Your Increase in demand supply constant graph images are ready. Increase in demand supply constant graph are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Get the Increase in demand supply constant graph files here. Download all royalty-free photos.
If you’re searching for increase in demand supply constant graph images information related to the increase in demand supply constant graph interest, you have visit the right blog. Our website always gives you hints for seeking the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly search and find more informative video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
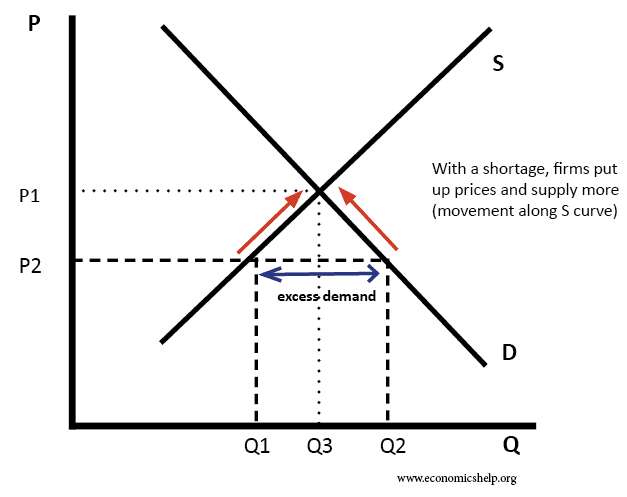
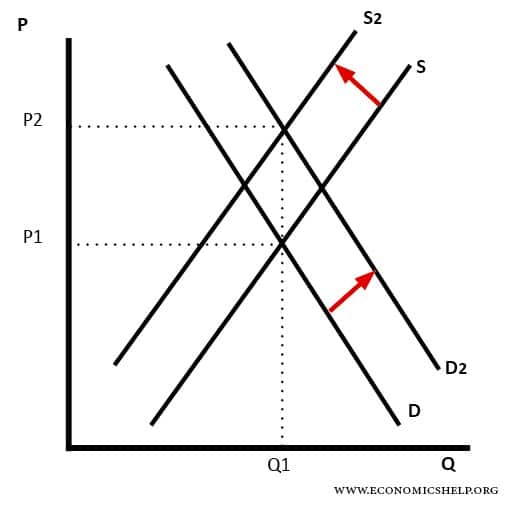
Increase In Demand Supply Constant Graph. D P or we can draw it graphically as in Figure 22. What can cause the long-run equilibrium to move up along the short-run aggregate supply curve from the long-run supply curve to the demand curve. By transferring to a graph the supply and demand behaviors we have just explained it is understood that the supply curve 0 blue line is increasing and the demand curve D red line is decreasing. A higher price causes an extension along the supply curve more is supplied A lower price causes a contraction along the supply curve less is supplied Supply Shifts to the left.
 Explaining Supply And Demand Economics Help From economicshelp.org
Explaining Supply And Demand Economics Help From economicshelp.org
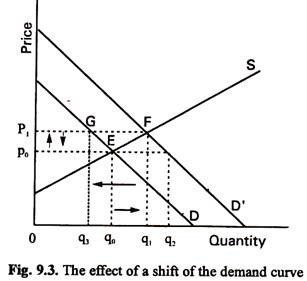
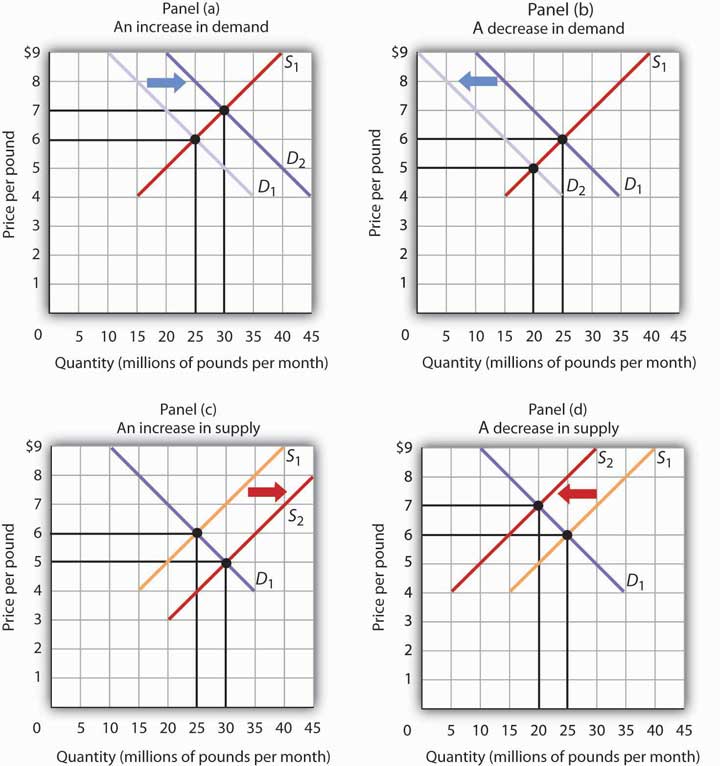
In the above figure the initial demand curve DD and supply curve SS intersect to each other at a point denoted by e 1. Here p 0 is the original equilibrium price and q 0 is the equilibrium quantity. Movement in the demand curve shows expansion contraction of supply but the demand curves shift exhibits either a gain or reduction of the supply schedule. The law of demand implies holding everything else constant that as the price of yogurt A increases