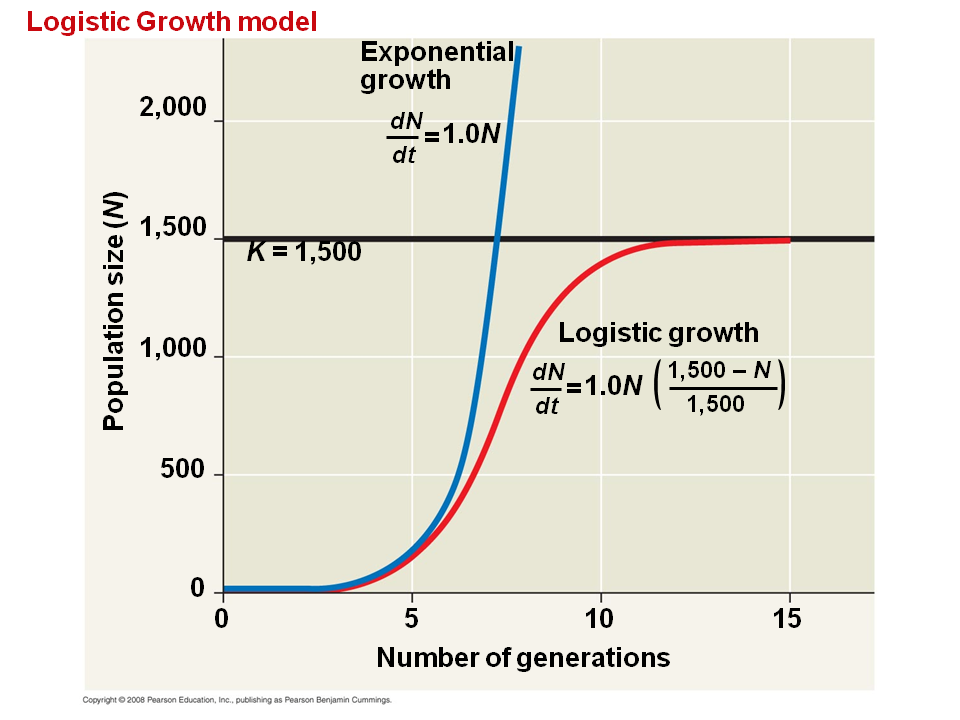
The logistic growth model Chapter 11 focused on a single population. All individuals are identical. From which you can see that the differential equation of population growth takes on a. In fact given an initial population with growth and reproductivity capacity the theoretical expectation would be that the population size will approach infinity as the time increases indefinitely. The geometric or exponential growth of all populations is eventually curtailed by food availability competition for other resources predation disease or some other ecological factor.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
It allows you to discover that for a population to stabilize per capita birth and death rates must change as the population grows and they must become equal at some equilibrium population size. 23 Logistic population growth The pattern of rapid initial growth that later stabilizes at a constant number of individuals is common in biological systems whether you are describing the growth of bacteria in culture duckweed in a pond or wildebeest in the Serengeti. As seen in Figure 21 the world population is approaching the capacity of carrying K in the formula of logistic differential equation rather than increasing exponentially. It allows you to discover that for a population to stabilize per capita birth and death rates must change as the population grows and they must become equal at some equilibrium population size. Relationship between them determines logistic population growth and whether the population eventually stabilizes.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
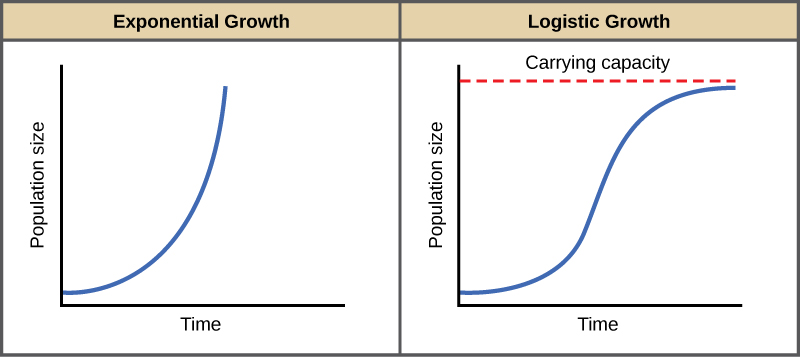
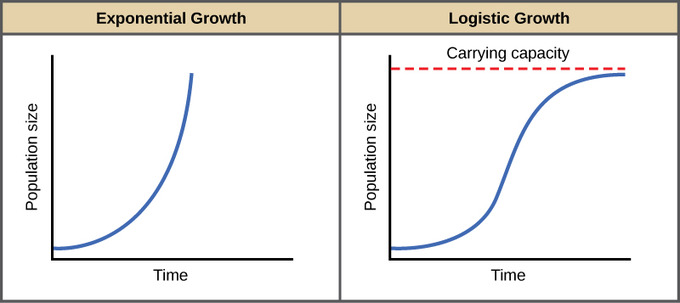
Exponential growth produces a J-shaped curve while logistic growth produces an S-shaped curve. Verhulsts Logistic growth theory of population. Next there is the Logistic Population Growth. Exponential growth produces a J-shaped curve while logistic growth produces an S-shaped curve. Ii The relative growth rate 1.
