Your Law of demand meaning in econ images are available in this site. Law of demand meaning in econ are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Law of demand meaning in econ files here. Get all royalty-free images.
If you’re searching for law of demand meaning in econ pictures information connected with to the law of demand meaning in econ keyword, you have visit the ideal blog. Our site always provides you with hints for downloading the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more informative video content and graphics that fit your interests.
Law Of Demand Meaning In Econ. Naturally people prioritize more urgent wants and needs over less urgent ones in their economic behavior and this carries over into how people choose among the limited means. The law of demand is a principle of economics that states that when the price of a good increases demand will decrease and vice versa. The law of demand in economics states that as the price of goods fall the quantity demanded increases. The theory defines the relationship between the price of the commodity and the willingness of the buyers to either buy or sell that commodity.
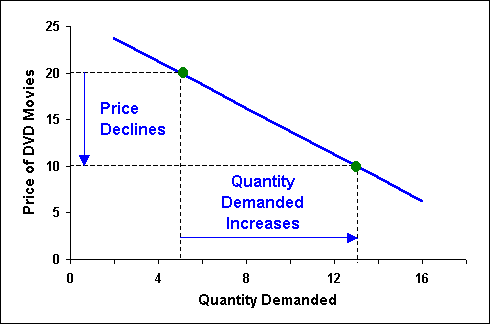 Introduction To Macroeconomics 3 Microeconomic Laws Of Demand And Supply From lidderdale.com
Introduction To Macroeconomics 3 Microeconomic Laws Of Demand And Supply From lidderdale.com
The law of demand focuses on those unlimited wants. People will buy less of something when its price rises. Naturally people prioritize more urgent wants and needs over less urgent ones in their economic behavior and this carries over into how people choose among the limited means. The other factors that can affect the quantity demanded of a product such as the price of relative good the income of consumers tastes and preferences are assumed to be constant. The law of demand expresses a relationship between the quantity demanded and its price. Demand is an economic principle referring to a consumers desire and willingness to pay a price for a specific good or service.
If the demand equation is linear it will be of the form.
The Law of demand is the concept of the economics according to which the prices of the goods or services and their quantity demanded is inversely related to each other when the other factors remain constant. In other words when the price of any product increases then its demand will fall and when its price decreases then its demand will increase. Demand is derived from the law of diminishing marginal utility the fact that consumers use economic goods to satisfy their most urgent needs first. In other words there is an inverse relationship between quantity demanded of a commodity and its price. The other factors that can affect the quantity demanded of a product such as the price of relative good the income of consumers tastes and preferences are assumed to be constant. Law of Demand and Elasticity of Demand 9 Law of Demand Law of demand states that People will Buy more at Lower Prices and Buy less at Higher Prices Ceteris paribus or other things Remaining the Same.
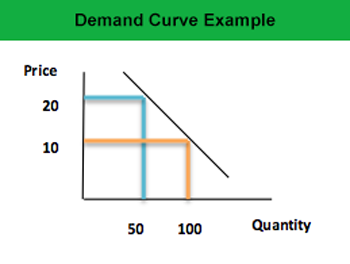 Source: myaccountingcourse.com
Source: myaccountingcourse.com
Demand is based on needs and wantsa consumer may be able to differentiate between a need and a want but from an economists perspective they are the same thing. In other words customers buy a high quantity of products at lower prices and vice versa. When the price of a product increases the demand for the same product will fall. The law of demand expresses a relationship between the quantity demanded and its price. Explore the definition and examples of the law of demand and discover exceptions to the rule.
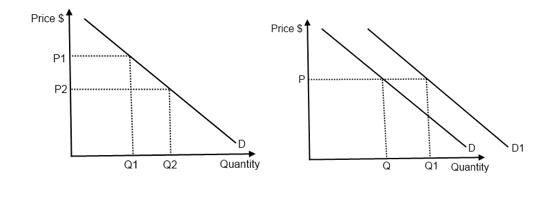 Source: ibguides.com
Source: ibguides.com
Law of Demand The Law of Demand States that other things being constant Ceteris Peribus the demand for a good extends with a decrease in price and contracts with an increase in price. The law of demand is a principle of economics that states that when the price of a good increases demand will decrease and vice versa. Demand is based on needs and wantsa consumer may be able to differentiate between a need and a want but from an economists perspective they are the same thing. People will buy less of something when its price rises. The law of demand and supply is a theory that establishes the relationship between the sellers and buyers of a particular commodity.