the demand for yogurt will increase. Figure 317 Changes in Demand and Supply combines the information about changes in the demand and supply of coffee presented in Figure 32 An Increase in Demand Figure 33 A Reduction in Demand Figure 39 An Increase in Supply and Figure 310 A Reduction in Supply In each case the original equilibrium price is 6 per pound and the corresponding equilibrium. The equilibrium price and quantity both increase d.
The equilibrium price decreases while quantity increases b.
An increase in aggregate demand with constant aggregate supply will result in actual GDP being. A Aggregate demand must have decreased. An increase in aggregate demand with constant aggregate supply will result in actual GDP being. D The supply curve for airline tickets has shifted to the left more than the demand curve has. A demand curve or a supply curve is a relationship between two and only two variables. The intersection of the aggregate demand and aggregate supply curve determines.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
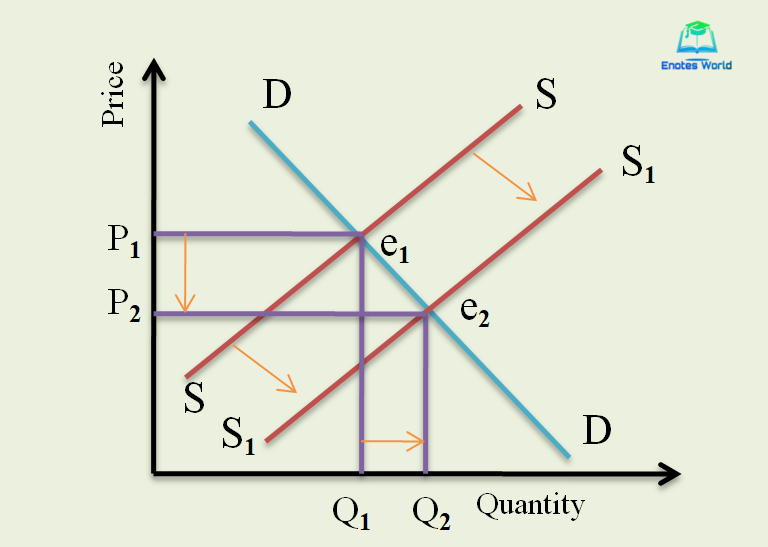
At that point the equilibrium price is OP 1 and quantity is OQ 1. Let us first consider a rise in demand as in Fig. Quantity on the horizontal axis and price on the vertical axis. When demand rises and supply stays. A demand curve or a supply curve is a relationship between two and only two variables.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
An increase in demand for coffee shifts the demand curve to the right as shown in Panel a of Figure 310 Changes in Demand and Supply. Because the graphs for demand and supply curves both have price on the vertical axis and quantity on the horizontal axis the demand curve and supply curve for a particular good or service can appear on the same graph. B A temporary reduction in production due to bad weather. Here p 0 is the original equilibrium price and q 0 is the equilibrium quantity. Quantity on the horizontal axis and price on the vertical axis.
