Your Law of demand economics ib definition images are available in this site. Law of demand economics ib definition are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Law of demand economics ib definition files here. Download all free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for law of demand economics ib definition pictures information linked to the law of demand economics ib definition topic, you have pay a visit to the right site. Our website frequently gives you suggestions for downloading the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly surf and find more enlightening video content and images that match your interests.
Law Of Demand Economics Ib Definition. The Schedule is based on the Assumption that. The limited availability of economic resources relative to. Y and so on - so demand is a function of its own price the price of substitutes the price of complements with an e income fashion. When the price of a product increases the demand for the same product will fall.
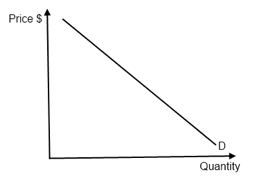 Ib Economics Notes 1 2 Demand From ibguides.com
Ib Economics Notes 1 2 Demand From ibguides.com
Cross elasticity of demand XED The measure of responsiveness of the demand for a good or service to a change in the price of a related good. Consumers will demand more of a good at a lower price and less at a higher price ceteris paribus – this is an inverse relationship. States that as the price of a product falls the quantity demanded of the product will usually increase ceteris paribus. The law of demand states that other factors being constant cetris peribus price and quantity demand of any good and service are inversely related to each other. The non-price determinants of supply factors that change supply or shift the supply curve Price of relating product jointcompetitive supply. If the price of the good increases then the demand falls because the consumer is usually reluctant to spend more and more money on her purchase.
The law of demand states that other factors being constant cetris peribus price and quantity demand of any good and service are inversely related to each other.
As income rises the demand for the product will also rise. Y and so on - so demand is a function of its own price the price of substitutes the price of complements with an e income fashion. When an economy can match the nations aggregate supply and aggregate demand it is said to be in economic equilibrium. The Balance Julie Bang. However if they have more demand than supply they are missing out on profits. The quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price in a given time period.
 Source: ibdeconomics.com
Source: ibdeconomics.com
States that as the price of a product falls the quantity demanded of the product will usually increase ceteris paribus. Cross elasticity of demand XED The measure of responsiveness of the demand for a good or service to a change in the price of a related good. Explain why Veblen goods are an exception to the law of demand. Goods that can be used instead of each other. Law of Demand and Elasticity of Demand 14 Market Demand Schedule It is defined as the Quantities of a Given Commodity which all Consumers will buy at all Possible Prices at a given Moment of Time.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The change in price of a good or service will cause a proportionally smaller change in quantity demanded. If the economy has more supply than demand it is wasting resources. 11 Competitive Markets Demand. Matters of economics that are based upon opinion and so are incapable of being proved to be right or wrong. It also works the other way around.
 Source: cz.pinterest.com
Source: cz.pinterest.com
If producer could produce another product with higher profit due to limited resources the supply for the existing product decreases. Law of Demand and Elasticity of Demand 14 Market Demand Schedule It is defined as the Quantities of a Given Commodity which all Consumers will buy at all Possible Prices at a given Moment of Time. When the price of a product increases the demand for the same product will fall. Effective demand is the amount of a good people are willing to buy at given prices over a given period of time backed by the ability to pay. Definition of Law Of Demand.
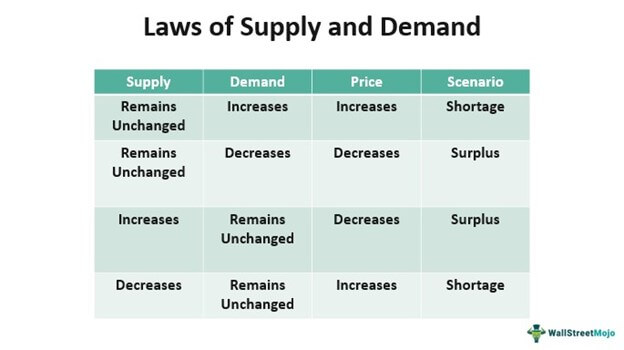 Source: wallstreetmojo.com
Source: wallstreetmojo.com
Goods that can be used instead of each other. As price of a good decreases ceteris paribus quantity demanded will increase. The change in the price of a good causes a movement along the demand curve. The quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price in a given time period. The law of demand explains why the demand curve is downward sloping.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
We have a team of editors who proofread every paper to make sure there Law Of Demand Definition Economics are no grammar errors and typos. Y and so on - so demand is a function of its own price the price of substitutes the price of complements with an e income fashion. Explain why Veblen goods are an exception to the law of demand. Economics involves the study of how people use limited means to satisfy unlimited wants. The limited availability of economic resources relative to.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The law of demand is a fundamental principle of economics that states that at a higher price consumers will demand a lower quantity of a good. The law of demand focuses on those unlimited wants. Cross elasticity of demand XED The measure of responsiveness of the demand for a good or service to a change in the price of a related good. Law of Demand and Elasticity of Demand 14 Market Demand Schedule It is defined as the Quantities of a Given Commodity which all Consumers will buy at all Possible Prices at a given Moment of Time. Growth in output and income are considered.