 Source: investopedia.com
Source: investopedia.com
Economics involves the study of how people use limited means to satisfy unlimited wants. P a - b Qd. If the demand equation is linear it will be of the form. The law of demand is a fundamental principle of economics that states that at a higher price consumers will demand a lower quantity of a good. Demand is derived from the law of diminishing marginal utility the fact that consumers use economic goods to satisfy their most urgent needs first.

The maximum amount of a good which consumers would be willing to buy at a given price. It may be defined in Marshalls words as the amount demanded increases with a fall in price and diminishes with a rise in price. In other words customers buy a high quantity of products at lower prices and vice versa. In other words there is an inverse relationship between quantity demanded of a commodity and its price. The Law of demand is the concept of the economics according to which the prices of the goods or services and their quantity demanded is inversely related to each other when the other factors remain constant.
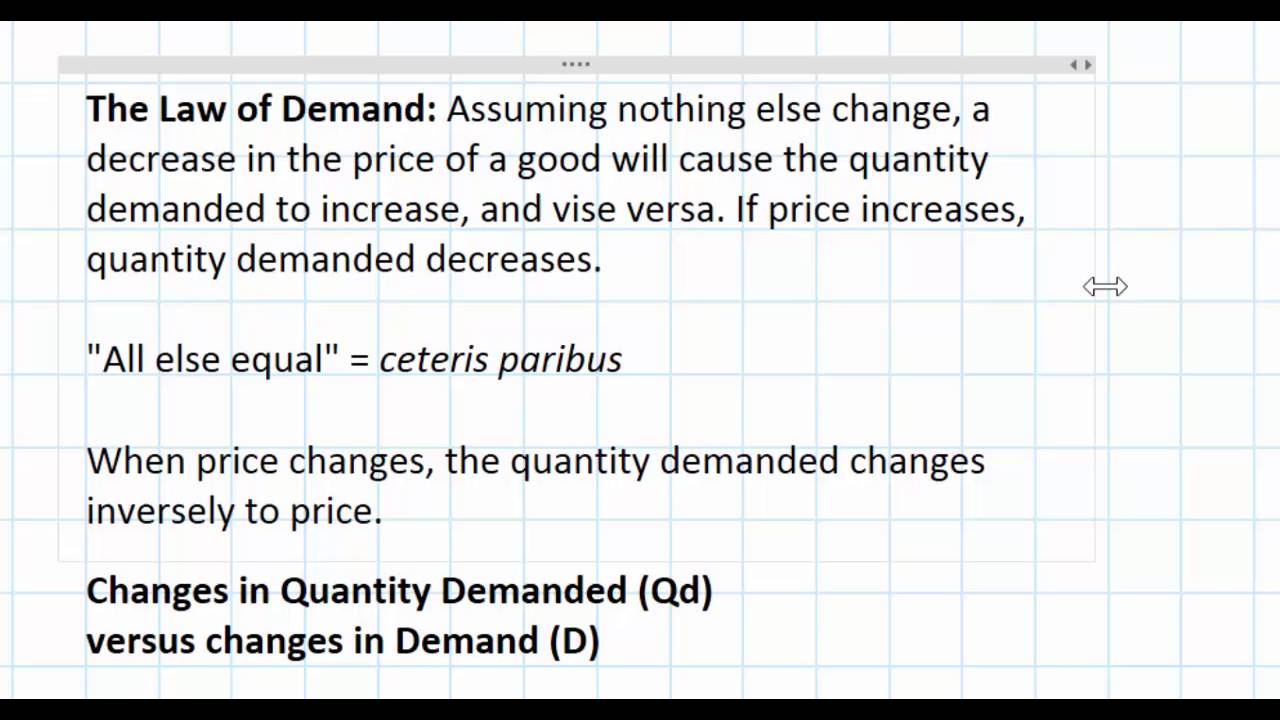 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The law of demand is a fundamental principle of economics that states that at a higher price consumers will demand a lower quantity of a good. Demand is the quantity of consumers who are willing and able to buy products at various prices during a given period of time. Demand is an economic principle referring to a consumers desire and willingness to pay a price for a specific good or service. In normal conditions as the price increases sellers are willing to supply more and. The demand for a good that the consumer chooses depends on the price of it the prices of.
