Your Kinked demand curve theory of oligopoly each firm images are ready. Kinked demand curve theory of oligopoly each firm are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Kinked demand curve theory of oligopoly each firm files here. Download all free photos.
If you’re searching for kinked demand curve theory of oligopoly each firm pictures information connected with to the kinked demand curve theory of oligopoly each firm interest, you have come to the ideal site. Our website always provides you with suggestions for refferencing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly surf and find more enlightening video content and images that match your interests.
Kinked Demand Curve Theory Of Oligopoly Each Firm. The demand curve will be kinked at the current price. We analyze a model in which firms take turns choosing prices. In an oligopolistic market the kinked demand curve hypothesis states that the firm faces a demand curve with a kink at the prevailing price level. In the Kinked Demand Curve theory it is assumed that.
 Kinked Demand Wikipedia From en.wikipedia.org
Kinked Demand Wikipedia From en.wikipedia.org
We analyze a model in which firms take turns choosing prices. It has been observed that many oligopolistic industries exhibit an appreciable degree of price rigidity or stability. In the Kinked Demand Curve model. In an oligopolistic market the kinked demand curve hypothesis states that the firm faces a demand curve with a kink at the prevailing price level. A kinked demand curve occurs when the demand curve is not a straight line but has a different elasticity for higher and lower prices. The Kinked Demand Curve A business in an oligopoly faces a downward sloping demand curve but the price elasticity of demand may depend on the likely reaction of rivals to changes in one firms price and output a Rivals are assumed not to follow a price increase by one firm so the acting firm will lose market share - therefore demand will be relatively elastic and a rise in price.
PRICE COMPETITION KINKED DEMAND CURVES AND EDGEWORTH CYCLES BY ERIC MASKIN AND JEAN TIROLE1 We provide game theoretic foundations for the classic kinked demand curve equilibrium and Edgeworth cycle.
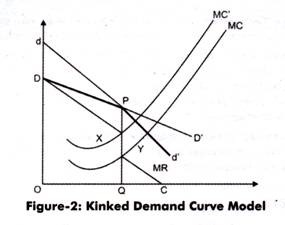
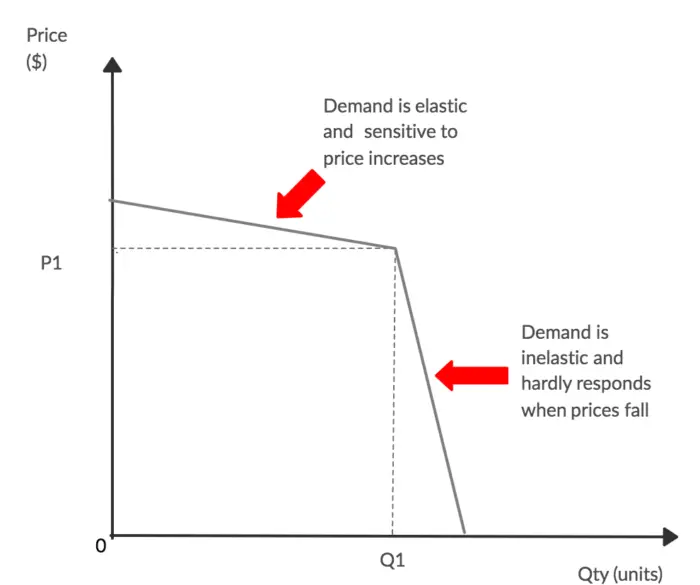
Kinked Demand Curve Diagram. Kinked demand curve The reaction of rivals to a price change depends on whether price is raised or lowered. In an oligopolistic market the kinked demand curvehypothesis states that the firm faces a demand curvewith a kinkat the prevailing price level. The curveis more elastic above the kinkand less elastic below it. A decrease in price by the firm is followed by d. This means that the response to a price increase is less than the response to a price decrease.
