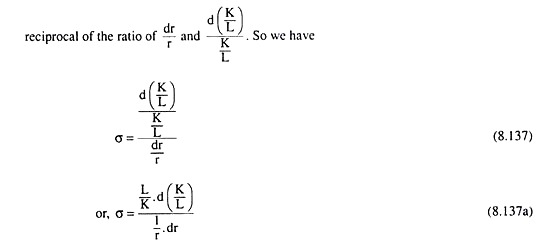Your How to calculate elasticity of demand for monopoly images are ready in this website. How to calculate elasticity of demand for monopoly are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the How to calculate elasticity of demand for monopoly files here. Download all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re searching for how to calculate elasticity of demand for monopoly images information related to the how to calculate elasticity of demand for monopoly topic, you have visit the right blog. Our website frequently gives you hints for downloading the highest quality video and image content, please kindly search and locate more informative video articles and images that match your interests.
How To Calculate Elasticity Of Demand For Monopoly. 20 - 6Q 2 10 5Q 2 or Q Q 2 091. When MR is positive the demand is elastic. Before we even dwell and discuss on the abovementioned topic it would vital for us to understand and define what Price Elasticity of Demand Excess Capacity and Monopolistic Competitive Market are all about from the. PED Q1 Q0 Q1 Q0 P1 P0 P1 P0 Q0 is the initial quantity.
 Market Of Monopoly From learneconomicsonline.com
Market Of Monopoly From learneconomicsonline.com
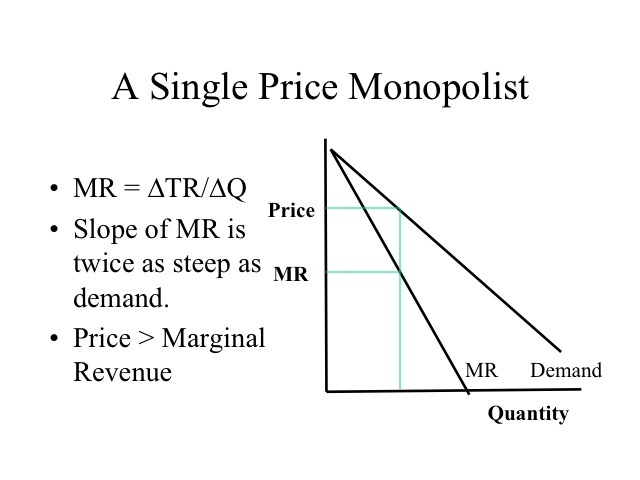
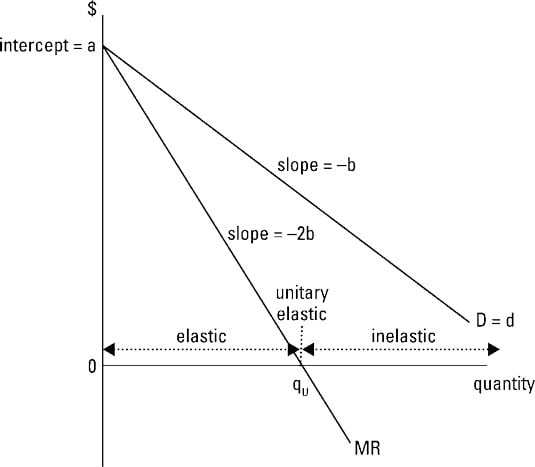
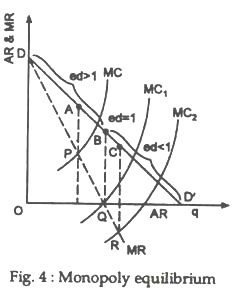
The equation can be further expanded to. Where P MCP is the mark-up over marginal cost as a proportion of price. Demand curve we know that the marginal revenue curve has the same vertical intercept but twice the slope or MR 20 - 6Q 2. My 60ish second explanation of how to identify the elastic and inelastic range of the demand curve for a monopoly. This does not change the revenue. Let us now establish the proposition that monopoly equilibrium will occur at a point where the demand for the product is relatively elasticThe proposition may be established easily with the help of the relation between AR p MR and e e is the numerical coefficient of price-elasticity of demand.
The relationship can be seen in Figure 33.
If the monopolist knows his marginal cost MC and price elasticity of demand E p it should set price P such that. Lerners index of monopoly power according to which degree of monopoly is given by. But not within this inelastic demand there is an elastic and inelastic portion. The relationship between the monopolists marginal revenue and price ie average revenue is reflected in the price elasticity of the industry demand curveSince PP 1 we can write equation 1 as. The relationship can be seen in Figure 33. 20 - 6Q 2 10 5Q 2 or Q Q 2 091.
