Your How to solve demand and supply equilibrium images are available. How to solve demand and supply equilibrium are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the How to solve demand and supply equilibrium files here. Download all royalty-free photos.
If you’re looking for how to solve demand and supply equilibrium images information linked to the how to solve demand and supply equilibrium interest, you have visit the right blog. Our site always provides you with hints for viewing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly search and find more enlightening video articles and graphics that match your interests.
How To Solve Demand And Supply Equilibrium. If the price is below the equilibrium level then the quantity demanded will exceed the quantity supplied. You just plug into the equilibrium expression and solve for K c. P 120 320 60. Suppose that our market consists of three.
 Demand Supply And Equilibrium Microeconomics For Managers From uw.pressbooks.pub
Demand Supply And Equilibrium Microeconomics For Managers From uw.pressbooks.pub
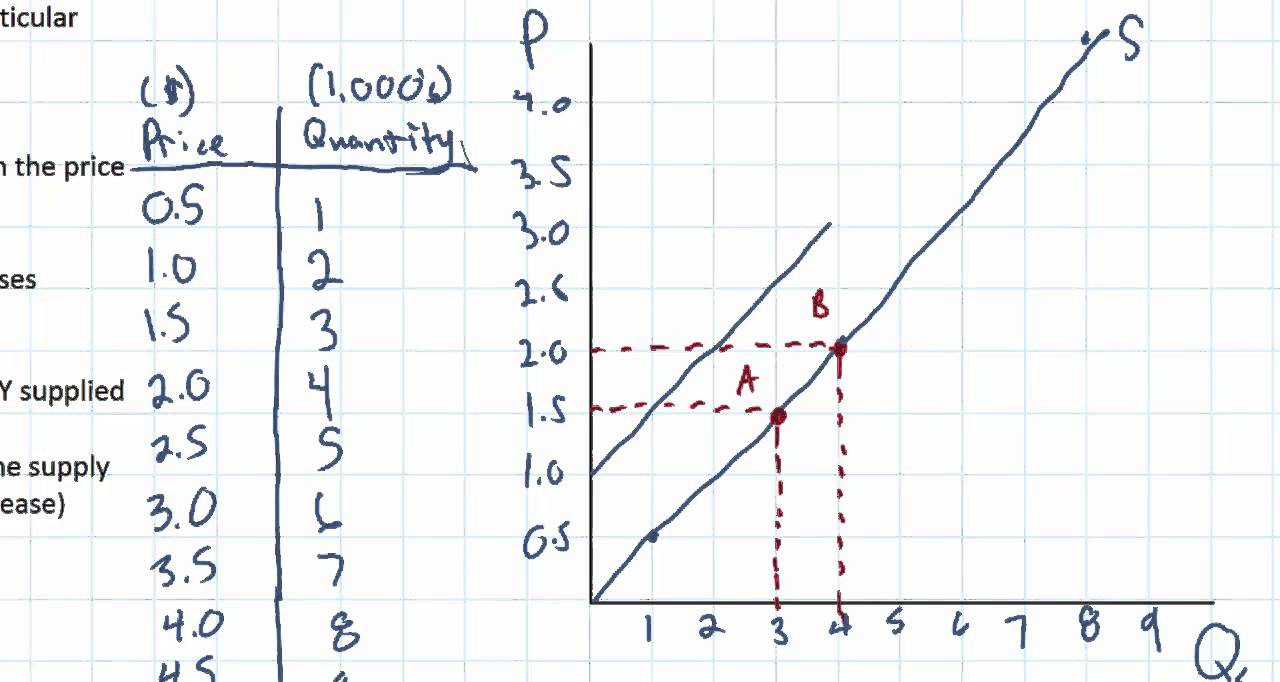
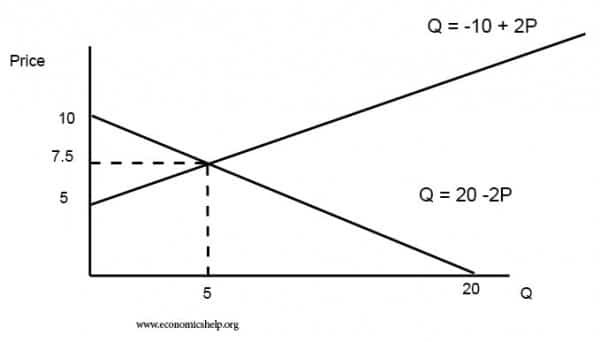
A basic market model for the equilibrium point of supply and demand. Comment on the effect that the signs of the model parameters have on the solution. How to find the equilibrium point. How do we solve for the overall equilibrium in the two. The equilibrium point is the price at which the supply is equal to the demand. D demand 20 - 2P price.