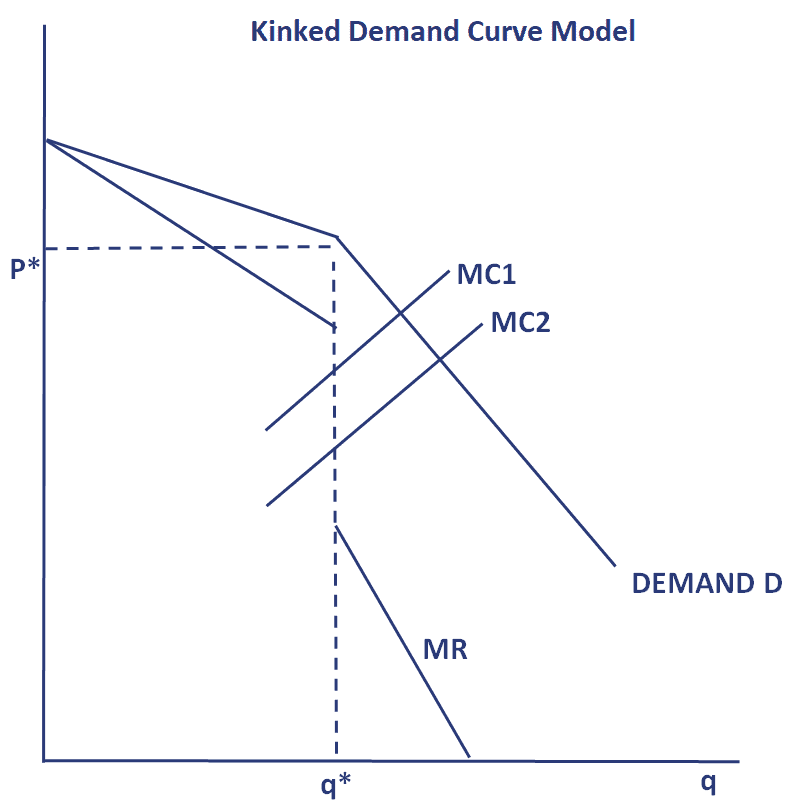 Source: breakingdownfinance.com
Source: breakingdownfinance.com
The kinked demand curve model of oligopoly predicts that A the price the firm sets does not change if there are small changes in the firms marginal costs. How will this affect the price the firm chooses. Firms collude to fix the price. C price wars in the industry are common. The market demand curve that each oligopolist faces is determined by the output and price decisions of the other firms in the oligopoly.

Each firm believes that if it raises its price none of its competitors will follow but if it lowers its price all of its competitors will follow. It is important to bear in mind there are different possible ways that firms in Oligopoly can behave. A THEORY OF DYNAMIC OLIGOPOLY II. The kinked demand curve model of oligopoly can explain why prices of some goods tend to be sticky any decrease in price is met by competitors but any increase in price is not so changing price in either direction lowers profits. In the kinked demand curve model the firm maximises profits at Q1 P1 where MRMC.
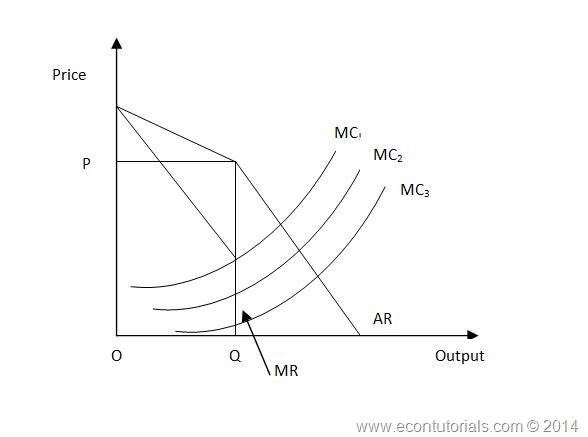 Source: econtutorials.com
Source: econtutorials.com
An oligopoly is comprised of a few mutually interdependent firms each with a very large share of the market. It is important to bear in mind there are different possible ways that firms in Oligopoly can behave. According to the kinked demand curve theory of oligopoly each firm thinks that the demand curve just below the existing price is A flatter than the curve just above the existing price. We have seen that because of these reactions the demand curve of each oligopolistic firm will be kinked and the MR curve of this demand curve will have two separate segments and there will be a vertical gap between them. According to the kinked demand curve theory of oligopoly each firm thinks.
 Source: financetrain.com
Source: financetrain.com
One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. In the kinked demand curve model the firm maximises profits at Q1 P1 where MRMC. In an oligopolistic market the kinked demand curvehypothesis states that the firm faces a demand curvewith a kinkat the prevailing price level. PRICE COMPETITION KINKED DEMAND CURVES AND EDGEWORTH CYCLES BY ERIC MASKIN AND JEAN TIROLE1 We provide game theoretic foundations for the classic kinked demand curve equilibrium and Edgeworth cycle. In the Kinked Demand Curve model.
![]() Source: ezyeducation.co.uk
Source: ezyeducation.co.uk
Thus a change in MC may not change the market price. An oligopoly is comprised of a few mutually interdependent firms each with a very large share of the market. Sweezys Kinked Demand Curve Model. The demand curve will be kinked at the current price. A kinked demand curve occurs when the demand curve is not a straight line but has a different elasticity for higher and lower prices.

It suggests prices will be quite stable. It has been observed that many oligopolistic industries exhibit an appreciable degree of price rigidity or stability. The kinkeddemand theory of oligopoly illustrates the high degree of interdependence that exists among the firms that make up an oligopoly. Firms collude to fix the price. The kinked demand curve model of oligopoly can explain why prices of some goods tend to be sticky any decrease in price is met by competitors but any increase in price is not so changing price in either direction lowers profits.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
A kinked demand curve occurs when the demand curve is not a straight line but has a different elasticity for higher and lower prices. According to the kinked demand curve theory of oligopoly each firm thinks. This means that the response to a price increase is less than the response to a price decrease. The curveis more elastic above the kinkand less elastic below it. Likewise people ask what is the kinked demand curve model of oligopoly.