 Source: 2012books.lardbucket.org
Source: 2012books.lardbucket.org
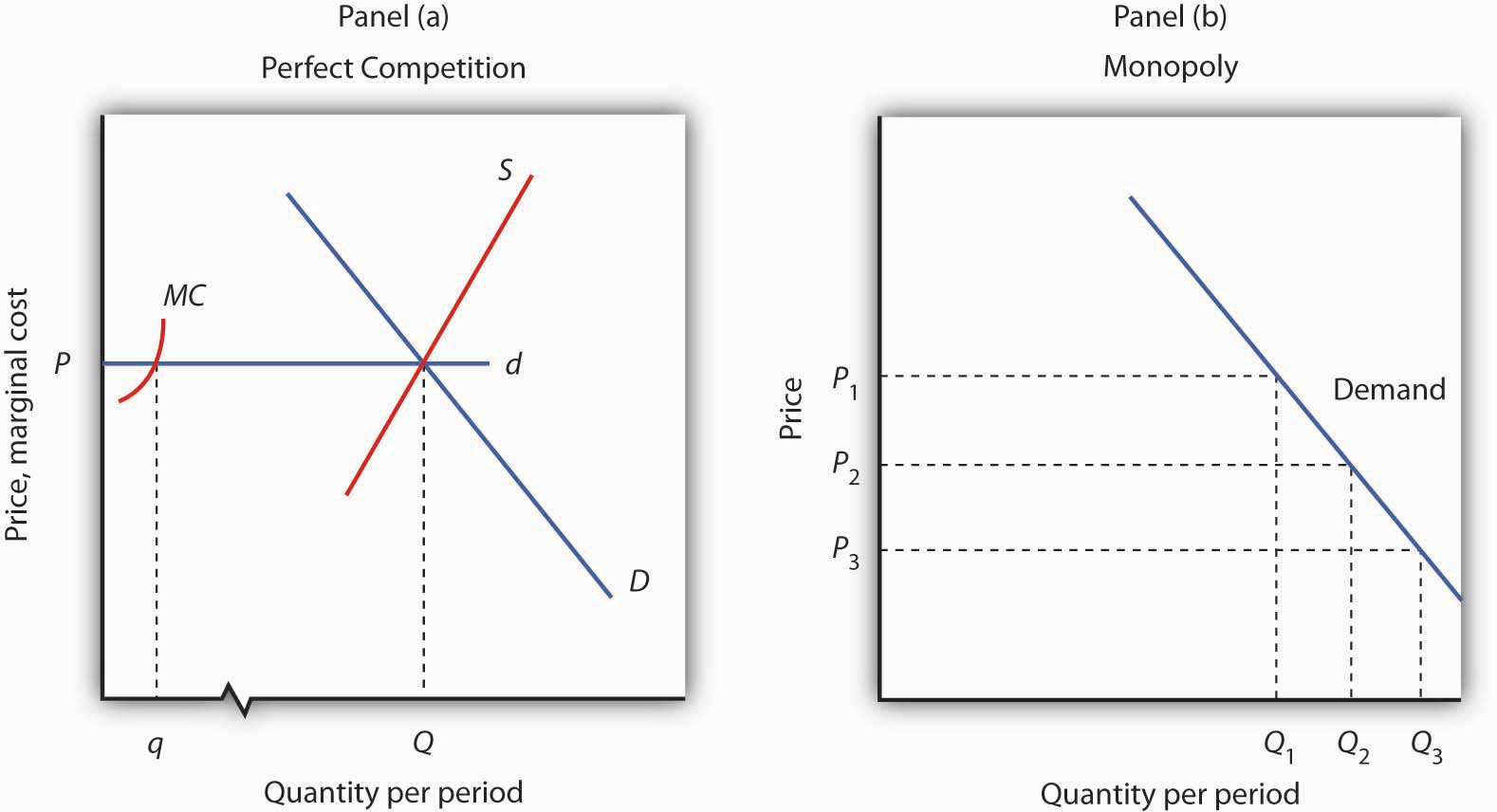
My 60ish second explanation of how to identify the elastic and inelastic range of the demand curve for a monopoly. A monopolist seeking to maximise profits will never be on the inelastic part of the demand curve E 1 which is why elasticity will always be such as E 1. Clearly marginal revenue equals zero if the price elasticity equals one. The Price Elasticity of demand is inversely related to excess capacity in the monopolistic competitive market Discuss. This does not change the revenue.