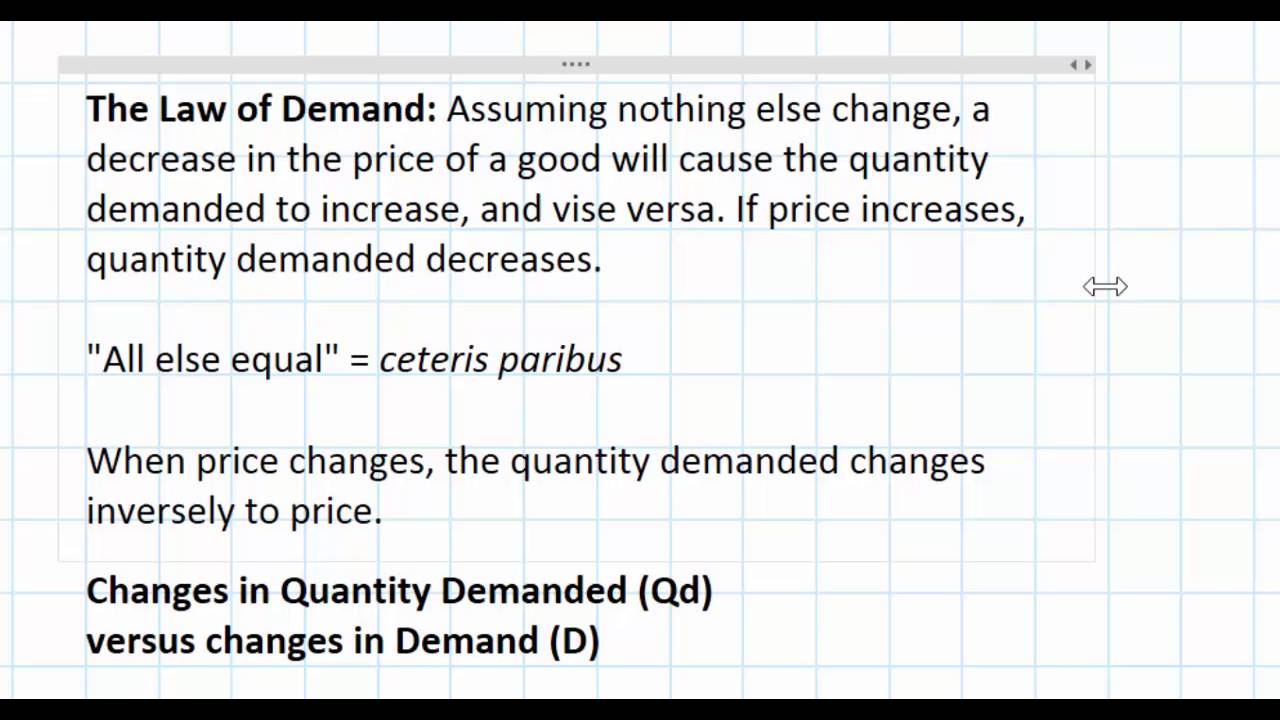 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The law of demand. States that as the price of a product falls the quantity demanded of the product will usually increase ceteris paribus. Definition of the law of demand with reference to a time period and including the ceteris paribus clause definition of Veblen goods with examples diagram or explanation indicating an upward-sloping demand. We have a team of editors who proofread every paper to make sure there Law Of Demand Definition Economics are no grammar errors and typos. The law of demand explains why the demand curve is downward sloping.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
States that as the price of a product falls the quantity demanded of the product will usually increase ceteris paribus. If the price of the good increases then the demand falls because the consumer is usually reluctant to spend more and more money on her purchase. Understanding the Law of Demand. Cross elasticity of demand XED The measure of responsiveness of the demand for a good or service to a change in the price of a related good. The law of demand says that as the price of a good or service increases the quantity demanded decreases and vice versa for a decrease in price assuming ceteris paribus.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The law of demand states that other factors being constant cetris peribus price and quantity demand of any good and service are inversely related to each other. The law of demand states that as price of a good increases ceteris paribus all else being equal quantity demanded will decrease. Law of demand is one of the basic laws of economics according to which demand rises in response to a fall in prices while other factors remain constant such as consumer preferences and level of income of consumers. The Law of demand is the concept of the economics according to which the prices of the goods or services and their quantity demanded is inversely related to each other when the other factors remain constant. When the price of a product increases the demand for the same product will fall.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
Is the total amount of goods and services that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price in a given time period. The change in price of a good or service will cause a proportionally smaller change in quantity demanded. In other words when the price of any product increases then its demand will fall and when its price decreases then its demand will increase. The law of demand explains why the demand curve is downward sloping. Goods that can be used instead of each other.
