Your How to calculate perfectly elastic collision images are available in this site. How to calculate perfectly elastic collision are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the How to calculate perfectly elastic collision files here. Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for how to calculate perfectly elastic collision pictures information related to the how to calculate perfectly elastic collision topic, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our site frequently gives you suggestions for viewing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly search and locate more enlightening video articles and graphics that fit your interests.
How To Calculate Perfectly Elastic Collision. V 1 Final velocity of the first body. All other collisions are inelastic as some energy is lost E i E f. How to calculate an elastic collision. V 2 Final velocity of the second body.
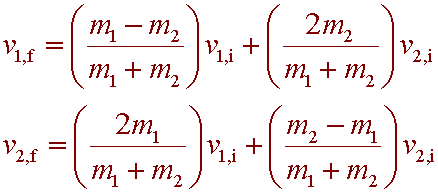 Lecture 17 From www4.uwsp.edu
Lecture 17 From www4.uwsp.edu
Answer 1 of 2. If the kinetic energy is the same then the collision is elastic. The momentum of the objects before the collision is conserved but the total energy is not conserved. In an ideal perfectly elastic collision there is no net conversion of kinetic energy into other forms such as heat noise or potential energy. An elastic collision is an encounter between two bodies in which the total kinetic energy of the two bodies remains the same. M 2 Mass of 2nd body.
Elastic collisions are defined as collisions in which no energy leaves the system ie.
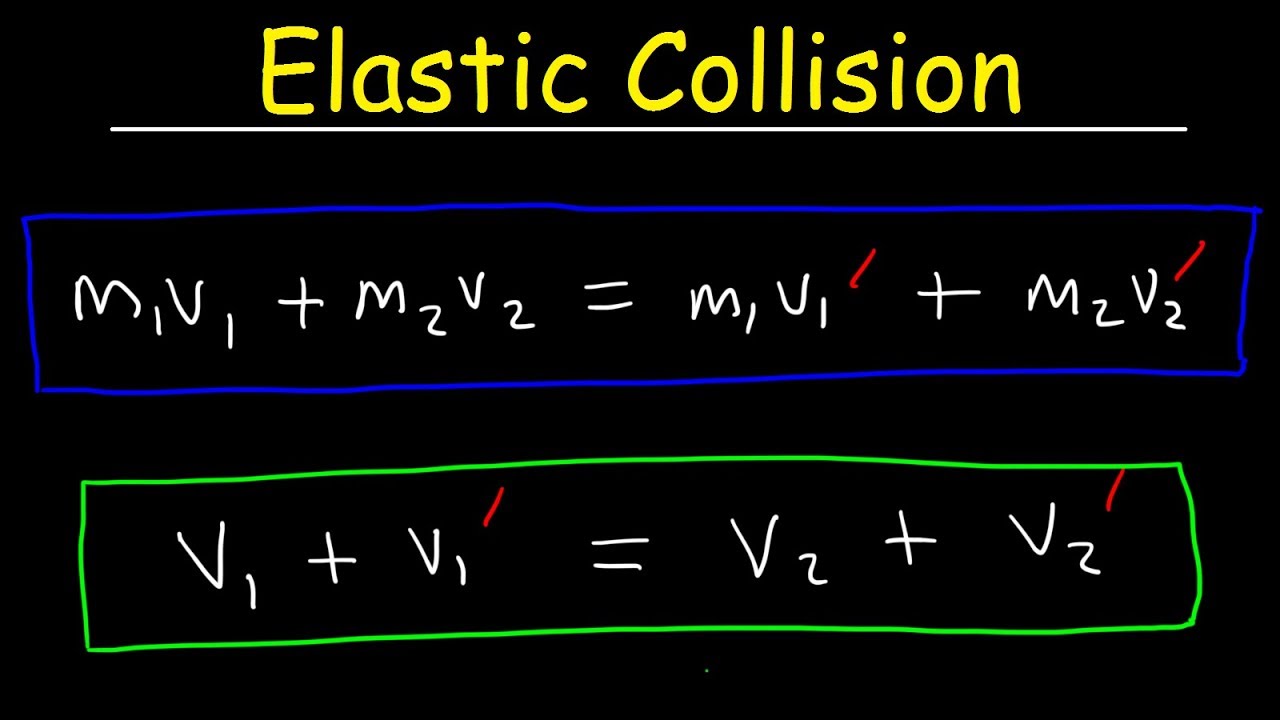
E i E f. The Elastic collision formula is given as m1u1 m2u2 m1v1 m2v2 10 12 8 4 10 v1 8 0 120 32 10 v1 0 152 10 v1 v1 152 ms For more such valuable equations and formulas stay tuned with BYJUS. If the kinetic energy changes then the collision is inelastic regardless of whether the objects stick together or not. Final Velocity after a head-on Inelastic collision Calculator. In a perfectly inelastic collision two objects collide and stick together. 1-D Elastic Collisions Equations for post-collision velocity for two objects in one dimension based on masses and initial velocities.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
