Your Kinked demand definition marketing images are ready in this website. Kinked demand definition marketing are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Kinked demand definition marketing files here. Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for kinked demand definition marketing images information related to the kinked demand definition marketing topic, you have come to the ideal site. Our website frequently gives you hints for downloading the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly search and find more informative video articles and graphics that match your interests.
Kinked Demand Definition Marketing. The curve is more elastic above the kink and less elastic below it. It shows how at higher and lower prices the elasticity of demand changes. This is explained now in brief. A kinked demand curve represents the behavior pattern of oligopolistic organizations in which rival organizations lower down the prices to secure their market share but restrict an increase in the prices.
 The Kinked Demand Model With Diagram From economicsdiscussion.net
The Kinked Demand Model With Diagram From economicsdiscussion.net
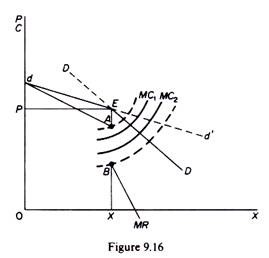
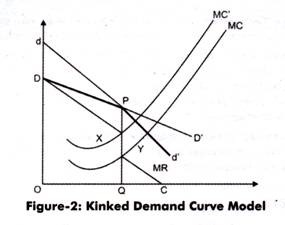
Starting from point P corresponding to the point OP 1 any increase in price above it will considerably reduce his sales as his rivals will not follow his price increase. It shows how at higher and lower prices the elasticity of demand changes. This model was directed to explain the Price rigidity in the oligopoly market especially when there is product differentiation. This means that the response to a price increase is less than the response to a price decrease. Following are the assumption of a kinked demand curve. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly.
The kinked demand curve model assumes that a business might face a dual demand curve for its product based on the likely reactions of other firms to a change in its price or another variable.
One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. A kinked demand curve is a behavior that occurs when the demand curve is not a straight line but has a different elasticity for higher and lower prices. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. The gap in the MR curve results from the abrupt change in the slope of the demand curve at the going price. A tight curl twist or bend in a length of thin material as one caused by the tensing of a looped section of wire. A kinked demand curve represents the behavior pattern of oligopolistic organizations in which rival organizations lower down the prices to secure their market share but restrict an increase in the prices.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
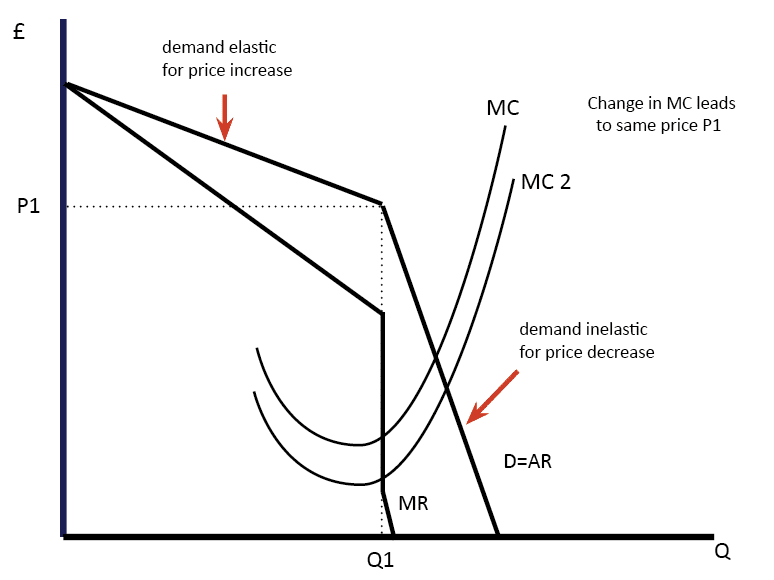
A kinked demand curve occurs when the demand curve is not a straight line but has a different elasticity for higher and lower prices. According to the kinkeddemand theory each firm will face two market demand curves for its product. At high prices the firm faces the relatively elastic market demand curve labeled MD 1 in Figure. At higher prices the demand curve is highly elastic. This model of oligopoly suggests that prices are rigid and that firms will face different effects for both increasing price or decreasing price.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. A the Stackelberg Model. A kinked demand curve occurs when the demand curve is not a straight line but has a different elasticity for higher and lower prices. At higher prices the demand curve is highly elastic. A kinked demand curve often occurs in an oligopolistic market structure where few firms offer similar or differentiated products.
 Source: biznewske.com
Source: biznewske.com
It shows how at higher and lower prices the elasticity of demand changes. The gap in the MR curve results from the abrupt change in the slope of the demand curve at the going price. The kinked demand curve is distinctive of an oligopolistic market. The kink is present at the intersection of the two demand curves. And at lower prices the demand curve is relatively inelastic.