 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
The equilibrium price rises to 7 per pound. The Demand for goods or services is defined as the desire of a consumer to purchase that commodity. Graphical Representation of Law and Supply Demand. A Rise in Demand. Economists call this assumption ceteris paribus a Latin phrase meaning other things being equal Any given demand or supply curve is based on the ceteris paribus assumption that all else.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
By transferring to a graph the supply and demand behaviors we have just explained it is understood that the supply curve 0 blue line is increasing and the demand curve D red line is decreasing. Equilibrium means the point where the supply and demand curve intersect each other. Due to the effects of the determinants demand or supply of a product may change and demand and supply curve may shift. The Supply of goods or services is the overall availability of that commodity in the market. An increase in aggregate demand with constant aggregate supply will result in actual GDP being.
 Source: research.stlouisfed.org
Source: research.stlouisfed.org
B A temporary reduction in production due to bad weather. Let us first consider a rise in demand as in Fig. When demand rises and supply stays. A decrease in. Both supply and demand for goods may change simultaneously causing a change in market equilibrium.
 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
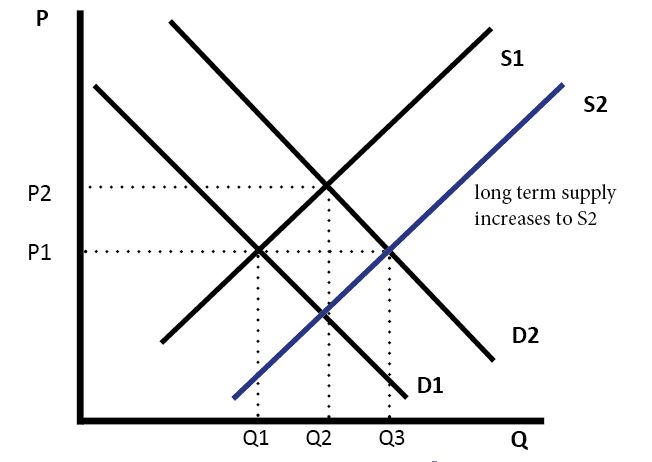
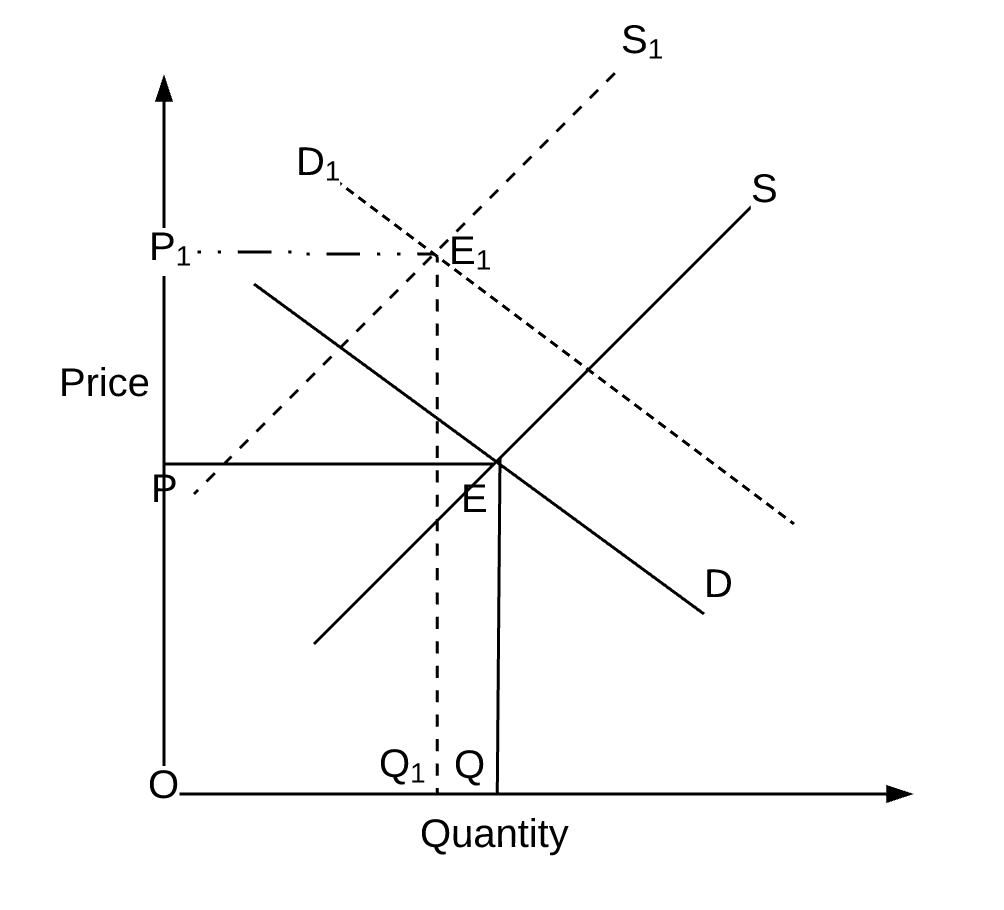
However when demand increases and supply remains the same the higher demand leads to a higher equilibrium price and vice versa. D P or we can draw it graphically as in Figure 22. Slaughtering the cows will result in an increase in the supply of beef to the market which will in turn lead to a decrease in the equilibrium price of beef and an increase in the equilibrium quantity of beef. The equilibrium price rises to 7 per pound. The Demand for goods or services is defined as the desire of a consumer to purchase that commodity.
