Your How to calculate velocity of elastic collision images are ready in this website. How to calculate velocity of elastic collision are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the How to calculate velocity of elastic collision files here. Find and Download all free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for how to calculate velocity of elastic collision images information linked to the how to calculate velocity of elastic collision interest, you have visit the ideal blog. Our website frequently gives you hints for viewing the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video articles and images that match your interests.
How To Calculate Velocity Of Elastic Collision. When two objects having different masses and velocities elastically collide with each other their individual kinetic energies may get changed. Dividing by 0500 we get. It explains how to solve one dimension elastic collision physics problems. M2 is the mass of 2nd body.
 Collisions Boundless Physics From courses.lumenlearning.com
Collisions Boundless Physics From courses.lumenlearning.com
V_1 fracu_1m_1-m_22m_2u_2m_1m_2 v_2 fracu_2m_2-m_12m_1u_1m_1m_2. How to calculate velocity after collisionexplaining gender pronouns. Namely the relative velocity of two objects at a given time that is the difference. V2f final velocity of second object. But more generally if KE is conserved in a straight line collision then v 2f -v 1f v 1i -v 2i regardless of the masses. The elastic collision formula is given as.
V2 is the final velocity of the second body.
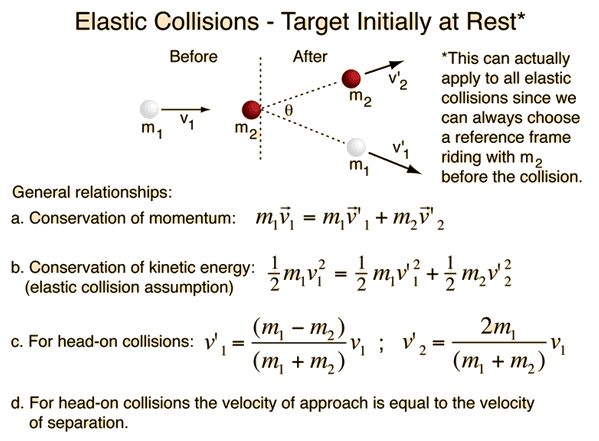
V 1 Final velocity of the first body. For non-head-on collisions the angle between projectile and target is always less than 90 degrees. In a head-on elastic collision where the projectile is much more massive than the target the velocity of the target particle after the collision will be about twice that of the projectile and the projectile velocity will be essentially unchanged. Strategy and Concept First visualize what the initial conditions meana small object strikes a larger object that is initially. For an elastic collision kinetic energy is conserved. 10 kgms 0 0 025 kg v 2f 2 Use the equation for conservation of kinetic energy in an elastic collision to determine the final velocity for the blue ball.

The Elastic Collision formula of momentum is given. Dividing by 0500 we get. The elastic collision formula is given as. V_1 fracu_1m_1-m_22m_2u_2m_1m_2 v_2 fracu_2m_2-m_12m_1u_1m_1m_2. V2 is the final velocity of the second body.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
M₁V₁ M₂V₂ M₁W₁ M₂W₂. The mass of the 2nd ball m 2 020kg. That is the rate at which two objects approach each other before an elastic collision is the same as the rate at which they separate afterward. Example 84 Calculating Velocities Following an Elastic Collision Calculate the velocities of two objects following an elastic collision given that 836 m 1 0500 kg m 2 350 kg v 1 400 ms and v 2 0. Combining the above equations gives a solution to the final velocities for an elastic collision of two objects.
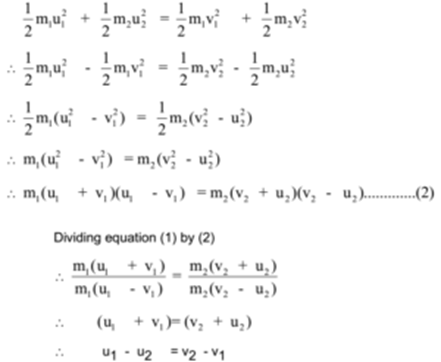 Source: thefactfactor.com
Source: thefactfactor.com
Example 84 Calculating Velocities Following an Elastic Collision Calculate the velocities of two objects following an elastic collision given that 836 m 1 0500 kg m 2 350 kg v 1 400 ms and v 2 0. Assign a unique variable to represent the mass of each of the particles. U 1 Initial velocity of 1st body. U 2 Initial velocity of the second body. It explains how to solve one dimension elastic collision physics problems.