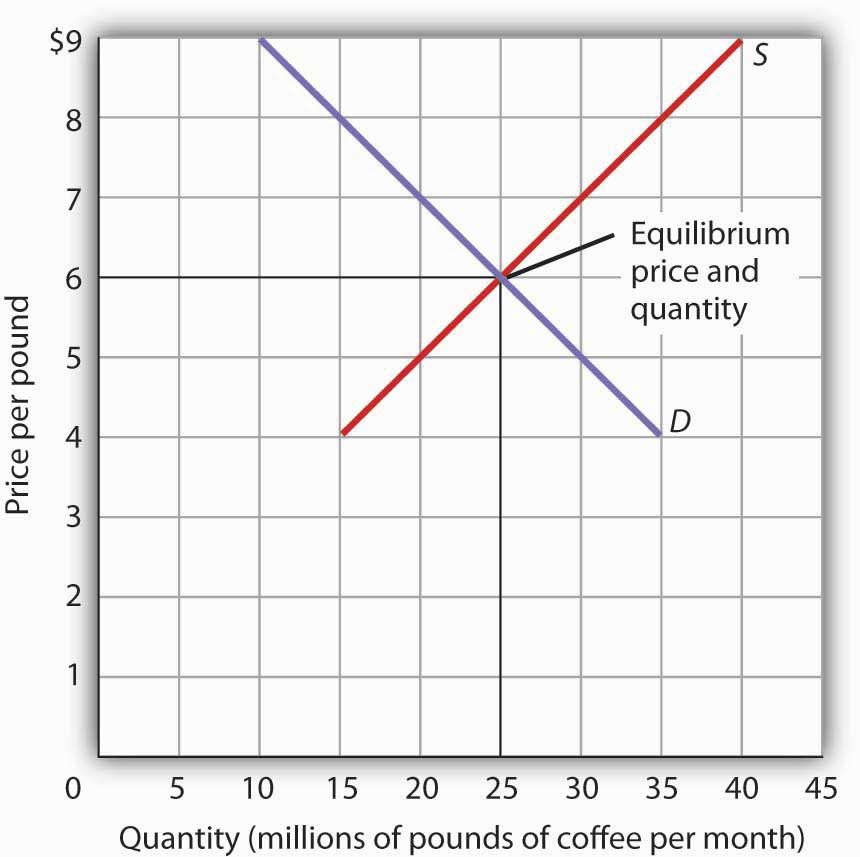
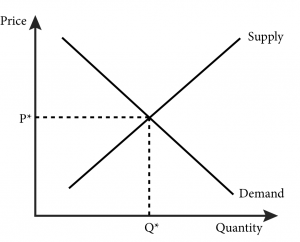
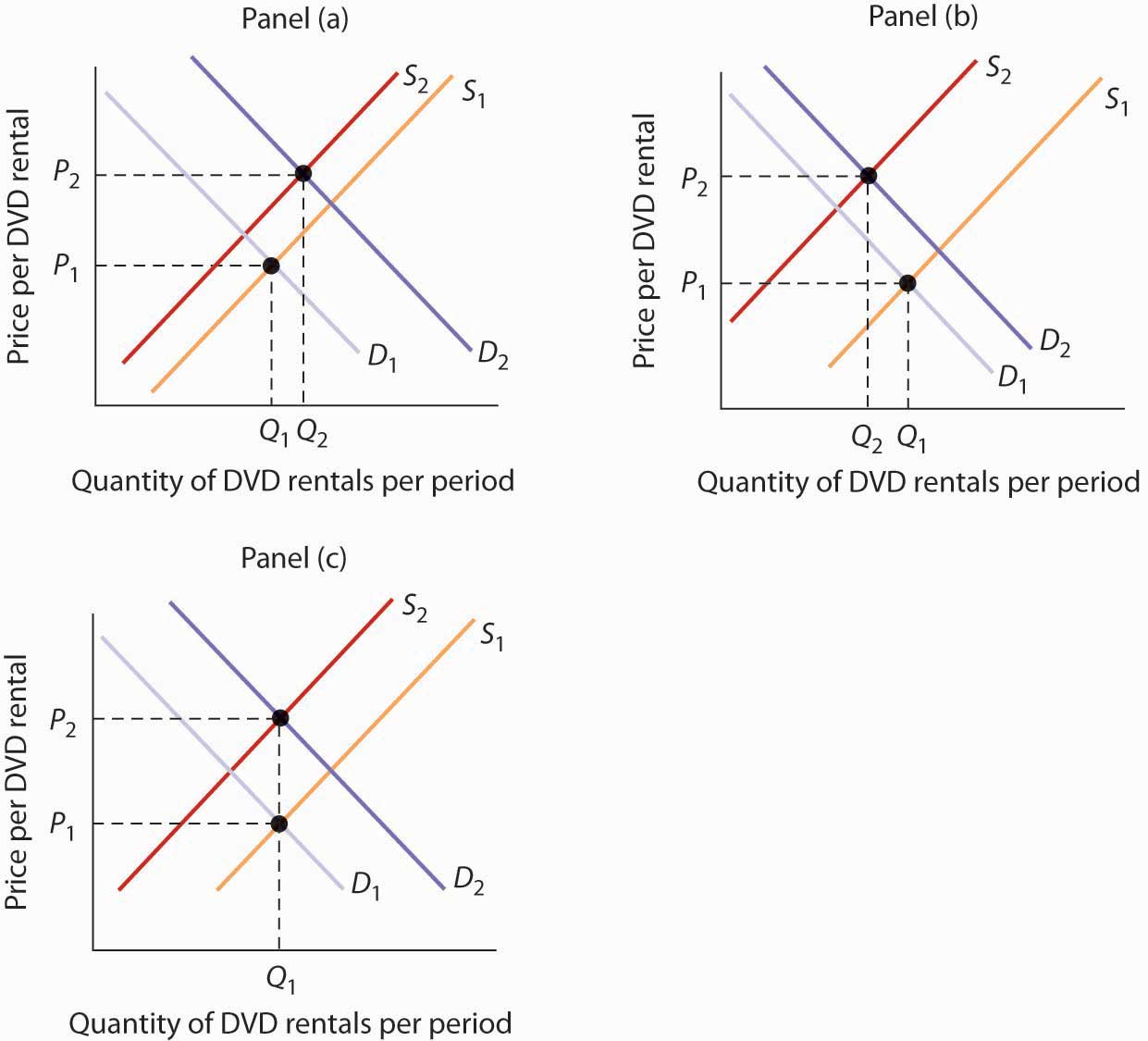
The equilibrium of supply and demand in each market determines the price and quantity of that item.
Solving for equilibrium in two markets. Now that youve mastered demand and supply equations its time to put them together to determine the equilibrium price and quantity in a market. Excess demand or a shortage will exist. Moreover a change in equilibrium in one market will affect equilibrium in related markets. How do we solve for the overall equilibrium in the two. In this type of problem the K c value will be given The best way to explain is by example.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Comment on the effect that the signs of the model parameters have on the solution. Next we describe the characteristics of supply. Solve this system using Cramers rule. The fact that demand increases slightly due to the change in the price of peanut butter is likewise called a second- or third-order effect. Weve just explained two ways of finding a market equilibrium.
 Source: uw.pressbooks.pub
Source: uw.pressbooks.pub
D demand 20 - 2P price. How do we solve for the overall equilibrium in the two. We can solve for the new equilibrium P and Q. Comment on the effect that the signs of the model parameters have on the solution. Solve this system using Cramers rule.