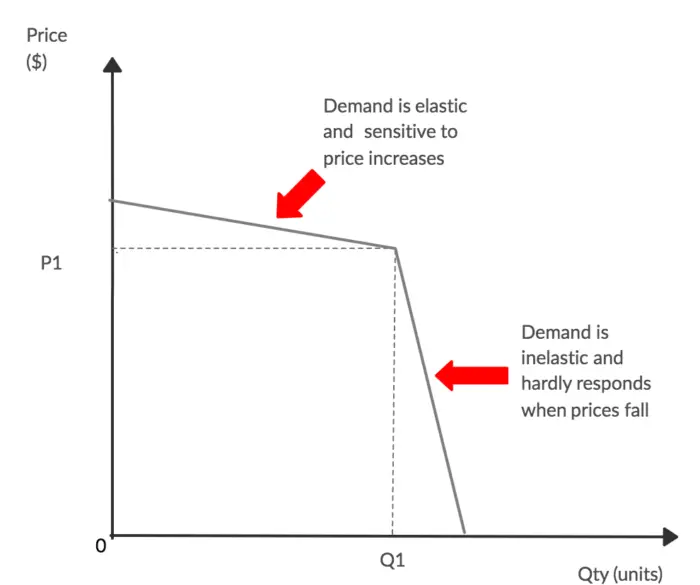 Source: biznewske.com
Source: biznewske.com
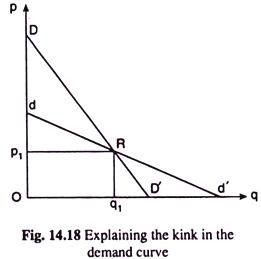
A kinked demand curve is composed effectively of two demand curves which meet at the prevailing market price. Kinked Demand l C MdC urve Model Assumes that managers will inflict maximum damage on other firms Implies oligopoly prices tend to be sticky and not change asand not change as they would in other market structures Does not explain why price P 1 exists initially 2005 Prentice Hall Inc. A kinked demand curve represents the habits sample of oligopolistic organizations during which rival organizations decrease down the costs to safe their market share however prohibit a rise within the costs. There is a kink at the point R p 1 q 1 on this curve because the curve consists of a segment dR of the relatively flatter curve dd and another segment RD of the relatively steeper curve DD. A kinked demand curve occurs when the demand curve is not a straight line but has a different elasticity for higher and lower prices.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Starting from point P corresponding to the point OP 1 any increase in price above it will considerably reduce his sales as his rivals will not follow his price increase. Kinked synonyms kinked pronunciation kinked translation English dictionary definition of kinked. The kinked demand curve is distinctive of an oligopolistic market. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. The kink is formed at the prevailing price level because the segment of the demand curve above the prevailing price level is highly elastic and the segment of the demand curve below the prevailing price level is inelastic.
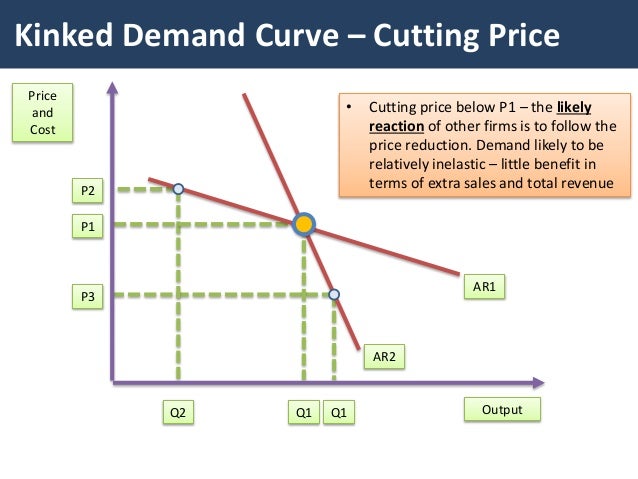 Source: es.slideshare.net
Source: es.slideshare.net
Kinked Demand Curve Model of Oligopoly Kinked demand Curve model of oligopoly was developed by Paul Sweezy. Following are the assumption of a kinked demand curve. The kink is formed at the prevailing price level because the segment of the demand curve above the prevailing price level is highly elastic and the segment of the demand curve below the prevailing price level is inelastic. The kinked demand curve of the firm in this Fig. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly.