 Source: courses.byui.edu
Source: courses.byui.edu
Let us now establish the proposition that monopoly equilibrium will occur at a point where the demand for the product is relatively elasticThe proposition may be established easily with the help of the relation between AR p MR and e e is the numerical coefficient of price-elasticity of demand. P MCP 1e. A monopolist seeking to maximise profits will never be on the inelastic part of the demand curve E 1 which is why elasticity will always be such as E 1. So the equilibrium price and quantity is q 2 and p 2 23 for the consumer. This demand equation implies the demand schedule.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The equation can be further expanded to. Depending on which one there is another elasticity inside. If demand is unit elastic then 1 price cut increase the quantity sold by 1. Let us now establish the proposition that monopoly equilibrium will occur at a point where the demand for the product is relatively elasticThe proposition may be established easily with the help of the relation between AR p MR and e e is the numerical coefficient of price-elasticity of demand. 20 - 6Q 2 10 5Q 2 or Q Q 2 091.
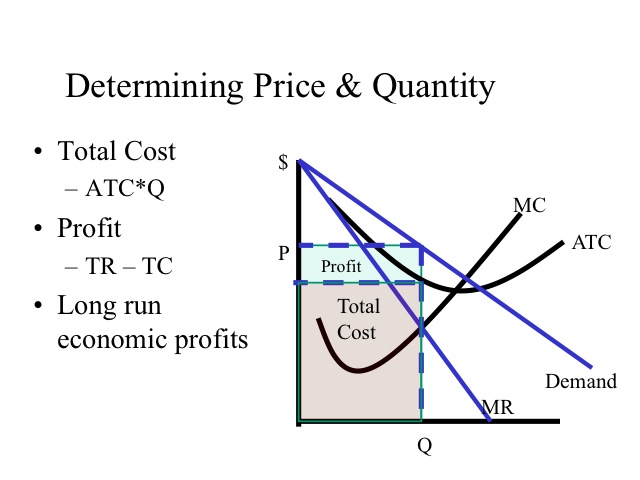 Source: courses.byui.edu
Source: courses.byui.edu
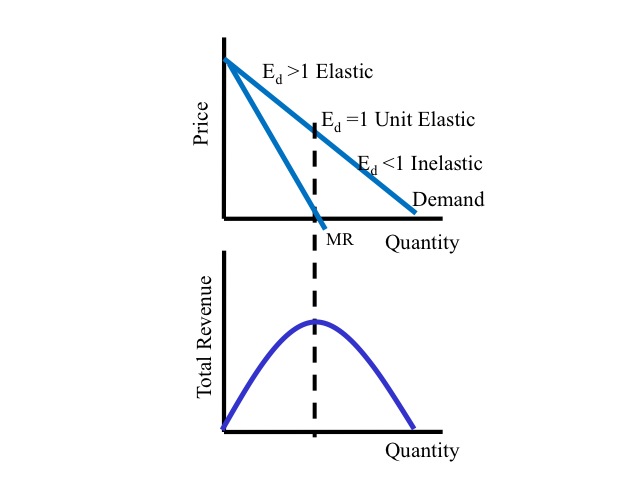
1 1 1 2 2 1 2 1 1 2 2 1 ηη η ηη η η η P P Price is lower in the market with the higher demand elasticity. 1 if Ed is large the firm has less market power and a small markup 2 if Ed is small the firm has more market power and a large markup. PED change in the quantity demanded change in price. Unit Elastic MR 0 R unchanged. Clearly marginal revenue equals zero if the price elasticity equals one.
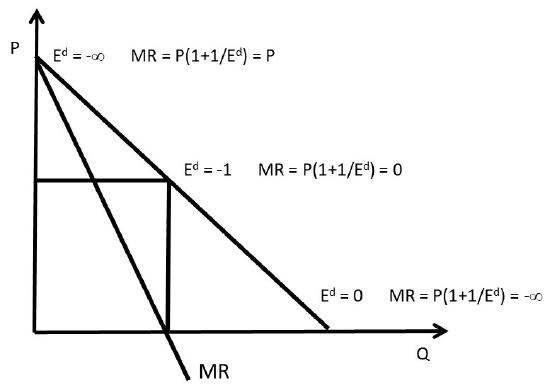 Source: socialsci.libretexts.org
Source: socialsci.libretexts.org
Next divide and multiply by P. This demand equation implies the demand schedule shown in Figure 104 Demand Elasticity and Total Revenue. But not within this inelastic demand there is an elastic and inelastic portion. According to the above equation this mark-up over price is equal to inverse of the absolute value of the price elasticity of demand for the. That is 1.
