Your How to find mr from inverse demand function images are ready. How to find mr from inverse demand function are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the How to find mr from inverse demand function files here. Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for how to find mr from inverse demand function pictures information related to the how to find mr from inverse demand function interest, you have come to the right blog. Our website always provides you with suggestions for downloading the highest quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and locate more informative video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
How To Find Mr From Inverse Demand Function. The x-intercept of the MR function is one-half the value. Generally MR_iy_1y_2 neq MC_iy_i that is the functions are not the same. For example if the demand functionhas the form Q 240 - 2P then the inverse demand function would be P 120. TR 120 -.
 Solved Suppose That The Demand Function Is Given By The Chegg Com From chegg.com
Solved Suppose That The Demand Function Is Given By The Chegg Com From chegg.com
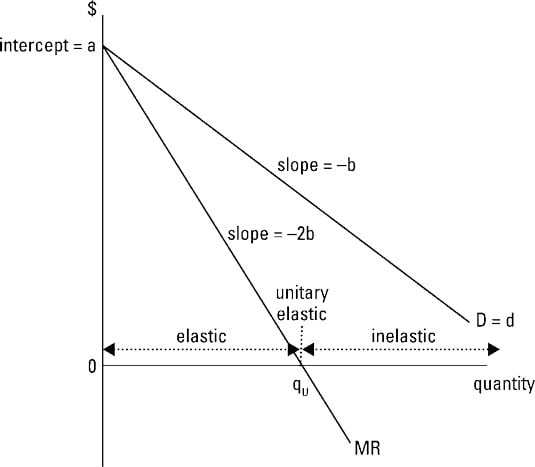
Note that the MR function has the same y-intercept as the inverse demand function in this linear example. Multiply the inverse demand function by Q to derive the total revenue function. 5Q Q 120Q 05Q²The marginal revenue function is the first derivative of the total revenue function or MR 120 Q. MR 300 1Q Where. Is measured by calculating different elasticities. TR 120.
To compute theinverse demand function simply solve for P from thedemand function.
Multiply the inverse demand function by Q to derive the total revenue function. Find the profit maximizing price and quantity and economic profit for the monopoly. TR 120 -. The marginal revenue function is the first derivative of the total revenue function. One change in revenue Total Revenue Old Revenue and two change in quantity Total Quantity Old Quantity. To compute theinverse demand function simply solve for P from thedemand function.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
Find the profit maximizing price and quantity and economic profit for the monopoly. Multiply the inverse demand function by Q to derive the total revenue function. 2 To get the MR function we need to double the slope of the inverse demand curve make it twice as steep. For example if the demand functionhas the form Q 240 - 2P then the inverse demand function would be P 120. Multiply the inverse demand function by Q to derive the total revenue function.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
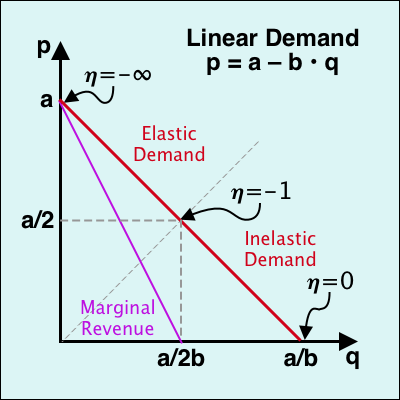