 Source: enotesworld.com
Source: enotesworld.com
The equilibrium price rises to 7 per pound. Because the graphs for demand and supply curves both have price on the vertical axis and quantity on the horizontal axis the demand curve and supply curve for a particular good or service can appear on the same graph. A higher price causes an extension along the supply curve more is supplied A lower price causes a contraction along the supply curve less is supplied Supply Shifts to the left. Economists call this assumption ceteris paribus a Latin phrase meaning other things being equal Any given demand or supply curve is based on the ceteris paribus assumption that all else. Movement in the demand curve shows expansion contraction of supply but the demand curves shift exhibits either a gain or reduction of the supply schedule.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Figure 317 Changes in Demand and Supply combines the information about changes in the demand and supply of coffee presented in Figure 32 An Increase in Demand Figure 33 A Reduction in Demand Figure 39 An Increase in Supply and Figure 310 A Reduction in Supply In each case the original equilibrium price is 6 per pound and the corresponding equilibrium. Economists call this assumption ceteris paribus a Latin phrase meaning other things being equal Any given demand or supply curve is based on the ceteris paribus assumption that all else. What can cause the long-run equilibrium to move up along the short-run aggregate supply curve from the long-run supply curve to the demand curve. At that point the equilibrium price is OP 1 and quantity is OQ 1. Let us first consider a rise in demand as in Fig.
 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
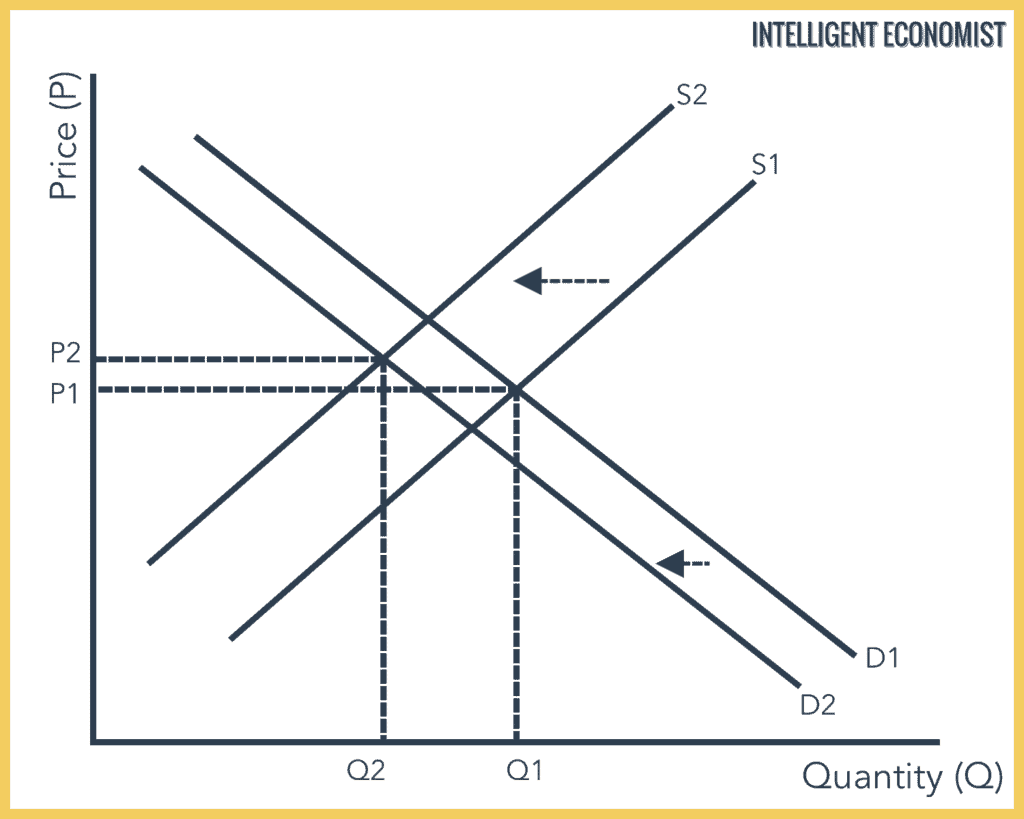