It also implies that if the speed of the head of your golf club is 110 mileshr the limiting speed on the golf ball off the tee is 220 mileshr in the ideal case. The momentum of the objects before the collision is conserved but the total energy is not conserved. Their line of collision and initial velocity directions are all aligned then in an perfectly elastic collision both would rebound with same velocity as initial velocity and no loss. How to calculate elastic collision. A 1 dimensional perfectly elastic collision.
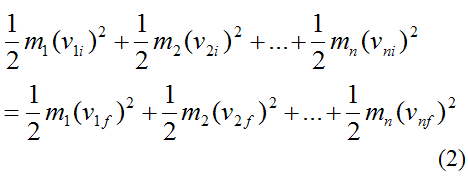 Source: real-world-physics-problems.com
Source: real-world-physics-problems.com
If the kinetic energy changes then the collision is inelastic regardless of whether the objects stick together or not. An elastic collision is an encounter between two bodies in which the total kinetic energy of the two bodies remains the same. In an ideal perfectly elastic collision there is no net conversion of kinetic energy into other forms such as heat noise or potential energy. V 1 Final velocity of the first body. What is the equation for an elastic collision.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
A perfectly inelastic collision is a type of inelastic collision where all the kinetic energy of the system is lost E f 0. First determine the masses of each object. Do pay attention to HGreenwood Hansma. In an ideal perfectly elastic collision there is no net conversion of kinetic energy into other forms such as heat noise or potential energy. 1-D Elastic Collisions Equations for post-collision velocity for two objects in one dimension based on masses and initial velocities.
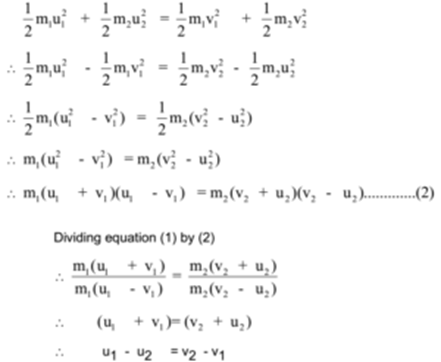 Source: thefactfactor.com
Source: thefactfactor.com
The perfectly elastic collision formula of momentum is followed as m_1u_1 m_2u_2 m_1v_1 m_2v_2 Likewise the conservation of the total kinetic energy is represented as. What is the equation for an elastic collision. U 1 Initial velocity of 1st body. The perfectly elastic collision formula of momentum is followed as m_1u_1 m_2u_2 m_1v_1 m_2v_2 Likewise the conservation of the total kinetic energy is represented as. It also implies that if the speed of the head of your golf club is 110 mileshr the limiting speed on the golf ball off the tee is 220 mileshr in the ideal case.