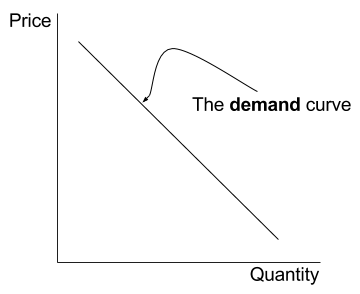 Source: ibeconomist.com
Source: ibeconomist.com
The Balance Julie Bang. Understanding the Law of Demand. It also works the other way around. In other words customers buy a high quantity of products at lower prices and vice versa. The law of demand says that as the price of a good or service increases the quantity demanded decreases and vice versa for a decrease in price assuming ceteris paribus.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The law of demand explains why the demand curve is downward sloping. Learn more about the law of demand how it works and the way it fits into the business cycle. If the economy has more supply than demand it is wasting resources. As price of a good decreases ceteris paribus quantity demanded will increase. Naturally people prioritize more urgent wants and needs over less urgent ones in their economic behavior and this carries over into how people choose among the limited means.
 Source: dineshbakshi.com
Source: dineshbakshi.com
Law of Demand Definition. Understanding the Law of Demand. The law of demand states that all other things being equal the quantity bought of a good or service is a function of price. The law of demand. This section of the IB Economics course examines economic activity by modeling the the circular flow model before turning attention to how economys total output and income can be measured.
 Source: ibguides.com
Source: ibguides.com
In other words when the price of any product increases then its demand will fall and when its price decreases then its demand will increase. They follow your instructions and Law Of Demand Definition Economics make sure a thesis statement and topic sentences are designed in compliance with the standard guidelines. Matters of economics that are based upon opinion and so are incapable of being proved to be right or wrong. Definition of Law Of Demand. Effective demand is the amount of a good people are willing to buy at given prices over a given period of time backed by the ability to pay.
 Source: ar.pinterest.com
Source: ar.pinterest.com
Law of Demand Definition. This section of the IB Economics course examines economic activity by modeling the the circular flow model before turning attention to how economys total output and income can be measured. The law of demand says that as the price of a good or service increases the quantity demanded decreases and vice versa for a decrease in price assuming ceteris paribus. The law of demand focuses on those unlimited wants. The law of demand states that other factors being constant cetris peribus price and quantity demand of any good and service are inversely related to each other.
 Source: ibguides.com
Source: ibguides.com
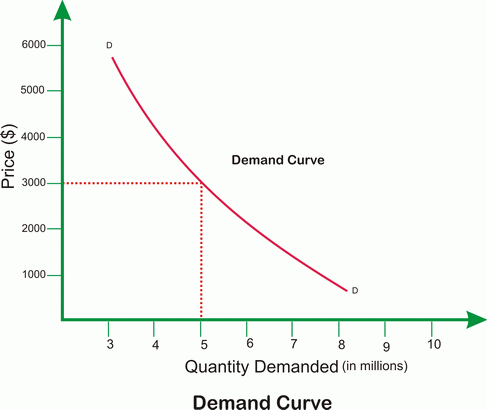
The Law of Demand. The Schedule is based on the Assumption that. There is an inverse or negative association between price and. The quantity of a good or service that consumers are willing and able to purchase at a given price in a given time period. Understanding the Law of Demand.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The law of demand describes an inverse relationship between price and quantity demanded of a good. As price of a good decreases ceteris paribus quantity demanded will increase. The law of demand states that all other things being equal the quantity bought of a good or service is a function of price. The law of demand states that other factors being constant cetris peribus price and quantity demand of any good and service are inversely related to each other. The change in the price of a good causes a movement along the demand curve.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
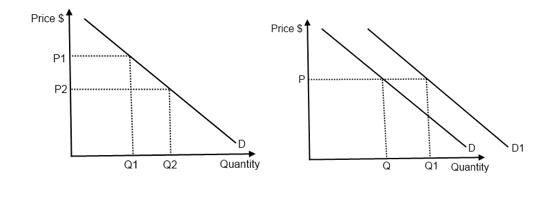
Definition of the law of demand with reference to a time period and including the ceteris paribus clause definition of Veblen goods with examples diagram or explanation indicating an upward-sloping demand. For instance as price falls from P to P1 the demand moves down the demand curve which increase the quantity demanded from Q to Q1. The law of demand. Matters of economics that are based upon opinion and so are incapable of being proved to be right or wrong. When an economy can match the nations aggregate supply and aggregate demand it is said to be in economic equilibrium.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title law of demand economics ib definition by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