An extension on the demand curve is due to lower price leading to higher demand. Graphical Representation of Law and Supply Demand. If the demand curve decreases while the supply curve is held constant what will be the result in terms of the new equilibrium price and quantity. Movement in the demand curve shows expansion contraction of supply but the demand curves shift exhibits either a gain or reduction of the supply schedule. They both are denoted by D 1 D 1 and S 1 S 1.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Economists call this assumption ceteris paribus a Latin phrase meaning other things being equal Any given demand or supply curve is based on the ceteris paribus assumption that all else. An extension on the demand curve is due to lower price leading to higher demand. An increase in aggregate demand with constant aggregate supply will result in actual GDP being. Here changes mean increase or decrease in the volume of demand and supply from its equilibrium. The Supply of goods or services is the overall availability of that commodity in the market.
 Source: dummies.com
Source: dummies.com
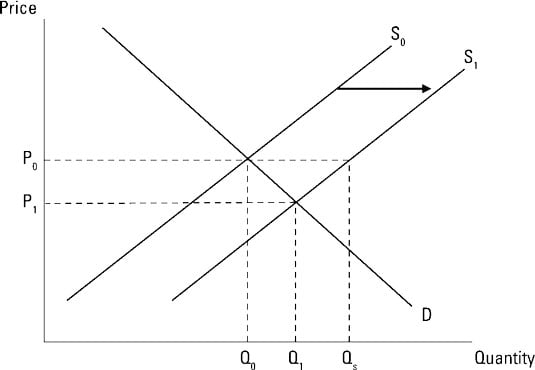
Supply and demand rise and fall until an equilibrium price is reached. The relationship between this quantity and the price level is different in the long and short run. So we will develop both a short-run and long-run aggregate supply curve. However the equilibrium quantity rises. This is the initial equilibrium point.
 Source: dummies.com
Source: dummies.com
Illustrate using a supply and demand diagram. Shows how much of a good consumers are willing to buy as the price per unit changes. The equilibrium price and quantity both increase d. At that point the equilibrium price is OP 1 and quantity is OQ 1. Slaughtering the cows will result in an increase in the supply of beef to the market which will in turn lead to a decrease in the equilibrium price of beef and an increase in the equilibrium quantity of beef.
 Source: uw.pressbooks.pub
Source: uw.pressbooks.pub
What can cause the long-run equilibrium to move up along the short-run aggregate supply curve from the long-run supply curve to the demand curve. Shows how much of a good consumers are willing to buy as the price per unit changes. This is the initial equilibrium point. A decrease in. At that point the equilibrium price is OP 1 and quantity is OQ 1.