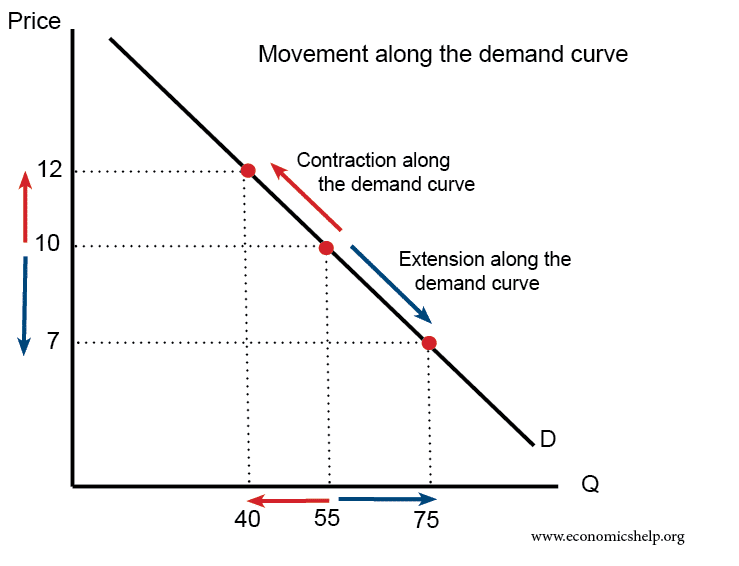 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
The law of demand is a principle of economics that states that when the price of a good increases demand will decrease and vice versa. Understanding the Law of Demand. The law of demand is one of the fundamental concepts of economics that is used to explain the relationship between the quantity demanded of a product and its price. In normal conditions as the price increases sellers are willing to supply more and. Law of Demand The Law of Demand States that other things being constant Ceteris Peribus the demand for a good extends with a decrease in price and contracts with an increase in price.
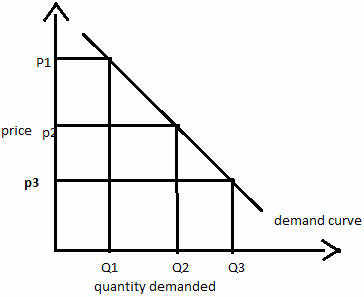 Source: m.economictimes.com
Source: m.economictimes.com
The demand for a good that the consumer chooses depends on the price of it the prices of. Understanding the Law of Demand. Introduction to the Law of Demand. The law of demand states that quantity purchased varies inversely with price. When the price of a product increases the demand for the same product will fall.
 Source: slideshare.net
Source: slideshare.net
Marshall who is defining the law of demand definition economics The greater the amount to be sold the smaller must be the price at which it is offered in order that it may find purchasers. If the demand equation is linear it will be of the form. Law of demand is one of the basic laws of economics according to which demand rises in response to a fall in prices while other factors remain constant such as consumer preferences and level of income of consumers. The Law of demand is the concept of the economics according to which the prices of the goods or services and their quantity demanded is inversely related to each other when the other factors remain constant. The maximum amount of a good which consumers would be willing to buy at a given price.
 Source: boycewire.com
Source: boycewire.com
Explore the definition and examples of the law of demand and discover exceptions to the rule. Naturally people prioritize more urgent wants and needs over less urgent ones in their economic behavior and this carries over into how people choose among the limited means. Law of demand is one of the basic laws of economics according to which demand rises in response to a fall in prices while other factors remain constant such as consumer preferences and level of income of consumers. So in the economic law of demand works with the law of supply for determining and explaining that how the resources are being allocated in the this has been a guide to what is the law of demand and its a definition. The law of demand affirms the inverse relationship between price and demand.