Let us introduce the notation MR_iy_1y_2 fracpartial py_1 y_2partial y_i. Given a linear demand curve in inverse form P 100 - 001Q we know that the marginal revenue curve will have twice the slope of the demand curve. Q is monthly production and P is price measured in unit The firm also has a total cost TC function. P 300 05Q Which has the corresponding marginal revenue function. Here MR 120 - Q.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Marginal cost is simply the slope of the total cost curve. The formula above breaks this calculation into two parts. The inverse demand function is the same as the average revenue function since P AR. Given a linear demand curve in inverse form P 100 - 001Q we know that the marginal revenue curve will have twice the slope of the demand curve. 2 To get the MR function we need to double the slope of the inverse demand curve make it twice as steep.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Note that the MR function has the same y-intercept as the inverse demand function in this linear example. Third as the inverse supply function the inverse demand function is useful when drawing demand curves and determining the slope of the curve. For example if the demand functionhas the form Q 240 - 2P then the inverse demand function would be P 120. The marginal revenue function is the first derivative of the total revenue function. Multiply the inverse demand function by Q to derive the total revenue function.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
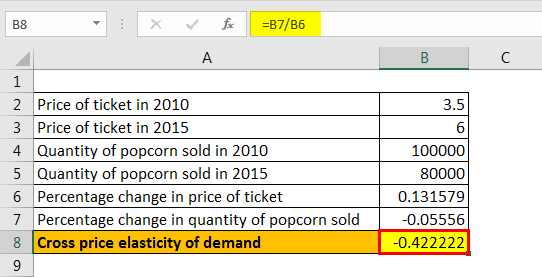
A firm faces the inverse demand curve. TR 120 - 5Q Q 120Q - 05Q². Algebra of Marginal Revenue. The first derivative of TR equals 50 Q hence MR 50 Q. Example of calculation of inverse demand functionQd fPQd 12 05PP Qd-12 05 2Qd 24Second calculating quantities that maximize profit also becomes easy.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
MR 1000 - 10Q Cost of producing at facility 1. TR 120. So the companys profit will be at maximum if it producessells 2 units. The x-intercept of the MR function is one-half the value. MR 120 Q is the first derivative of the marginal revenue function which is the first derivative of the total revenue function.
 Source: dummies.com
Source: dummies.com
Multiply the inverse demand function by Q to derive the total revenue function. MR 120 Q is the first derivative of the marginal revenue function which is the first derivative of the total revenue function. Algebra of Marginal Revenue. The 5Q is equal to 120Q 0. To compute theinverse demand function simply solve for P from thedemand function.
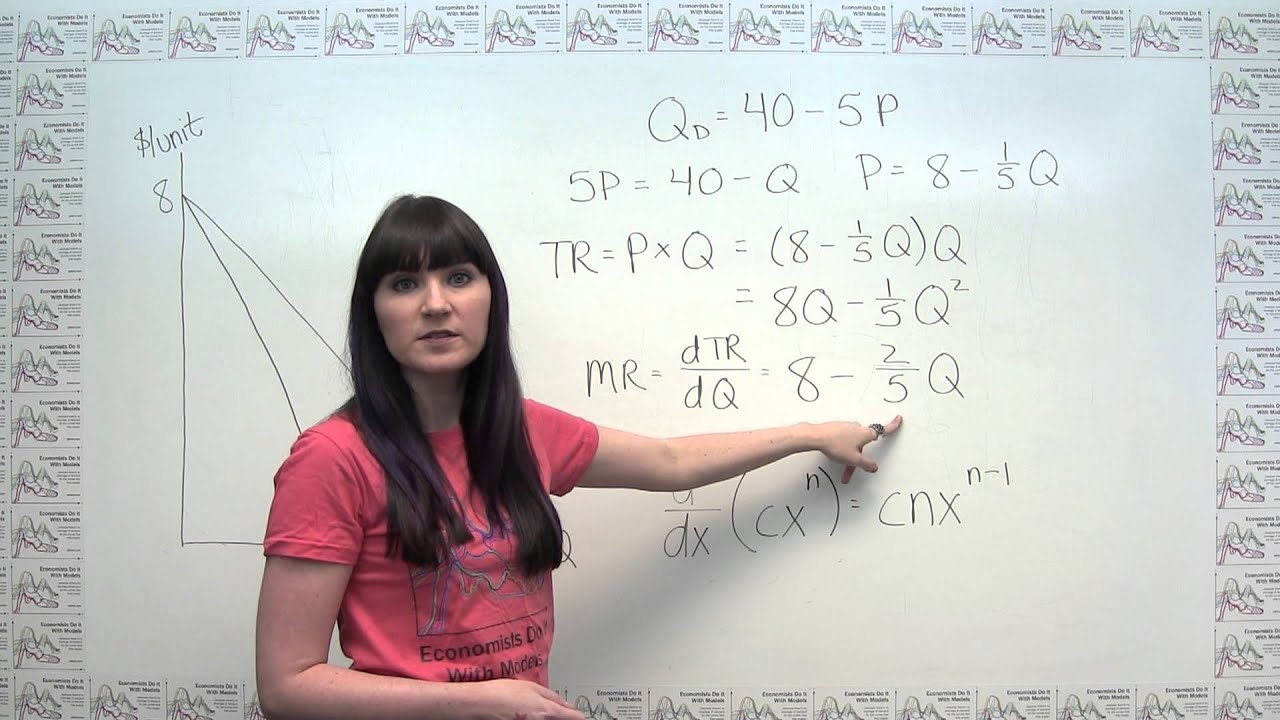 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Thus the marginal revenue curve for the firm is MR 100 - 002Q. For example if the demand functionhas the form Q 240 - 2P then the inverse demand function would be P 120. P 300 05Q Which has the corresponding marginal revenue function. MC MR 12 2Q 24 4Q 6Q 24 12 Q 2. The marginal revenue function is the first derivative of the total revenue function.