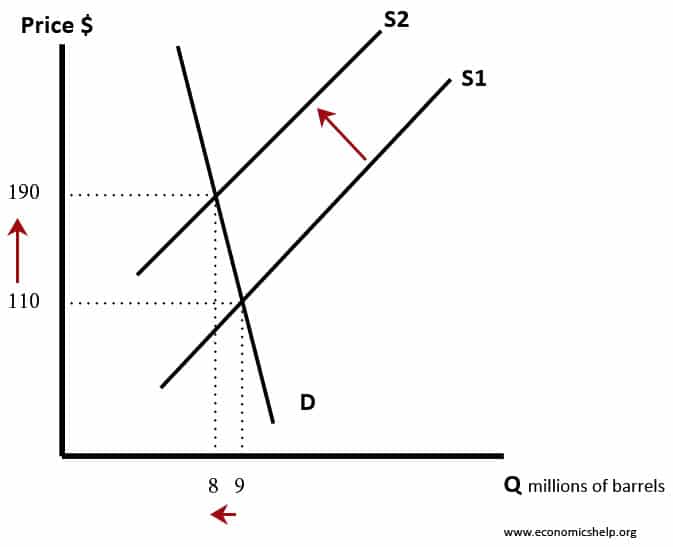 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
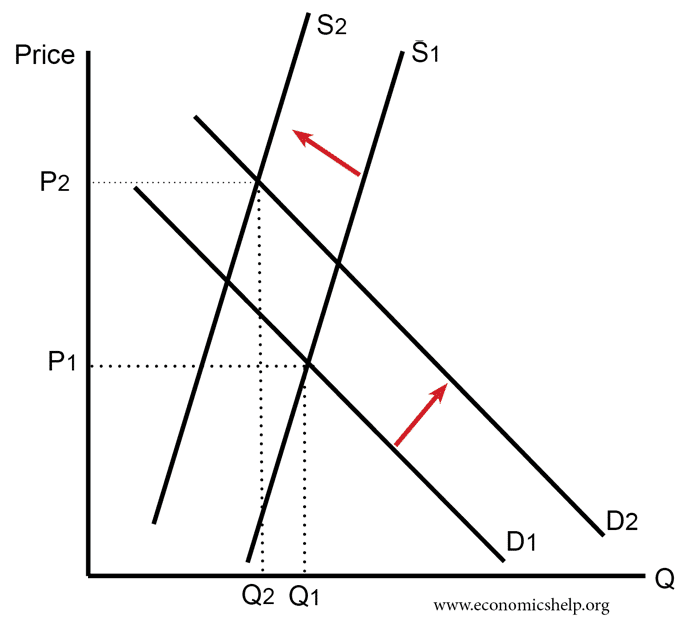
There is an inverse relationship between the supply and prices of goods and services when demand is unchanged. However when demand increases and supply remains the same the higher demand leads to a higher equilibrium price and vice versa. A Rise in Demand. Overtime if aggregate demand and aggregate supply increases proportionately real GDP will rise and there is no demand-pull inflation and no cyclical unemployment. Graphical Representation of Law and Supply Demand.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
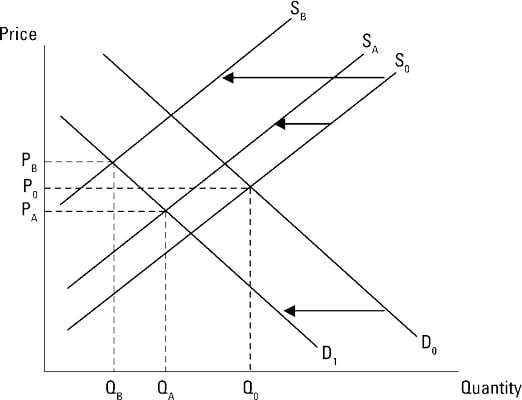
Consequently the equilibrium price remains the same. At that point the equilibrium price is OP 1 and quantity is OQ 1. Chicken and beef are substitute goods. C Input prices must have increased causing long-runa ggregate supply to increase. The demand curve and the supply curve for airline tickets have both shifted to the right.
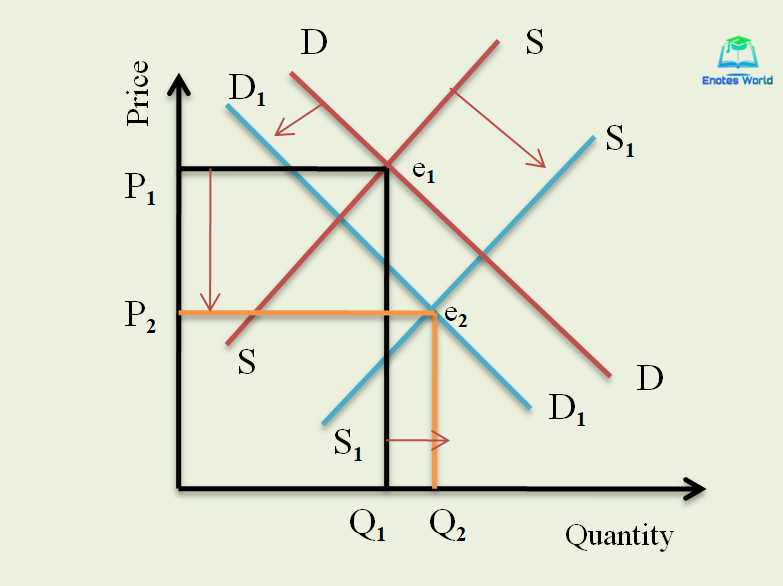 Source: enotesworld.com
Source: enotesworld.com
A decrease in. The point where they cross is known as market equilibrium. Quantity on the horizontal axis and price on the vertical axis. The original demand curve is D and the supply is S. B A temporary reduction in production due to bad weather.