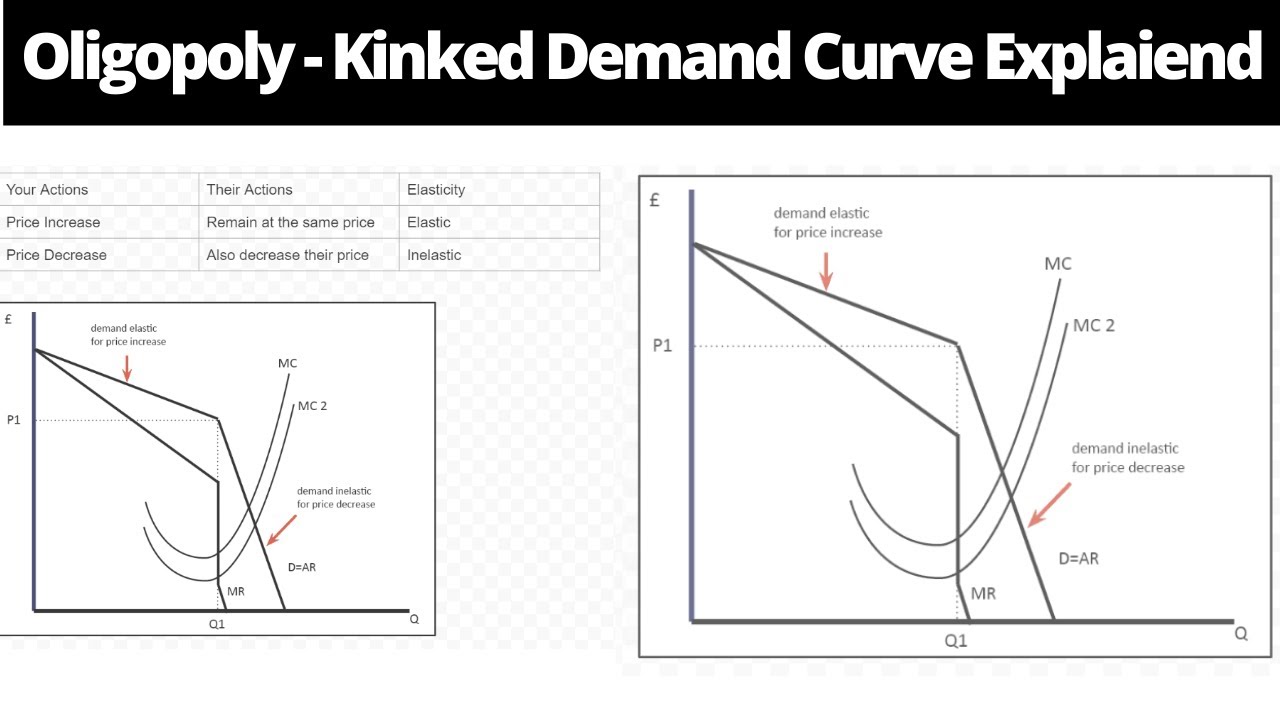 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
In the kinked demand curve model the firm maximises profits at Q1 P1 where MRMC. In the Kinked Demand Curve model. In the kinked demand curve model the firm maximises profits at Q1 P1 where MRMC. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. 4 According to the kinked demand curve theory of oligopoly each firm thinks that demand just below the price at the kink is A less elastic than the demand just above the.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
PRICE COMPETITION KINKED DEMAND CURVES AND EDGEWORTH CYCLES BY ERIC MASKIN AND JEAN TIROLE1 We provide game theoretic foundations for the classic kinked demand curve equilibrium and Edgeworth cycle. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. Firms collude to fix the price. We have seen that because of these reactions the demand curve of each oligopolistic firm will be kinked and the MR curve of this demand curve will have two separate segments and there will be a vertical gap between them. Kinked demand curve The reaction of rivals to a price change depends on whether price is raised or lowered.
 Source: macrobank.blogspot.com
Source: macrobank.blogspot.com
The curveis more elastic above the kinkand less elastic below it. It is important to bear in mind there are different possible ways that firms in Oligopoly can behave. Each firm believes that if it raises its price none of its competitors will follow but if it lowers its price all of its competitors will follow. The kinked-demand curve model also called Sweezy model posits that price rigidity exists in an oligopoly because an oligopolistic firm faces a kinked demand curve a demand curve in which the segment above the market price is relatively more elastic than the segment below it. A decrease in price by the firm is followed by d.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Instead of laying emphasis on price-output determination the model explains the behavior of oligopolistic organizations. In the Kinked Demand Curve model. D the prices charged by any of the firms in the industry never change. Sweezys Kinked Demand Curve Model. The Kinked Demand Curve A business in an oligopoly faces a downward sloping demand curve but the price elasticity of demand may depend on the likely reaction of rivals to changes in one firms price and output a Rivals are assumed not to follow a price increase by one firm so the acting firm will lose market share - therefore demand will be relatively elastic and a rise in price.