 Source: in.pinterest.com
Source: in.pinterest.com
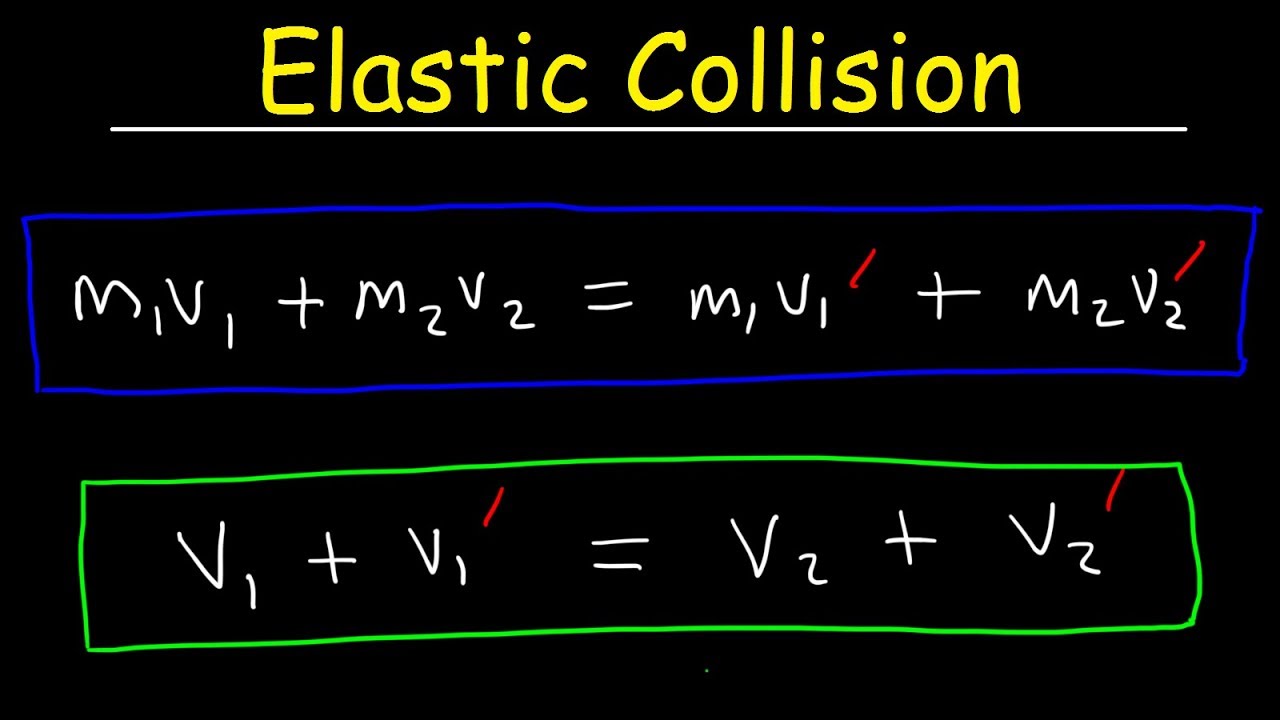
This physics video provides a basic introduction into elastic collisions. This CalcTown calculator calculates the final velocities of two bodies after a head-on 1-D inelastic collision. V1 is the final velocity of the first body. M 2 Mass of 2nd body. By conservation of momentum the final momentum of the system m1v1f m2v2f is a.
 Source: stuegli.com
Source: stuegli.com
The mass of the 1st ball m 1 02 kg. When two objects having different masses and velocities elastically collide with each other their individual kinetic energies may get changed. Equations for post-collision velocity for two objects in one dimension based on masses and initial velocities. V 1 is the final velocity of the first object after impact. M 2 Mass of 2nd body.