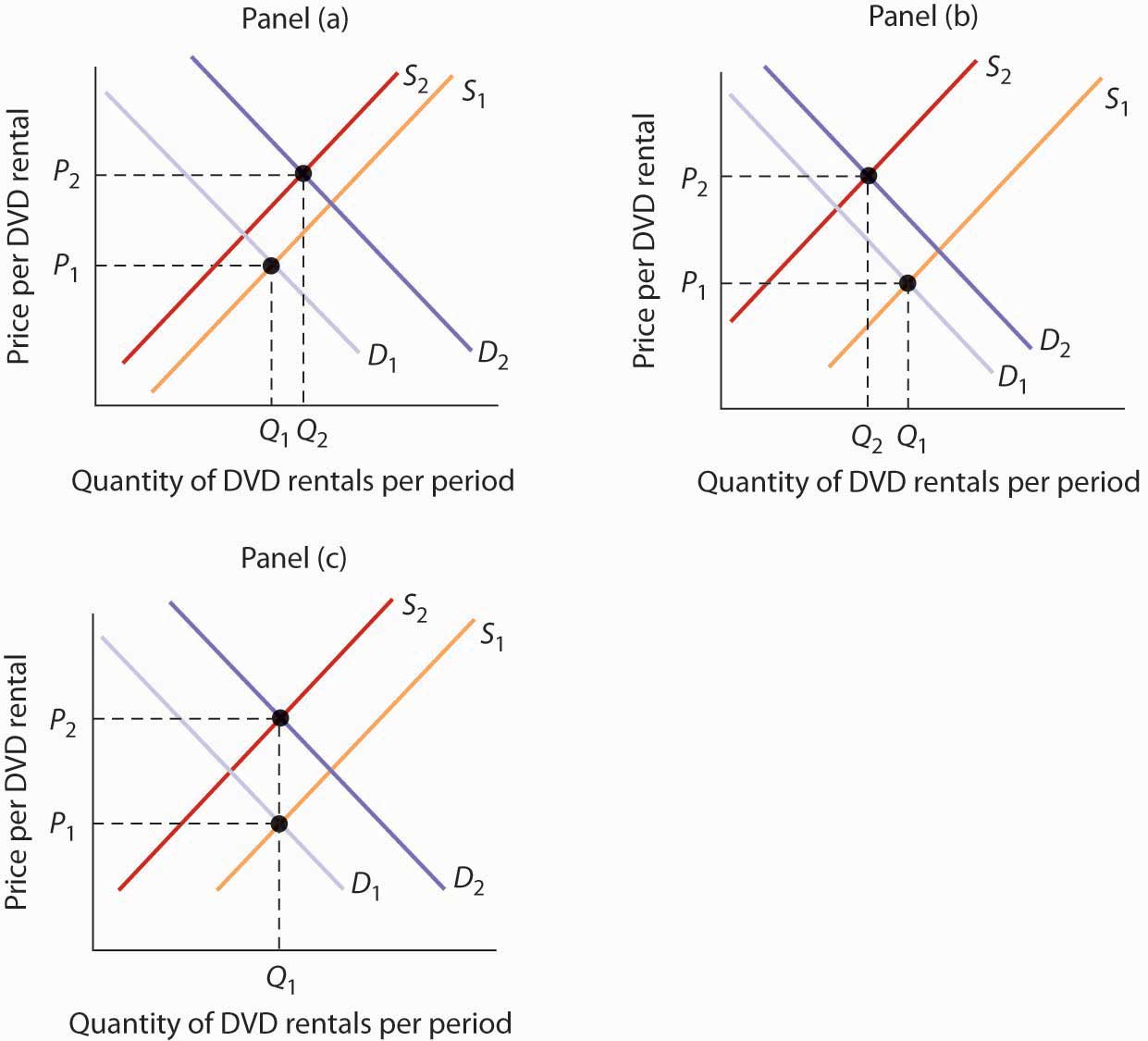 Source: uw.pressbooks.pub
Source: uw.pressbooks.pub
Similarly the increase or decrease in supply the demand curve remaining constant would have an impact on equilibrium price and quantity. Suppose there is an increase in demand and supply by the same amount. Slaughtering the cows will result in an increase in the supply of beef to the market which will in turn lead to a decrease in the equilibrium price of beef and an increase in the equilibrium quantity of beef. Chicken and beef are substitute goods. Shows how much of a good consumers are willing to buy as the price per unit changes.