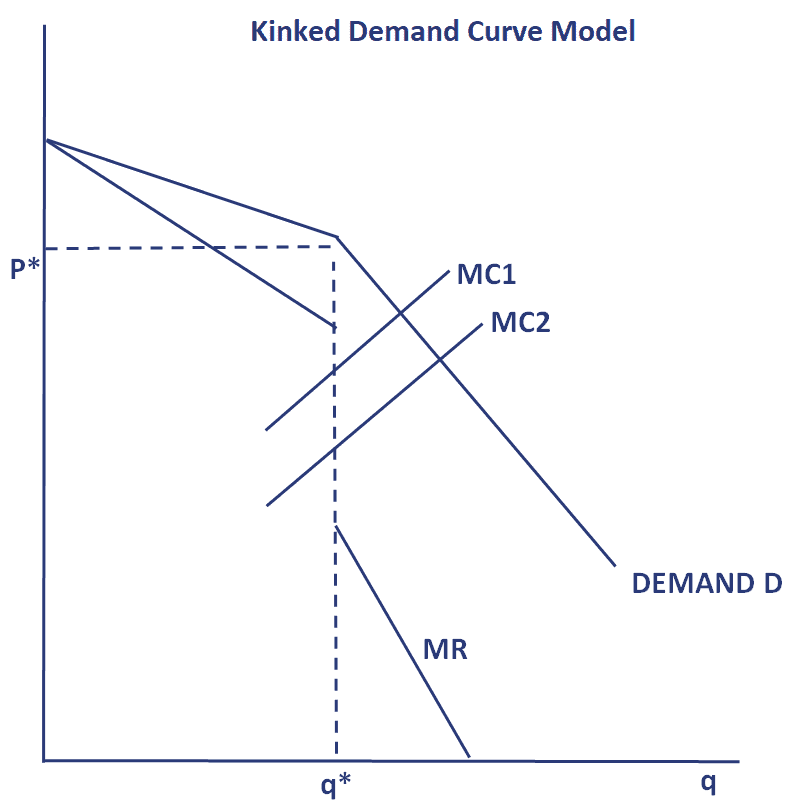 Source: breakingdownfinance.com
Source: breakingdownfinance.com
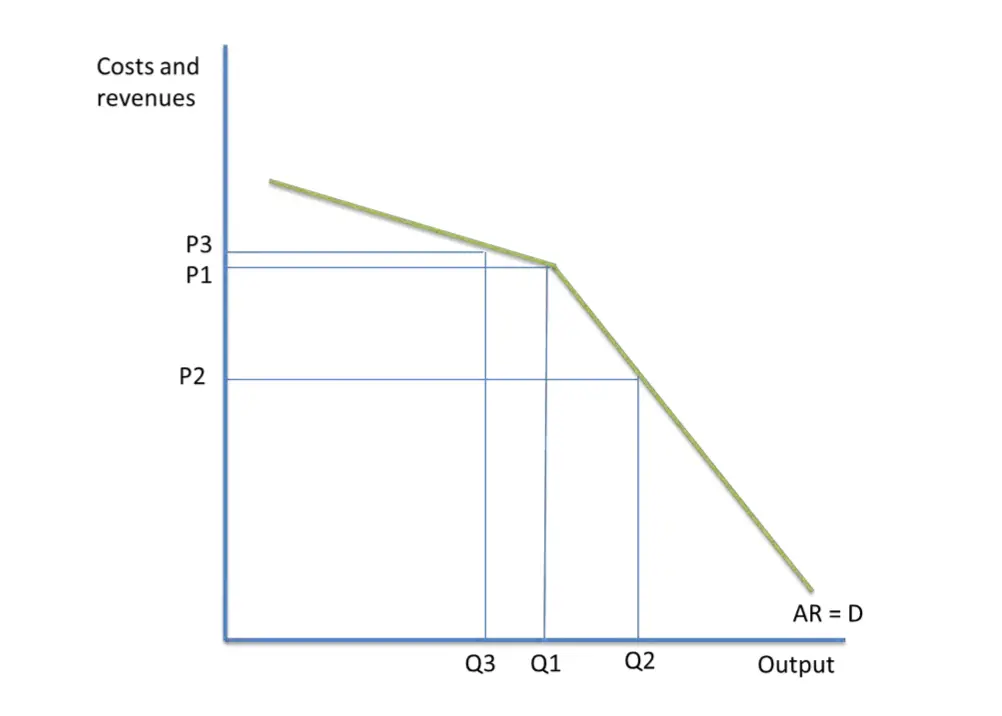
A kinked demand curve often occurs in an oligopolistic market structure where few firms offer similar or differentiated products. A kinked demand curve represents the habits sample of oligopolistic organizations during which rival organizations decrease down the costs to safe their market share however prohibit a rise within the costs. The segment of the demand curve above the prevailing price level 10 is highly elastic and the segment of the demand curve below the prevailing price level is fairly inelastic. The kinked demand curve model seeks to explain the reason of price rigidity under oligopolistic market situations. There is a kink at the point R p 1 q 1 on this curve because the curve consists of a segment dR of the relatively flatter curve dd and another segment RD of the relatively steeper curve DD.