 Source: wikiwand.com
Source: wikiwand.com
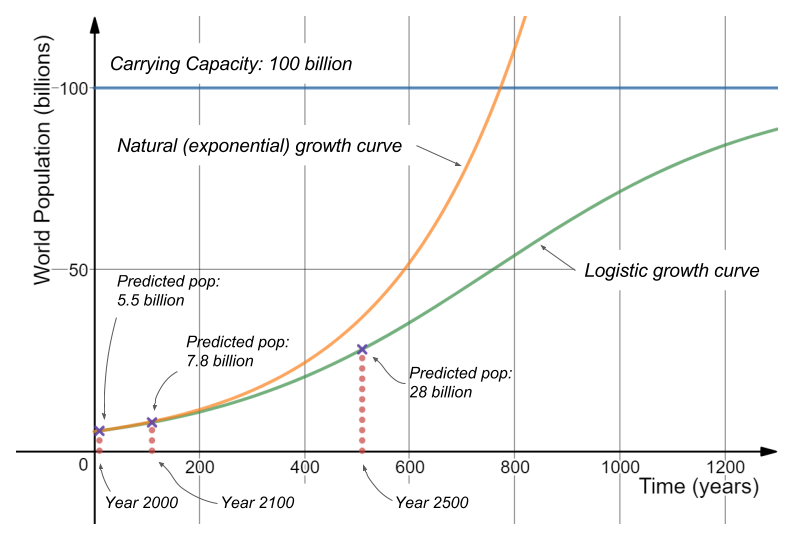
Use a logistic model with an assumed carrying capacity of 100 10 9 an ob-served population of 5 10 9 in 1986 and an observed rate of growth of 2 percent per year when population size is 5 10 9 to predict the population of the earth in the year 2000. 25 Assumptions of the logistic growth model. He said that the growth of population tends to slow down with the increase in density of population. Logistic differential equation model gives more realistic data with K carrying capacity compared to the exponential model in population growth modeling of a single species. Ii The relative growth rate 1.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
He said that the growth of population tends to slow down with the increase in density of population. Many animal species are fertile only for a brief period during the year and the young are born in a particular season so that by the time they are ready to eat solid food it will be plentiful. Because of the work of population ecologists in recent years the logistic growth model has features of immediate interest in cultural ecology. Logistic growth–spread of a disease–population of a species in a limited habitat fish in a lake fruit flies in a jar–sales of a new technological product Logistic Function For real numbers a b and c the function. Logistic differential equation model gives more realistic data with K carrying capacity compared to the exponential model in population growth modeling of a single species.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
The logistic equation is a model of population growth where the size of the population exerts negative feedback on its growth rate. We can use in developing this theory the carrying capacity. This growth model is normally for short lived organisms due to the introduction of a new or underexploited environment. Ii The relative growth rate 1. Logistic growth–spread of a disease–population of a species in a limited habitat fish in a lake fruit flies in a jar–sales of a new technological product Logistic Function For real numbers a b and c the function.
 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
We can use in developing this theory the carrying capacity. 25 Assumptions of the logistic growth model. Population growth Suppose that the size of the population of an. Use a logistic model with an assumed carrying capacity of 100 10 9 an ob-served population of 5 10 9 in 1986 and an observed rate of growth of 2 percent per year when population size is 5 10 9 to predict the population of the earth in the year 2000. Verhulst enhanced the exponential growth theory of population as saying that the populations growth is NOT ALWAYS growing but there is.
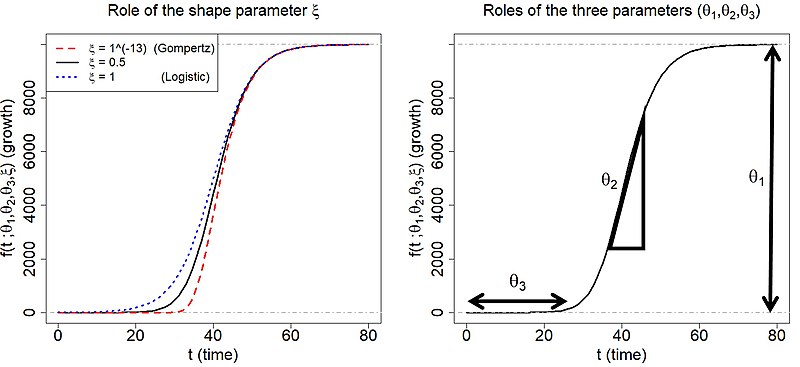
The three key features of the logistic growth are. In 1847 appeared a Second enquiry on the law of population growth in which Verhulst gave up the logistic equation and chose instead a differential equation that can be written in the form dP dt r 1 P K. This growth model is normally for short lived organisms due to the introduction of a new or underexploited environment. Equation 1 has solution 0 0 0 K N e N KN N t rt 2 where N0 is the population size at time t 0. That pattern is known as logistic population growth.