 Source: ictsd.org
Source: ictsd.org
In this video I show every step of algebra necessary to derive a demand curve from an inverse demand curve. In this video I show every step of algebra necessary to derive a demand curve from an inverse demand curve. Find the profit maximizing price and quantity and economic profit for the monopoly. C To maximize total revenue we find the value of x where marginal revenue is zero. The slope of TC 30000 50Q is 50.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Multiply the inverse demand function by Q to derive the total revenue function. P 300 05Q Which has the corresponding marginal revenue function. TR P x Q 2Q 24 Q 2Q2 24QMR 4Q 24120 40Q Q2MC 40 2Q. Here MR 120 - Q. Revenue pQ Q10Q-12 10Q12 MR 5Q-12 MC 5 Profit maximization implies MR MC so 5Q-12 5 or Q 1.
 Source: economics.stackexchange.com
Source: economics.stackexchange.com
C1 Q1 10050 5Q21 Therefore marginal cost at facility 1 equals to. Marginal cost is simply the slope of the total cost curve. The slope of TC 30000 50Q is 50. Because the profit will be maximum when MR MC then. The firm was producing output of 175 selling at a price of 325.

MR 120 Q is the first derivative of the marginal revenue function which is the first derivative of the total revenue function. The slope of TC 30000 50Q is 50. Is measured by calculating different elasticities. The marginal revenue function is the first derivative of the total revenue function. If these are known already skip to step 4.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
MR 300 1Q Where. Here MR 120 - Q. The model of a monopoly firm I made had a demand function of Q 500 P no fixed cost and a constant marginal cost of 150. So MC equals 50. For an inverse demand function of the form P a b Q MR a 2b Q.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
MR TR x 1000 x 5. TR 120 -. Marginal Revenue is easy to calculate. The formula above breaks this calculation into two parts. The slope of TC 30000 50Q is 50.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The 5Q is equal to 120Q 0. Here MR 120 - Q. Assuming the firm operates as a monopolist. Multiply the inverse demand function by Q to derive the total revenue function. 5Q Q 120Q 05Q²The marginal revenue function is the first derivative of the total revenue function or MR 120 Q.
 Source: wernerantweiler.ca
Source: wernerantweiler.ca
To compute theinverse demand function simply solve for P from thedemand function. Here MR 120 - Q. TR 120 - 5Q Q 120Q - 05Q². Q is monthly production and P is price measured in unit The firm also has a total cost TC function. To compute theinverse demand function simply solve for P from thedemand function.
 Source: yumpu.com
Source: yumpu.com
TR 120 - 5Q Q 120Q - 05Q². Multiply the inverse demand function by Q to derive the total revenue function. To compute theinverse demand function simply solve for P from thedemand function. The slope of TC 30000 50Q is 50. Marginal cost is simply the slope of the total cost curve.
 Source: studylib.net
Source: studylib.net
Generally MR_iy_1y_2 neq MC_iy_i that is the functions are not the same. Given a linear demand curve in inverse form P 100 - 001Q we know that the marginal revenue curve will have twice the slope of the demand curve. 2 To get the MR function we need to double the slope of the inverse demand curve make it twice as steep. View the full answer. Because marginal revenue is the derivative of total revenue we can construct the marginal revenue curve by calculating total revenue as a function of quantity and then taking the derivative.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title how to find mr from inverse demand function by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.