 Source: learneconomicsonline.com
Source: learneconomicsonline.com
P 83 which is equal to 2 23 which is higher than our cost to the monopolist which was 2. When MR is positive the demand is elastic. Let us now establish the proposition that monopoly equilibrium will occur at a point where the demand for the product is relatively elasticThe proposition may be established easily with the help of the relation between AR p MR and e e is the numerical coefficient of price-elasticity of demand. This demand equation implies the demand schedule shown in Figure 104 Demand Elasticity and Total Revenue. This does not change the revenue.
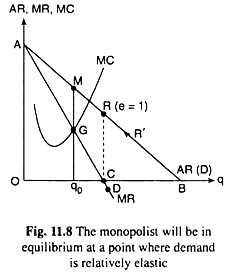 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
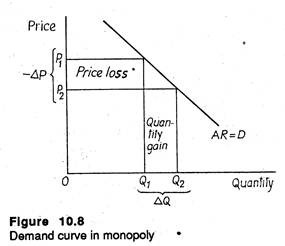
But not within this inelastic demand there is an elastic and inelastic portion. As the price is endogenous in the case of monopoly the price elasticity of supply is not defined unless you have some exogenous variable shifting the price. Q1 is the final quantity. Lerners index of monopoly power according to which degree of monopoly is given by. 1 if Ed is large the firm has less market power and a small markup 2 if Ed is small the firm has more market power and a large markup.
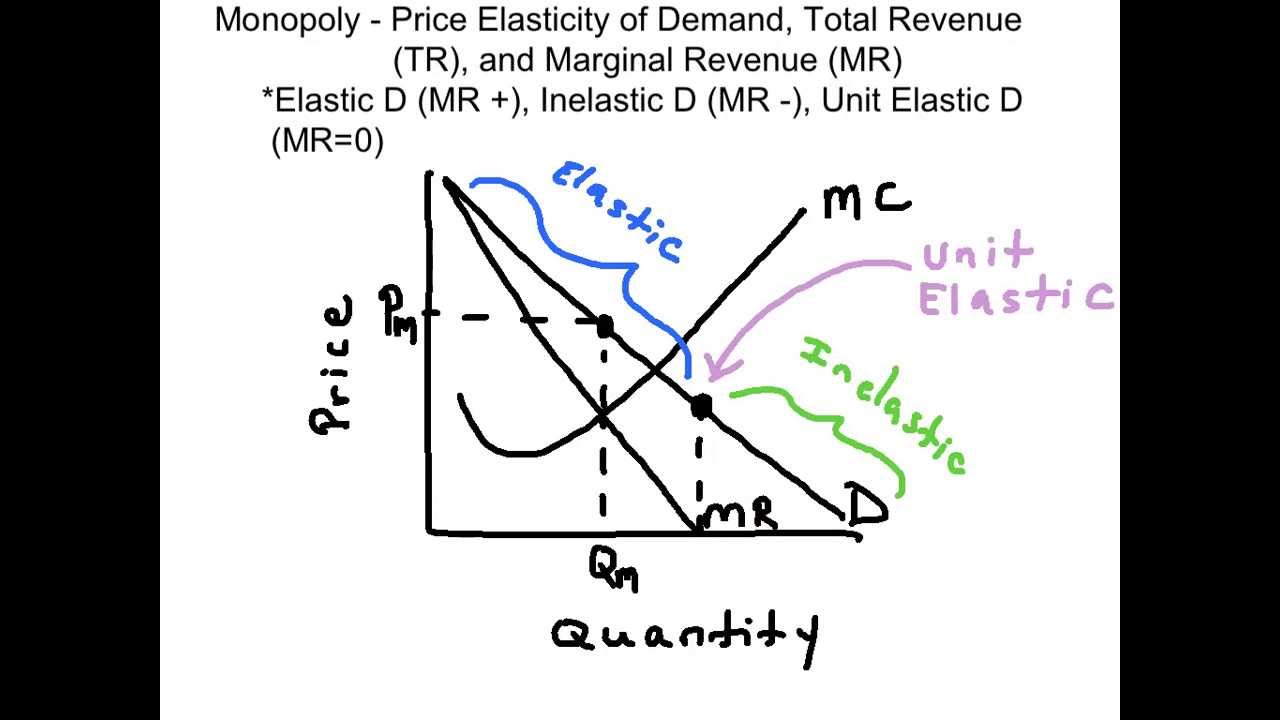 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Depending on which one there is another elasticity inside. Price is determined by substituting the profit-maximizing quantity into the demand equation. This does not change the revenue. The relationship between the monopolists marginal revenue and price ie average revenue is reflected in the price elasticity of the industry demand curveSince PP 1 we can write equation 1 as. Price Elasticity of Demand and Price Mark-Up.