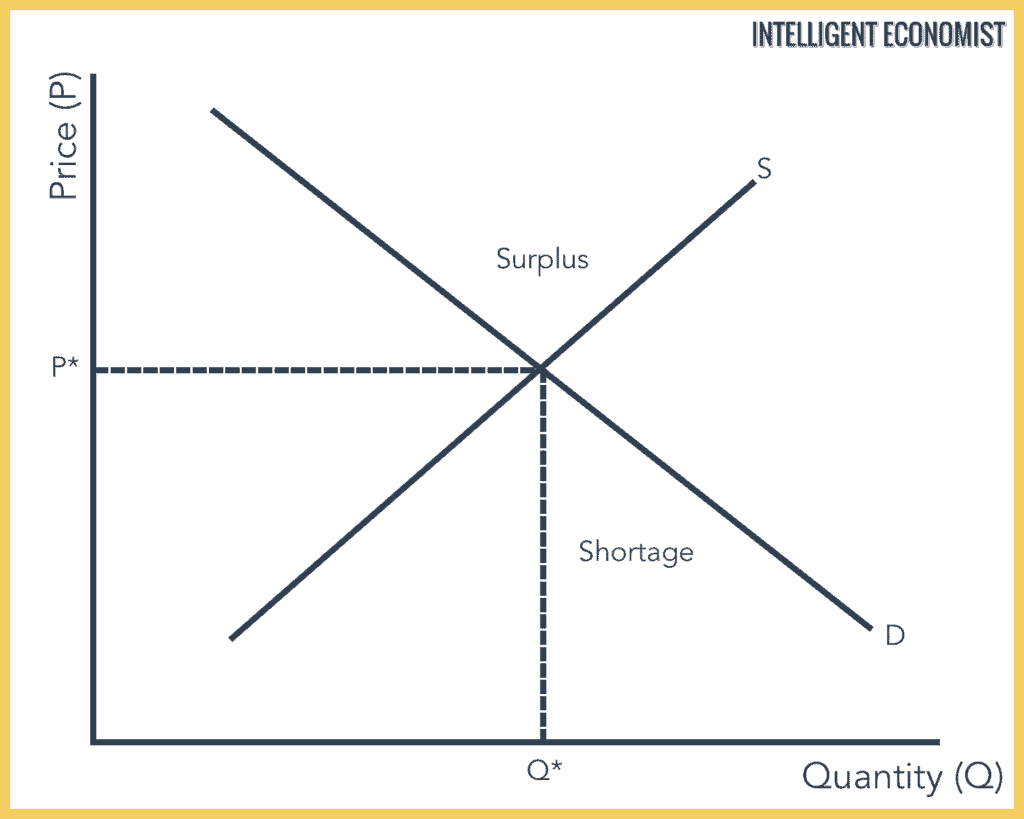 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Slaughtering the cows will result in an increase in the supply of beef to the market which will in turn lead to a decrease in the equilibrium price of beef and an increase in the equilibrium quantity of beef. These two forces influence the market economy of a particular product industry or even a nation. B A temporary reduction in production due to bad weather. The equilibrium price decreases while quantity increases b. There is an inverse relationship between the supply and prices of goods and services when demand is unchanged.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site helpful, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title increase in demand supply constant graph by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.