According to the kinked demand curve theory of oligopoly each firm thinks. The kinkeddemand theory of oligopoly illustrates the high degree of interdependence that exists among the firms that make up an oligopoly. A THEORY OF DYNAMIC OLIGOPOLY II. This is the major contribution of the kinkeddemand theory. According to the kinked demand curve theory of oligopoly each firm thinks that the demand curve just below the existing price is A flatter than the curve just above the existing price.
 Source: en.wikipedia.org
Source: en.wikipedia.org
PRICE COMPETITION KINKED DEMAND CURVES AND EDGEWORTH CYCLES BY ERIC MASKIN AND JEAN TIROLE1 We provide game theoretic foundations for the classic kinked demand curve equilibrium and Edgeworth cycle. Likewise people ask what is the kinked demand curve model of oligopoly. A kinked demand curve occurs when the demand curve is not a straight line but has a different elasticity for higher and lower prices. Each firm believes that if it raises its price none of its competitors will follow but if it lowers its price all of its competitors will follow. The demand curve is relatively inelastic in this context.
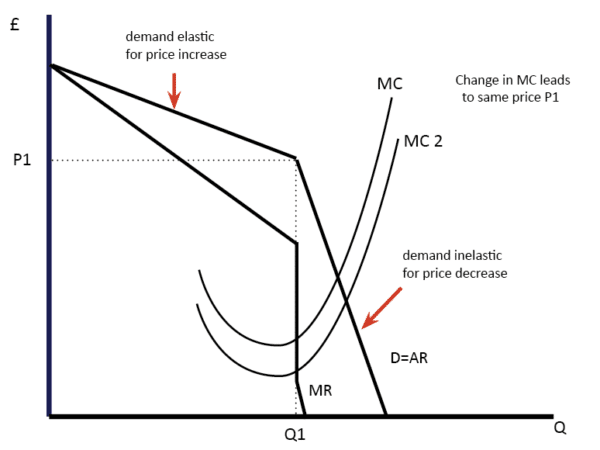 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
The kinkeddemand theory of oligopoly illustrates the high degree of interdependence that exists among the firms that make up an oligopoly. Demand curves in oligopolies are kinked because of price stickiness the phenomenon of prices staying the same in oligopolistic markets. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. Kinked demand curve The reaction of rivals to a price change depends on whether price is raised or lowered. Each firm believes that if it raises its price none of its competitors will follow but if it lowers its price all of its competitors will follow.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. The kinked demand curve model of oligopoly predicts that A the price the firm sets does not change if there are small changes in the firms marginal costs. The curveis more elastic above the kinkand less elastic below it. Instead of laying emphasis on price-output determination the model explains the behavior of oligopolistic organizations. Demand curves in oligopolies are kinked because of price stickiness the phenomenon of prices staying the same in oligopolistic markets.
 Source: sanandres.esc.edu.ar
Source: sanandres.esc.edu.ar
An increase in price by the firm is not followed by others b. An oligopoly is comprised of a few mutually interdependent firms each with a very large share of the market. The kinked-demand curve model also called Sweezy model posits that price rigidity exists in an oligopoly because an oligopolistic firm faces a kinked demand curve a demand curve in which the segment above the market price is relatively more elastic than the segment below it. Demand curves in oligopolies are kinked because of price stickiness the phenomenon of prices staying the same in oligopolistic markets. Kinked Demand Curve Diagram.

The kinkeddemand theory of oligopoly illustrates the high degree of interdependence that exists among the firms that make up an oligopoly. This model of oligopoly suggests that prices are rigid and that firms will face different effects for both increasing price or decreasing price. Firms collude to fix the price. According to the kinked demand curve theory of oligopoly each firm thinks that the demand curve just below the existing price is A flatter than the curve just above the existing price. It is important to bear in mind there are different possible ways that firms in Oligopoly can behave.
 Source: biznewske.com
Source: biznewske.com
This is the major contribution of the kinkeddemand theory. Thus a change in MC may not change the market price. One example of a kinked demand curve is the model for an oligopoly. The kink in the demand curve occurs because rival firms will behave differently to price cuts and price increases. The kinked demand curve model of oligopoly can explain why prices of some goods tend to be sticky any decrease in price is met by competitors but any increase in price is not so changing price in either direction lowers profits.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title kinked demand curve theory of oligopoly each firm by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