He said that the growth of population tends to slow down with the increase in density of population. The three key features of the logistic growth are. 23 Logistic population growth The pattern of rapid initial growth that later stabilizes at a constant number of individuals is common in biological systems whether you are describing the growth of bacteria in culture duckweed in a pond or wildebeest in the Serengeti. Bifurcation diagram rendered with 1D Chaos Explorer. Population growth Suppose that the size of the population of an.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Logistic growth–spread of a disease–population of a species in a limited habitat fish in a lake fruit flies in a jar–sales of a new technological product Logistic Function For real numbers a b and c the function. From which you can see that the differential equation of population growth takes on a. The geometric or exponential growth of all populations is eventually curtailed by food availability competition for other resources predation disease or some other ecological factor. It allows you to discover that for a population to stabilize per capita birth and death rates must change as the population grows and they must become equal at some equilibrium population size. The time course of this model is the familiar S-shaped growth that.
 Source: steemit.com
Source: steemit.com
The three key features of the logistic growth are. The logistic equation is a simple model of population growth in conditions where there are limited resources. Because of the work of population ecologists in recent years the logistic growth model has features of immediate interest in cultural ecology. 25 Assumptions of the logistic growth model. Many animal species are fertile only for a brief period during the year and the young are born in a particular season so that by the time they are ready to eat solid food it will be plentiful.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Population growth in the United States in 1920. If growth is limited by resources such as food the exponential growth of the population begins to slow as competition for those resources increases. All individuals are identical. As seen in Figure 21 the world population is approaching the capacity of carrying K in the formula of logistic differential equation rather than increasing exponentially. 25 Assumptions of the logistic growth model.
 Source: xaktly.com
Source: xaktly.com
In logistic growth a populations per capita growth rate gets smaller and smaller as population size approaches a maximum imposed by limited resources in the environment known as the carrying capacity. Given two species of animals interdependence might arise because one species the prey serves as a food source for the other species the predator. If the present population is 62500 then the population after 2 years can be denoted by. The logistic equation is a simple model of population growth in conditions where there are limited resources. Ii The relative growth rate 1.
The foundation of logistic curve theory was laid by Quetlet in 1835. Exponential growth produces a J-shaped curve while logistic growth produces an S-shaped curve. As seen in Figure 21 the world population is approaching the capacity of carrying K in the formula of logistic differential equation rather than increasing exponentially. That pattern is known as logistic population growth. Given two species of animals interdependence might arise because one species the prey serves as a food source for the other species the predator.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In fact given an initial population with growth and reproductivity capacity the theoretical expectation would be that the population size will approach infinity as the time increases indefinitely. Because of the work of population ecologists in recent years the logistic growth model has features of immediate interest in cultural ecology. But people did not give recognition to it. The three key features of the logistic growth are. In fact given an initial population with growth and reproductivity capacity the theoretical expectation would be that the population size will approach infinity as the time increases indefinitely.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
We can ignore differences between adults and juveniles or between males and females and simply keep track of the total population size N. Population growth Suppose that the size of the population of an. 23 Logistic population growth The pattern of rapid initial growth that later stabilizes at a constant number of individuals is common in biological systems whether you are describing the growth of bacteria in culture duckweed in a pond or wildebeest in the Serengeti. In fact given an initial population with growth and reproductivity capacity the theoretical expectation would be that the population size will approach infinity as the time increases indefinitely. In logistic growth a population will continue to grow until it reaches carrying capacity which is the maximum number of individuals the environment can support.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
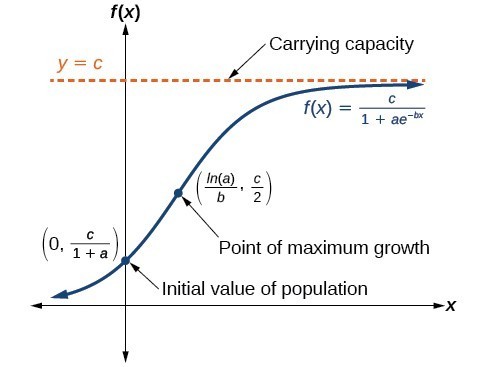
Introduction to Logistic Curve Theory. DN dt rN1 N K. The foundation of logistic curve theory was laid by Quetlet in 1835. Equation 1 has solution 0 0 0 K N e N KN N t rt 2 where N0 is the population size at time t 0. Is a logistic function.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title logistic population growth theory by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