 Source: econ101help.com
Source: econ101help.com
Calculating K c from a known set of equilibrium concentrations seems pretty clear. We can also identify the equilibrium with a little algebra if we have equations for the supply and demand curves. Heres the calculation with the demand equation. In terms of p and supply s we get. Let us suppose we.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
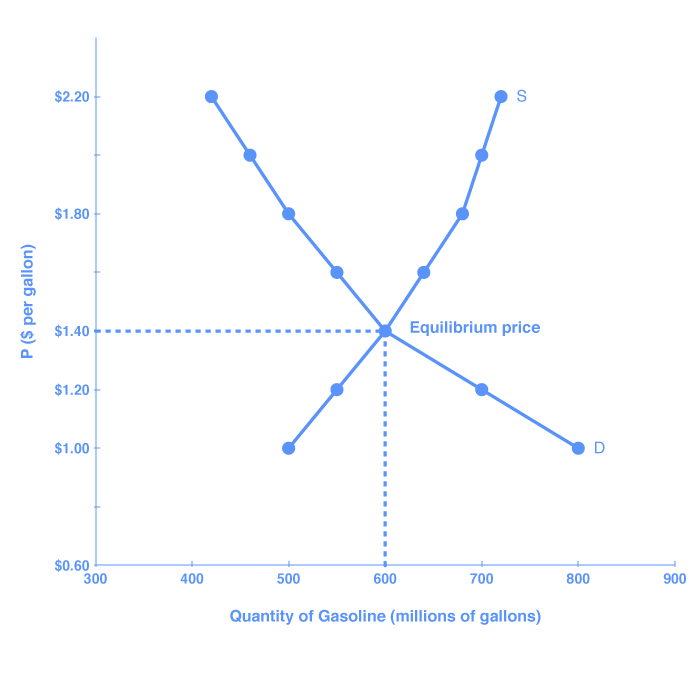
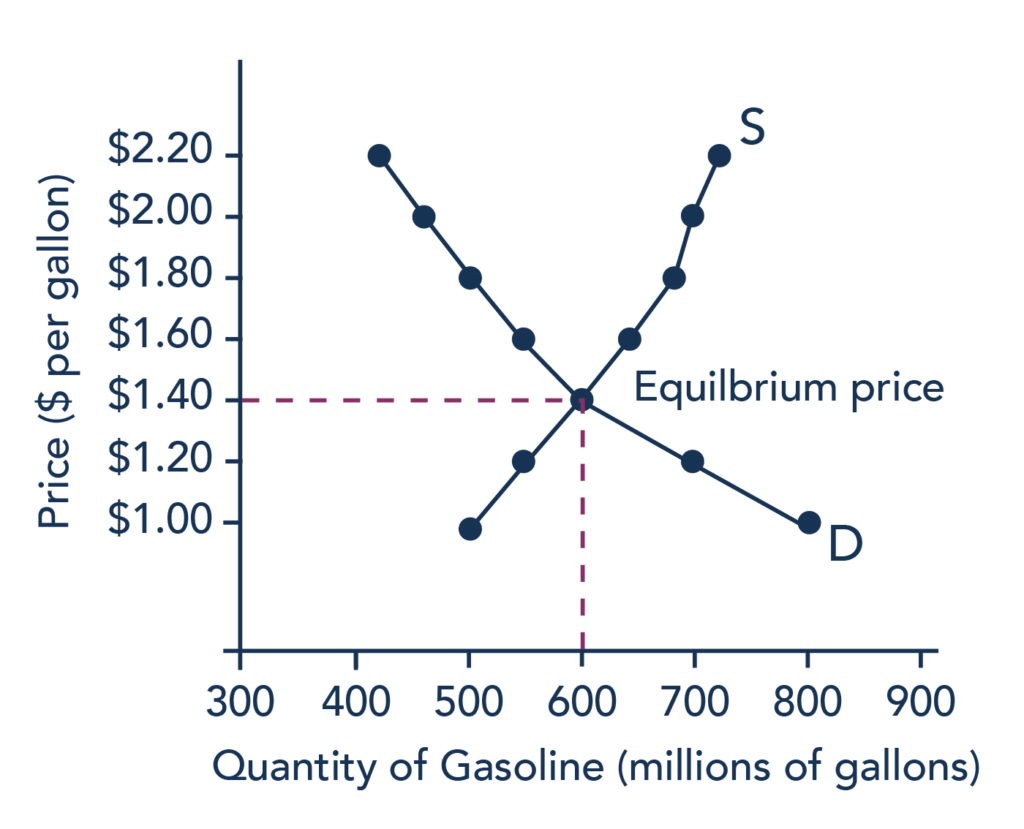
We start by deriving the demand curve and describe the characteristics of demand. These individual supply and demand functions will be aggregated to get market supply and demand mathematically and then market equilibrium will be calculated. So you are taking that demand figure of 20 and subtracting from it two multiplied by the price. 49 rows How to determine supply and demand equilibrium equations. If the price is below the equilibrium level then the quantity demanded will exceed the quantity supplied.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
After this a graph will be produced to visually show the markets interact and equilibrium price and quantity are determined. Lets practice solving a few equations that you will see later in the. S supply -10 2P price. Suppose that our market consists of three. D demand 20 - 2P price.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
You use the supply formula Qs x yP to find the supply line algebraically or on a graph. The equilibrium point is the price at which the supply is equal to the demand. How do we solve for the overall equilibrium in the two. Moreover a change in equilibrium in one market will affect equilibrium in related markets. The equilibrium of supply and demand in each market determines the price and quantity of that item.