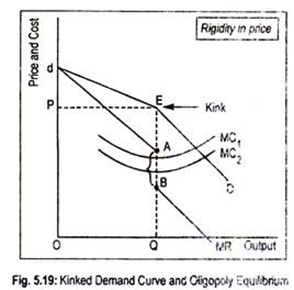 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
The kinkeddemand theory is illustrated in Figure and applies to oligopolistic markets where each firm sells a differentiated product. In an oligopolistic market the kinked demand curve hypothesis states that the firm faces a demand curve with a kink at the prevailing price level. And at lower prices the demand curve is relatively inelastic. B the kinked demand curve model. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly.
 Source: s-cool.co.uk
Source: s-cool.co.uk
The gap in the MR curve results from the abrupt change in the slope of the demand curve at the going price. This model was directed to explain the Price rigidity in the oligopoly market especially when there is product differentiation. There is a kink at the point R p 1 q 1 on this curve because the curve consists of a segment dR of the relatively flatter curve dd and another segment RD of the relatively steeper curve DD. A tight curl twist or bend in a length of thin material as one caused by the tensing of a looped section of wire. The gap in the MR curve results from the abrupt change in the slope of the demand curve at the going price.

The kink is present at the intersection of the two demand curves. The curve is more elastic above the kink and less elastic below it. According to the kinkeddemand theory each firm will face two market demand curves for its product. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. Starting from point P corresponding to the point OP 1 any increase in price above it will considerably reduce his sales as his rivals will not follow his price increase.

This model was directed to explain the Price rigidity in the oligopoly market especially when there is product differentiation. At high prices the firm faces the relatively elastic market demand curve labeled MD 1 in Figure. A kinked demand curve occurs when the demand curve is not a straight line but has a different elasticity for higher and lower prices. The demand curve is kinked or has a bend at point B. A kinked demand curve represents the behavior pattern of oligopolistic organizations in which rival organizations lower down the prices to secure their market share but restrict an increase in the prices.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
In an oligopolistic market the kinked demand curve hypothesis states that the firm faces a demand curve with a kink at the prevailing price level. This means that the response to a price increase is less than the response to a price decrease. A market structure in which there is one large firm that has a major share of the market and many smaller firms supplying the remainder of the market is called. The kink is formed at the prevailing market price level BM 10 per unit. At higher prices the demand curve is highly elastic.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
This model of oligopoly suggests that prices are rigid and that firms will face different effects for both increasing price or decreasing price. A kinked demand curve is a behavior that occurs when the demand curve is not a straight line but has a different elasticity for higher and lower prices. The kink is formed at the prevailing price level because the segment of the demand curve above the prevailing price level is highly elastic and the segment of the demand curve below the prevailing price level is inelastic. At higher prices the demand curve is highly elastic. This is explained now in brief.
 Source: sanandres.esc.edu.ar
Source: sanandres.esc.edu.ar
A market structure in which there is one large firm that has a major share of the market and many smaller firms supplying the remainder of the market is called. This means that the response to a price increase is less than the response to a price decrease. The kinked demand curve model assumes that a business might face a dual demand curve for its product based on the likely reactions of other firms to a change in its price or another variable. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In an oligopolistic market the kinked demand curve hypothesis states that the firm faces a demand curve with a kink at the prevailing price level. This model was directed to explain the Price rigidity in the oligopoly market especially when there is product differentiation. The kinked demand curve of the firm in this Fig. And at lower prices the demand curve is relatively inelastic. The kink is present at the intersection of the two demand curves.
 Source: edexceleconomicsrevision.com
Source: edexceleconomicsrevision.com
The demand curve is kinked or has a bend at point B. A kinked demand curve is composed effectively of two demand curves which meet at the prevailing market price. In an oligopolistic market the kinked demand curve hypothesis states that the firm faces a demand curve with a kink at the prevailing price level. Explanation of the Kinked-Demand Curve Model In the figure above KPD is the is the kinked-demand curve and OP 0 is the prevailing price in the oligopoly market for the OR product of one seller. The gap in the MR curve results from the abrupt change in the slope of the demand curve at the going price.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
The kink is present at the intersection of the two demand curves. Oligopolistic markets thus give rise to kinked demand curves. Kinked synonyms kinked pronunciation kinked translation English dictionary definition of kinked. Following are the assumption of a kinked demand curve. B the kinked demand curve model.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
This is explained now in brief. A kinked demand curve represents the behavior pattern of oligopolistic organizations in which rival organizations lower down the prices to secure their market share but restrict an increase in the prices. A kinked demand curve occurs when the demand curve is not a straight line but has a different elasticity for higher and lower prices. The kink is formed at the prevailing market price level BM 10 per unit. The kinked-demand curve assumes that rivals will match a price cut but ignore an increase in price.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title kinked demand definition marketing by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.