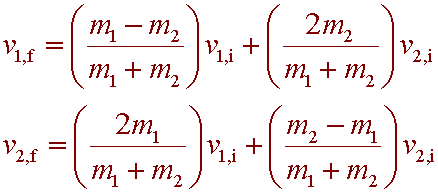 Source: www4.uwsp.edu
Source: www4.uwsp.edu
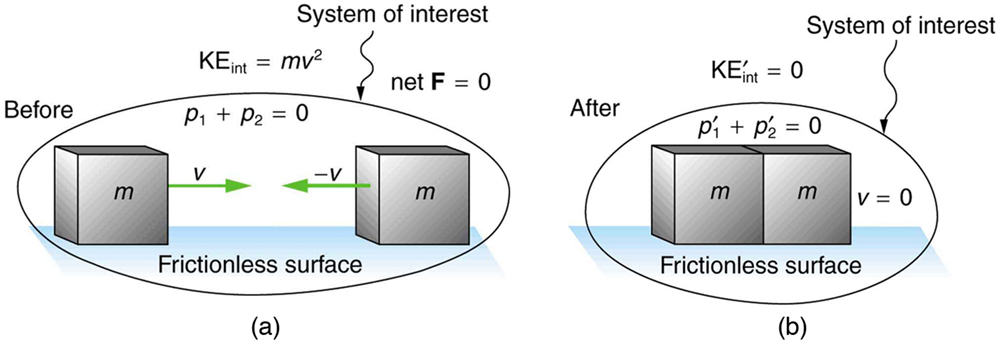
This means that KE 0 KE f and p o p f. How to calculate an elastic collision. You only have the masses of the objects and their initial velocities. If objects stick together then a collision is perfectly inelastic. How do you calculate both of their final velocities.
 Source: unacademy.com
Source: unacademy.com
Next measure the initial velocities of each object. This should be enough to give you a unique pair of velocities. How to calculate an elastic collision. Elastic Collision Formula An elastic collision is a collision where both kinetic energy KE and momentum p are conserved. A 1 dimensional perfectly elastic collision.
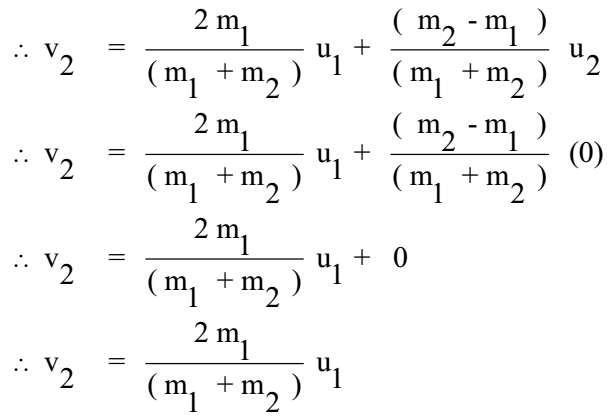 Source: thefactfactor.com
Source: thefactfactor.com
All other collisions are inelastic as some energy is lost E i E f. V 2 Final velocity of the second body. An elastic collision is an encounter between two bodies in which the total kinetic energy of the two bodies remains the same. The momentum of the objects before the collision is conserved but the total energy is not conserved. How to calculate elastic collision.

The perfectly elastic collision formula of momentum is followed as m_1u_1 m_2u_2 m_1v_1 m_2v_2 Likewise the conservation of the total kinetic energy is represented as. The perfectly elastic collision formula of momentum is followed as m_1u_1 m_2u_2 m_1v_1 m_2v_2 Likewise the conservation of the total kinetic energy is represented as. Final Velocity after a head-on Inelastic collision Calculator. If the kinetic energy is the same then the collision is elastic. Elastic collisions are defined as collisions in which no energy leaves the system ie.
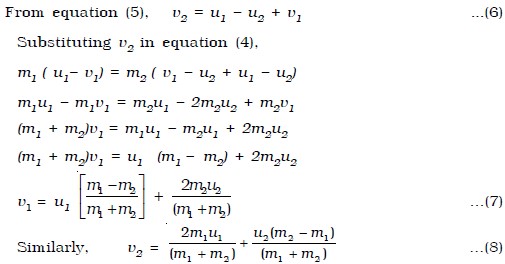 Source: engineersfield.com
Source: engineersfield.com
In a perfectly inelastic collision two objects collide and stick together. Answer 1 of 2. You only have the masses of the objects and their initial velocities. I would construct two exactly similar opposed inclined brief segmental circular troughs and roll one spherical object down a measured height to strike an exactly similar sphere stationary at. A perfectly elastic collision is defined as one in which there is no loss of kinetic energy in the collision.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
I would construct two exactly similar opposed inclined brief segmental circular troughs and roll one spherical object down a measured height to strike an exactly similar sphere stationary at. Using a speed radar or another formula calculate the initial velocities of the object. The Elastic Collision formula of kinetic energy is given by. Perfectly Elastic Collision In a perfectly elastic the coefficient of restitution is taken to be 1. First determine the masses of each object.