 Source: open.oregonstate.education
Source: open.oregonstate.education
D demand 20 - 2P price. Solving for P and Q. Set the two quantities equal in. This P is referred to as the market price P since it is the price where quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded. Finally we explore what happens when demand and supply interact and what happens when market conditions change.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
The direct effect of the shift in the supply curve is sometimes called a first-order effect. The equilibrium of supply and demand in each market determines the price and quantity of that item. How to find the equilibrium point. This P is referred to as the market price P since it is the price where quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded. Calculating K c from a known set of equilibrium concentrations seems pretty clear.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
Moreover a change in equilibrium in one market will affect equilibrium in related markets. The direct effect of the shift in the supply curve is sometimes called a first-order effect. D demand 20 - 2P price. In this unit we explore markets which is any interaction between buyers and sellers. The equilibrium point is the price at which the supply is equal to the demand.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Qs αβp α0qd γδp γ0qs qd. In terms of p and supply s we get. This P is referred to as the market price P since it is the price where quantity supplied is equal to quantity demanded. Lets practice solving a few equations that you will see later in the. So supply equals minus 10 multiplied by two multiplied by the price.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In terms of p and supply s we get. Excess demand or a shortage will exist. So you are taking that demand figure of 20 and subtracting from it two multiplied by the price. S 1200p -600. How to solve for equilibrium price.
 Source: dummies.com
Source: dummies.com
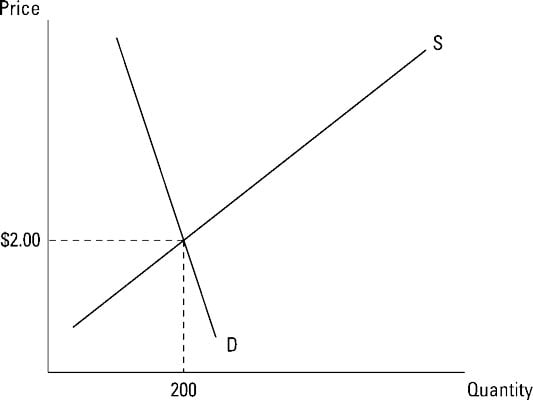
The equilibrium of supply and demand in each market determines the price and quantity of that item. Suppose that our market consists of three. Let us suppose we. Solving for P and Q. D demand 20 - 2P price.
 Source: open.oregonstate.education
Source: open.oregonstate.education
Let us suppose we. Lets practice solving a few equations that you will see later in the. Use the demand function for quantity. By looking at a table showing the quantity demanded and supplied at different prices and by looking at a graph of demand and supply. In terms of p and supply s we get.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The equilibrium point is the price at which the supply is equal to the demand. Heres the calculation with the demand equation. Heres where the equation works. 49 rows How to determine supply and demand equilibrium equations. Calculating equilibrium concentrations from a set of initial concentrations takes more calculation steps.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Calculating K c from a known set of equilibrium concentrations seems pretty clear. Now that youve mastered demand and supply equations its time to put them together to determine the equilibrium price and quantity in a market. The equilibrium point is the price at which the supply is equal to the demand. In this type of problem the K c value will be given The best way to explain is by example. Calculating equilibrium concentrations from a set of initial concentrations takes more calculation steps.