 Source: atlas101.ca
Source: atlas101.ca
The Price Elasticity of demand is inversely related to excess capacity in the monopolistic competitive market Discuss. Secondly when elasticity of demand is low the second expression has high absolute. Q 10 P Q 10 P. That is 1. PED change in the quantity demanded change in price.
 Source: courses.byui.edu
Source: courses.byui.edu
Elasticity between monopoly and perfect competition and 2. For instance if the inverse output demand function is pPyz where z denotes an exogenous variable population size aggregate unemployment rate etc then it is possible to compute the elasticity even in the. As the price is endogenous in the case of monopoly the price elasticity of supply is not defined unless you have some exogenous variable shifting the price. Monopoly Curran S Economics Pocket book Monopoly Policonomics Elasticity Of Demand Marginal Income Youtube Econ 150 Microeconomics Monopoly Revenue Maximization Nonlinear Fixed Elasticity Demand Youtube Managerial Economics The Relationship Between Demand Worth And Income In A Monopoly Dummies Marginal Income And Worth Elasticity Of. This demand equation implies the demand schedule.
 Source: dummies.com
Source: dummies.com
If the monopolist knows his marginal cost MC and price elasticity of demand E p it should set price P such that. Unit Elastic MR 0 R unchanged. M R P Q Q P P P 1 E d P P P 1 1 E d This is a useful equation for a monopoly as it links the price elasticity of demand with the price that maximizes profits. P MCP 1E p. P 20 30 91 17.
 Source: kstatelibraries.pressbooks.pub
Source: kstatelibraries.pressbooks.pub
Demand curve we know that the marginal revenue curve has the same vertical intercept but twice the slope or MR 20 - 6Q 2. Where ηi is absolute value of elasticity of demand From previous rule MR1 MR2 so P11 1η1 P21 1η2 which gives 1 1. Where P MCP is the mark-up over marginal cost as a proportion of price. P MCP 1E p. Since elasticity of demand is negative in most cases the second expression on the right-hand side is negative which means that marginal revenue is less than price P.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
P MCP 1e. So the equilibrium price and quantity is q 2 and p 2 23 for the consumer. It means that marginal revenue of a monopolist equals price P plus the price divided by elasticity of demand. When MR is positive the demand is elastic. Explains why monopolist produces on the elastic region of demand curve.
 Source: freeeconhelp.com
Source: freeeconhelp.com
Q 10 P Q 10 P. 1 if Ed is large the firm has less market power and a small markup 2 if Ed is small the firm has more market power and a large markup. M R P Q Q P P P 1 E d P P P 1 1 E d This is a useful equation for a monopoly as it links the price elasticity of demand with the price that maximizes profits. Let us now establish the proposition that monopoly equilibrium will occur at a point where the demand for the product is relatively elasticThe proposition may be established easily with the help of the relation between AR p MR and e e is the numerical coefficient of price-elasticity of demand. That is 1.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
P MCP 1E p. Elasticity between monopoly and perfect competition and 2. P 20 30 91 17. According to the above equation this mark-up over price is equal to inverse of the absolute value of the price elasticity of demand for the. Demand curve we know that the marginal revenue curve has the same vertical intercept but twice the slope or MR 20 - 6Q 2.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
This demand equation implies the demand schedule. If demand is unit elastic then 1 price cut increase the quantity sold by 1. This demand equation implies the demand schedule. As the price is endogenous in the case of monopoly the price elasticity of supply is not defined unless you have some exogenous variable shifting the price. My 60ish second explanation of how to identify the elastic and inelastic range of the demand curve for a monopoly.
 Source: studypug.com
Source: studypug.com
Price Elasticity of Demand and Price Mark-Up. Q1 is the final quantity. Next divide and multiply by P. That is 1. Explains why monopolist produces on the elastic region of demand curve.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Secondly when elasticity of demand is low the second expression has high absolute. The Price Elasticity of demand is inversely related to excess capacity in the monopolistic competitive market Discuss. For a monopoly that has a price elasticity equal to -2 P 2 MC. The expression shows that to maximise profit the price mark-up should equal the inverse of the demand elasticity. P MCP 1e.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title how to calculate elasticity of demand for monopoly by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.