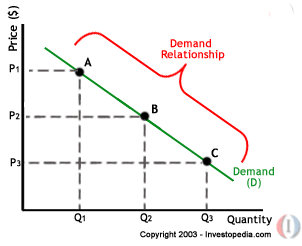 Source: econprojectsd.weebly.com
Source: econprojectsd.weebly.com
Naturally people prioritize more urgent wants and needs over less urgent ones in their economic behavior and this carries over into how people choose among the limited means. The law of demand is a fundamental principle of economics that states that at a higher price consumers will demand a lower quantity of a good. The law of demand and supply is a theory that establishes the relationship between the sellers and buyers of a particular commodity. When the price of a product increases the demand for the same product will fall. Or in other words the amount demanded increases with a.

Theyll buy more when its price falls The law of demand assumes that all determinants of demand except price remain unchanged. The law of demand focuses on those unlimited wants. Samuelson The Law of Demand states that Quantity Demanded Increases with a Fall in Price. A market demand curve expresses the sum of quantity demanded at each. Thus it expresses an inverse relation between price and demand.
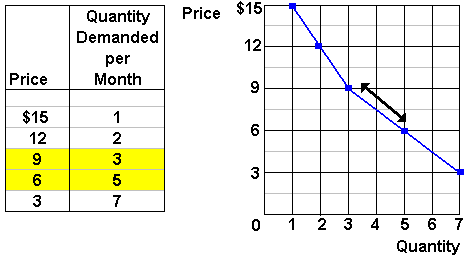 Source: www2.harpercollege.edu
Source: www2.harpercollege.edu
It may be defined in Marshalls words as the amount demanded increases with a fall in price and diminishes with a rise in price. So in the economic law of demand works with the law of supply for determining and explaining that how the resources are being allocated in the this has been a guide to what is the law of demand and its a definition. Demand for any commodity implies the consumers desire to acquire the good the willingness and ability to pay for it. It may be defined in Marshalls words as the amount demanded increases with a fall in price and diminishes with a rise in price. P a - b Qd.

The law of demand is a fundamental principle of economics that states that at a higher price consumers will demand a lower quantity of a good. The law of demand is a principle of economics that states that when the price of a good increases demand will decrease and vice versa. P a - b Qd. The law of demand in economics states that as the price of goods fall the quantity demanded increases. The law of demand states that quantity purchased varies inversely with price.
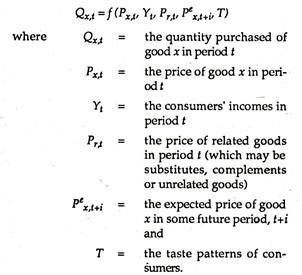 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Demand is based on needs and wantsa consumer may be able to differentiate between a need and a want but from an economists perspective they are the same thing. Or in other words the amount demanded increases with a. If the demand equation is linear it will be of the form. In other words there is an inverse relationship between quantity demanded of a commodity and its price. Economics involves the study of how people use limited means to satisfy unlimited wants.
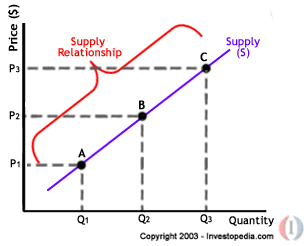 Source: econprojectsd.weebly.com
Source: econprojectsd.weebly.com
The Law of demand is the concept of the economics according to which the prices of the goods or services and their quantity demanded is inversely related to each other when the other factors remain constant. In other words when the price of any product increases then its demand will fall and when its price decreases then its demand will increase. The theory defines the relationship between the price of the commodity and the willingness of the buyers to either buy or sell that commodity. Economists use the term demand to refer to the amount of some good or service consumers are willing and able to purchase at each price. The demand for a good that the consumer chooses depends on the price of it the prices of.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The other factors that can affect the quantity demanded of a product such as the price of relative good the income of consumers tastes and preferences are assumed to be constant. So in the economic law of demand works with the law of supply for determining and explaining that how the resources are being allocated in the this has been a guide to what is the law of demand and its a definition. Thus it expresses an inverse relation between price and demand. Introduction to the Law of Demand. Law of Demand Definition.