 Source: penguinphysic.wordpress.com
Source: penguinphysic.wordpress.com
In an ideal perfectly elastic collision there is no net conversion of kinetic energy into other forms such as heat noise or potential energy. Their line of collision and initial velocity directions are all aligned then in an perfectly elastic collision both would rebound with same velocity as initial velocity and no loss. That is the limiting speed of the ball. You need to conserve energy and momentum. Elastic Collision Formula An elastic collision is a collision where both kinetic energy KE and momentum p are conserved.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Next measure the initial velocities of each object. All other collisions are inelastic as some energy is lost E i E f. The degree to which a collision is elastic or inelastic is quantified by the coefficient of restitution a value that generally ranges between zero and one. A special case of this is sometimes called the perfectly inelastic collision. How to calculate an elastic collision.

In an ideal perfectly elastic collision there is no net conversion of kinetic energy into other forms such as heat noise or potential energy. A perfectly-inelastic collision also called a perfectly-plastic collision is a limiting case of inelastic collision in which the two bodies stick together after impact. This should be enough to give you a unique pair of velocities. Elastic Collision Formula An elastic collision is a collision where both kinetic energy KE and momentum p are conserved. This means that KE 0 KE f and p o p f.
 Source: slidetodoc.com
Source: slidetodoc.com
E i E f. We know the initial velocity of the golf ball and its mass but we dont know the final velocities of either ball and the trick to make these calculations go faster for an elastic collision is to use this equation which says the initial velocity of one of the objects before the collision plus the final velocity of that same object after the collision should equal if its an elastic collision itll equal. A perfectly elastic collision is defined as one in which there is no loss of kinetic energy in the collision. How to calculate an elastic collision. U 2 Initial velocity of the second body.
 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
Any macroscopic collision between objects will convert some of the kinetic energy into internal energy and other forms of energy so no large scale impacts are perfectly elastic. Answer 1 of 2. This means that KE 0 KE f and p o p f. All other collisions are inelastic as some energy is lost E i E f. First determine the masses of each object.
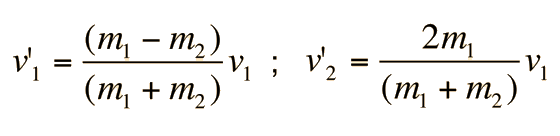 Source: stuegli.com
Source: stuegli.com
This CalcTown calculator calculates the final velocities of two bodies after a head-on 1-D inelastic collision. How to calculate an elastic collision. An elastic collision is an encounter between two bodies in which the total kinetic energy of the two bodies remains the same. Where m 1 Mass of 1st body. Its probably easiest to work in the center of mass frame.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
This CalcTown calculator calculates the final velocities of two bodies after a head-on 1-D inelastic collision. Elastic Collision Formula An elastic collision is a collision where both kinetic energy KE and momentum p are conserved. Any macroscopic collision between objects will convert some of the kinetic energy into internal energy and other forms of energy so no large scale impacts are perfectly elastic. E i E f. V 2 Final velocity of the second body.
 Source: m.youtube.com
Source: m.youtube.com
Elastic Collision Formula An elastic collision is a collision where both kinetic energy KE and momentum p are conserved. The degree to which a collision is elastic or inelastic is quantified by the coefficient of restitution a value that generally ranges between zero and one. U 2 Initial velocity of the second body. In an ideal perfectly elastic collision there is no net conversion of kinetic energy into other forms such as heat noise or potential energy. How to calculate elastic collision.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title how to calculate perfectly elastic collision by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.