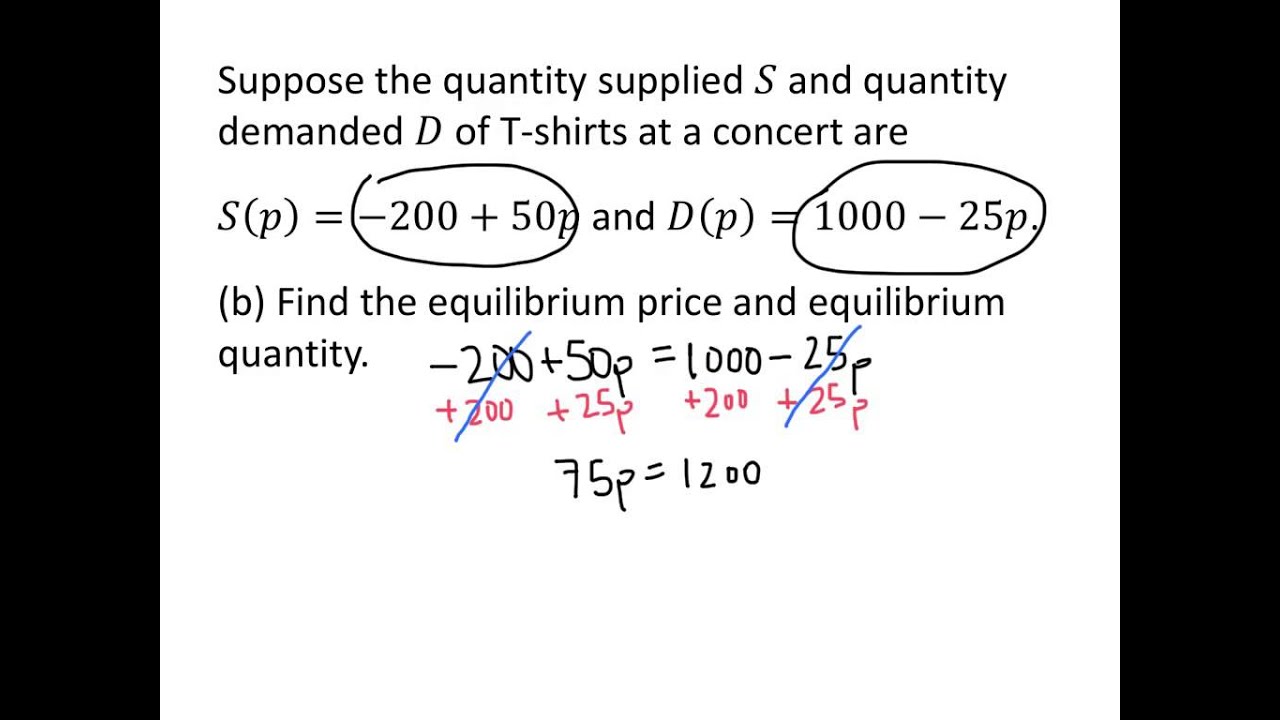 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
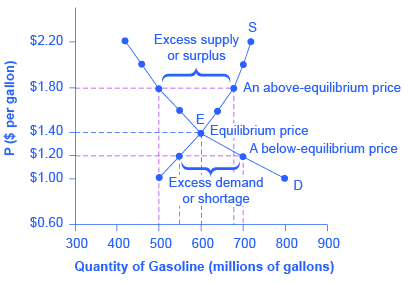
S supply -10 2P price. Once the supply and demand curves are substituted into the equilibrium condition its relatively straightforward to solve for P. By looking at a table showing the quantity demanded and supplied at different prices and by looking at a graph of demand and supply. Excess demand or a shortage will exist. The direct effect of the shift in the supply curve is sometimes called a first-order effect.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
How to solve for equilibrium price. We can solve for the new equilibrium P and Q. 49 rows How to determine supply and demand equilibrium equations. Calculating K c from a known set of equilibrium concentrations seems pretty clear. Excess demand or a shortage will exist.
 Source: pdfprof.com
Source: pdfprof.com
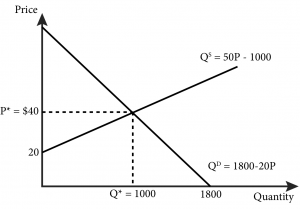
Heres where the equation works. D demand 20 - 2P price. How do we solve for the overall equilibrium in the two. Equilibrium price and quantity could rise in both markets. Demand Supply 120 3Q 20 2Q 120-20 3Q 5Q 100 5Q Q 20 Find price using either the supply or demand equation.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title how to solve demand and supply equilibrium by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.