 Source: lidderdale.com
Source: lidderdale.com
The law of demand affirms the inverse relationship between price and demand. In other words customers buy a high quantity of products at lower prices and vice versa. In other words there is an inverse relationship between quantity demanded of a commodity and its price. Theyll buy more when its price falls The law of demand assumes that all determinants of demand except price remain unchanged. Naturally people prioritize more urgent wants and needs over less urgent ones in their economic behavior and this carries over into how people choose among the limited means.
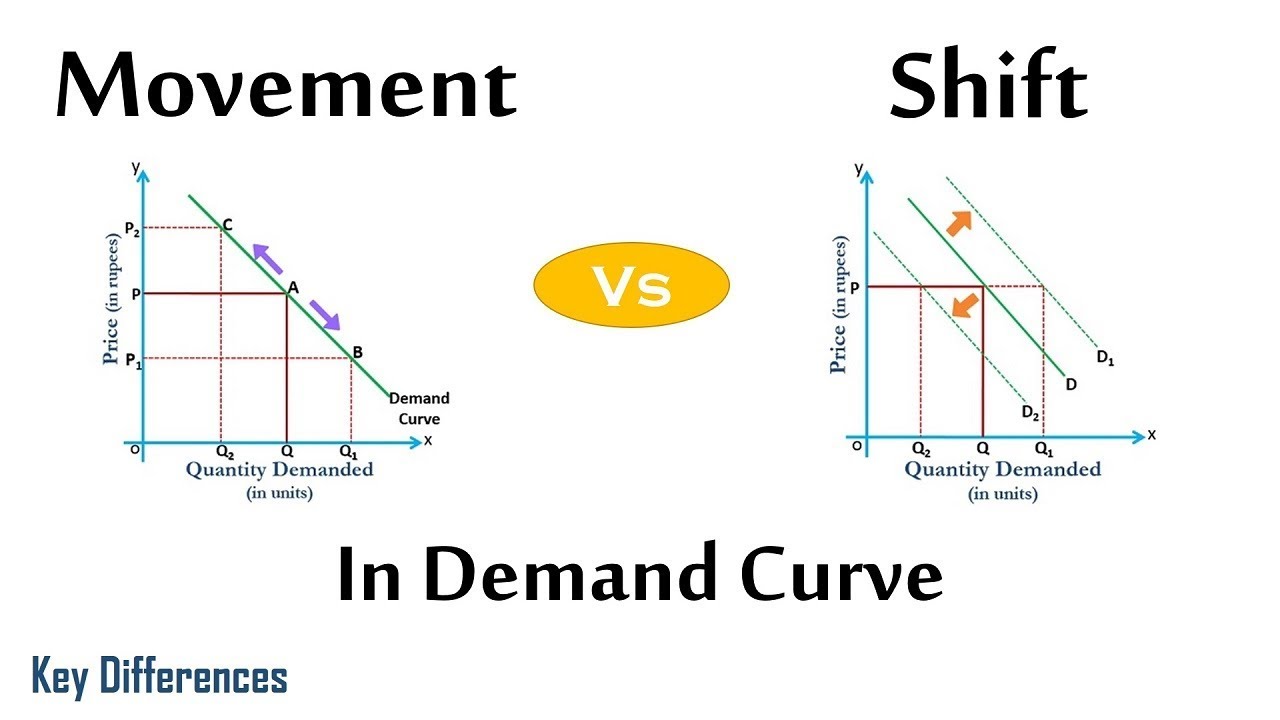 Source: keydifferences.com
Source: keydifferences.com
If the demand equation is linear it will be of the form. Law of demand explains consumer choice behavior when the price changes. In the market assuming other. Marshall who is defining the law of demand definition economics The greater the amount to be sold the smaller must be the price at which it is offered in order that it may find purchasers. The law of demand in economics states that as the price of goods fall the quantity demanded increases.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title law of demand meaning in econ by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