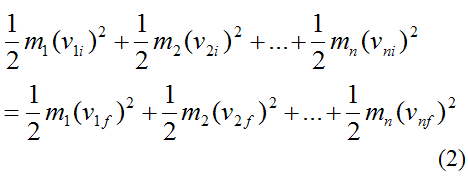 Source: real-world-physics-problems.com
Source: real-world-physics-problems.com
If the two objects stick together after the collision and move with a common velocity v f then the collision is said to be perfectly inelastic. That is the rate at which two objects approach each other before an elastic collision is the same as the rate at which they separate afterward. V2f final velocity of second object. V f1 m 1 - m 2v i1 2 m 2 v i2m 1 m. Assign a unique variable to represent the mass of each of the particles.

This CalcTown calculator calculates the final velocities of two bodies after a head-on 1-D inelastic collision. This CalcTown calculator calculates the final velocities of two bodies after a head-on 1-D inelastic collision. 10 kgms 0 0 025 kg v 2f 2 Use the equation for conservation of kinetic energy in an elastic collision to determine the final velocity for the blue ball. In elastic collision momentum is conserved. Assign a unique variable to represent the mass of each of the particles.
 Source: engineersfield.com
Source: engineersfield.com
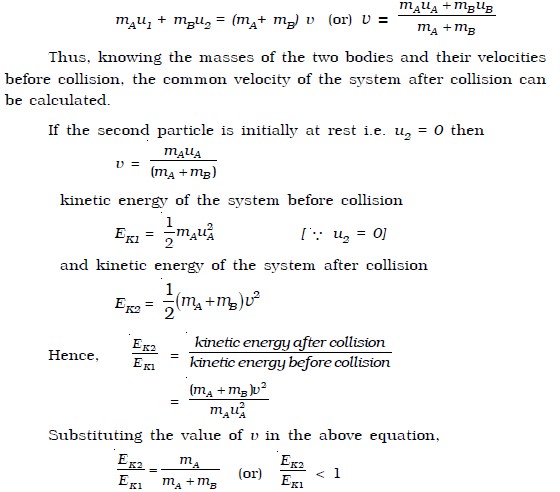
When a body moving with a uniform velocity v collides with another body at rest the second body after collision moves with the same velocity as the first one. V1 is the final velocity of the first body. Assign a unique variable to represent the mass of each of the particles. When two objects having different masses and velocities elastically collide with each other their individual kinetic energies may get changed. U 1 Initial velocity of 1st body.

U 2 Initial velocity of the second body. If two particles are involved in an elastic collision the velocity of the second particle after collision can be expressed as. The momentum before elastic collision is calculated using the conservation of energy. V2f2m1 m2m1v1i m2m1 m2m1v2i v 2 f 2 m 1 m 2 m 1. The Elastic Collision formula of momentum is given by.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
The Elastic Collision formula of kinetic energy is given by. V2f2m1 m2m1v1i m2m1 m2m1v2i v 2 f 2 m 1 m 2 m 1. M2 is the mass of 2nd body. Equations for post-collision velocity for two objects in one dimension based on masses and initial velocities. U 1 Initial velocity of 1st body.
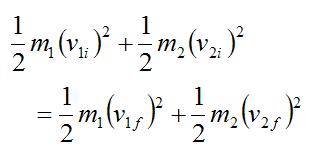 Source: real-world-physics-problems.com
Source: real-world-physics-problems.com
When two objects having different masses and velocities elastically collide with each other their individual kinetic energies may get changed. V 2 Final velocity of the second body. Formula of Elastic Collision. For an elastic collision kinetic energy is conserved. 05m 1 v i1 2 05m 2 v i2 2 05m 1 v f1 2 05m 2 v f2 2 The collision is fully specied given the two initial velocities and masses of the colliding objects.
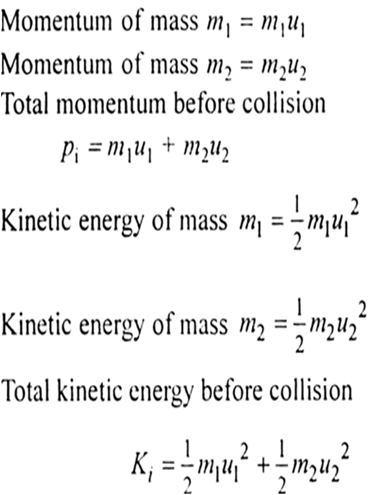 Source: zigya.com
Source: zigya.com
V 1 is the final velocity of the first object after impact. U1 is the initial velocity of 1st body. In elastic collision momentum is conserved. The momentum before elastic collision is calculated using the conservation of energy. Combining the above equations gives a solution to the final velocities for an elastic collision of two objects.

The Elastic Collision formula of kinetic energy is given by. Lets say the velocities after collision for M₁ and M₂ is W₁ and W₂ respectively. The mass of the 2nd ball m 2 020kg. V 1 is the final velocity of the first object after impact. M_1u_1 m_2u_2 m_1v_1 m_2v_2 15 x 16 10 x 6 15 x 0 10 x v_2 240 60 10v_2 v_2 frac30010 v_2 30 ms.
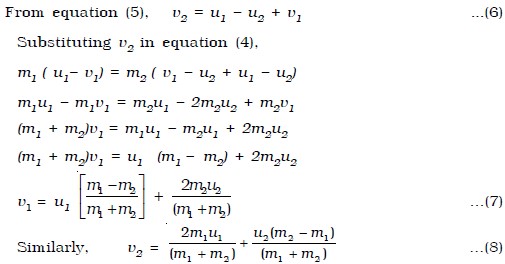 Source: engineersfield.com
Source: engineersfield.com
When a body moving with a uniform velocity v collides with another body at rest the second body after collision moves with the same velocity as the first one. V 1 Final velocity of the first body. This CalcTown calculator calculates the final velocities of two bodies after a head-on 1-D inelastic collision. M₁V₁ M₂V₂ M₁W₁ M₂W₂. It explains how to solve one dimension elastic collision physics problems.
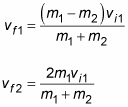 Source: dummies.com
Source: dummies.com
Namely the relative velocity of two objects at a given time that is the difference. V2 is the final velocity of the second body. U 1 Initial velocity of 1st body. The Elastic Collision formula of kinetic energy is given by. Formula of Elastic Collision.
 Source: m.youtube.com
Source: m.youtube.com
U 1 Initial velocity of 1st body. V2f final velocity of second object. How do you calculate velocity after a collision. M₁V₁ M₂V₂ M₁W₁ M₂W₂. V2f2m1 m2m1v1i m2m1 m2m1v2i v 2 f 2 m 1 m 2 m 1.
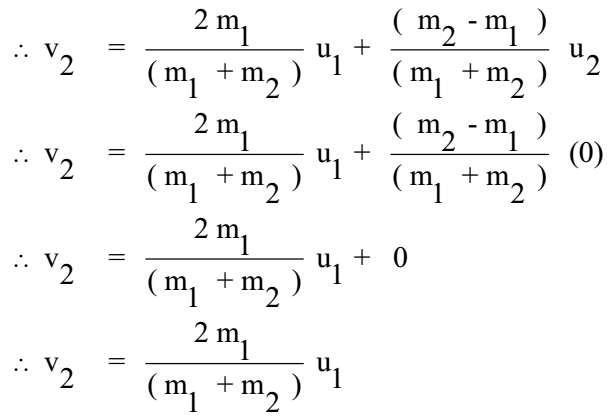 Source: thefactfactor.com
Source: thefactfactor.com
When a body moving with a uniform velocity v collides with another body at rest the second body after collision moves with the same velocity as the first one. How to calculate velocity after collisionexplaining gender pronouns. U 2 Initial velocity of the second body. V1 is the final velocity of the first body. But more generally if KE is conserved in a straight line collision then v 2f -v 1f v 1i -v 2i regardless of the masses.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
This physics video provides a basic introduction into elastic collisions. How to calculate velocity after collisionexplaining gender pronouns. The video makes use of an equation that results when conservation of moment. V 1 is the initial velocity of the first object before. The momentum before elastic collision is calculated using the conservation of energy.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site value, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title how to calculate velocity of elastic collision by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.