Your How do we show an increase in supply graphically images are ready. How do we show an increase in supply graphically are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the How do we show an increase in supply graphically files here. Download all free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for how do we show an increase in supply graphically images information connected with to the how do we show an increase in supply graphically topic, you have come to the ideal blog. Our site frequently gives you suggestions for downloading the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video content and images that fit your interests.
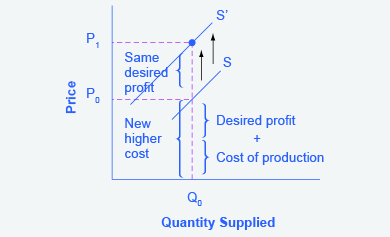
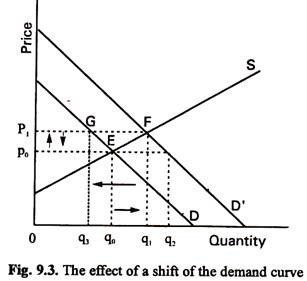
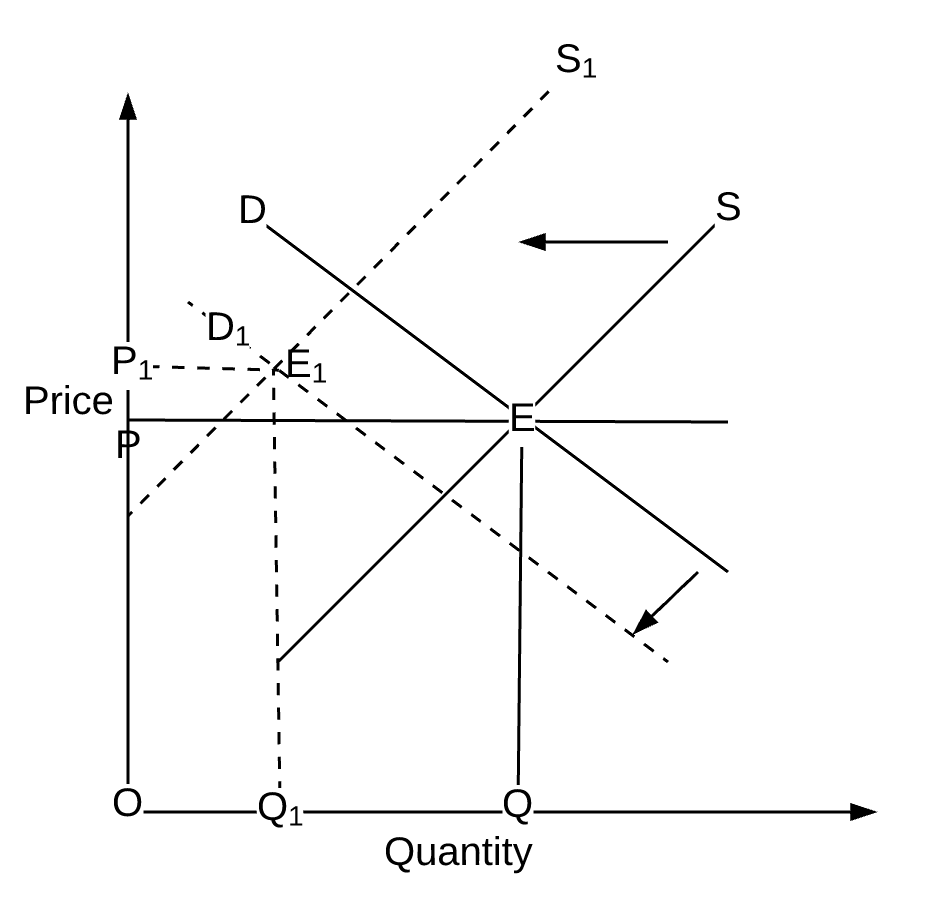
How Do We Show An Increase In Supply Graphically. As a result of the higher manufacturing costs the. The graph shows supply curve S sub 0 as the original supply curve. In other words an excess of supply of q 0 q 2 EH develops at the original price p 0. By keeping the price the same on both supply curves we can see that a downward shift in the supply curve an increase in supply causes the quantity supplied to increase.
The equations above correspond to the supply curve shown earlier. It may be due to the change in the price of related goods income taste and preference of consumers etc. How do we graph a change in supply. Supply curve S sub 1 represents a shift based on decreased supply. The following supply curve graph tracks the relationship between supply demand and the price of modern-day HDTVs. As the price of a given commodity increases.
I Increase in Supply Shift to the Right.
Five new sellers enter a market that previously had seven and begin producing a good. Supply curve S sub 2 represents a shift based on increased supply. In this example at a price of 20000 the quantity supplied decreases from 18 million on the original supply curve S 0 to 165 million on the supply curve S 1 which is labeled as point L. How do we graph a change in supply. The graph shows supply curve S sub 0 as the original supply curve. In this example at a price of 20000 the quantity supplied decreases from 18 million on the original supply curve S 0 to 165 million on the supply curve S 1 which is labeled as point L.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
The video discusses several factors that could lead to a change in supply. Figure 2 Interactive Graph. In most cases we wont be looking at consumer surplus and producer surplus in relation to an arbitrary price. We know that a supply curve shows the minimum price a firm will accept to produce a given quantity of output. The graph shows supply curve S sub 0 as the original supply curve.
 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
The supply curve is the visual representation of the law of supply. Supply curve S sub 2 represents a shift based on increased supply. Draw a graph of a supply curve for pizza. How do we graph a change in supply. A decrease in supply is shown as a shift to the left.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
The supply curve is the visual representation of the law of supply. The supply curve will move upward from left to right which expresses the law of supply. In this example at a price of 20000 the quantity supplied decreases from 18 million on the original supply curve S 0 to 165 million on the supply curve S 1 which is labeled as point L. We know that a supply curve shows the minimum price a firm will accept to produce a given quantity of output. A decrease in supply is shown as a shift to the left.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
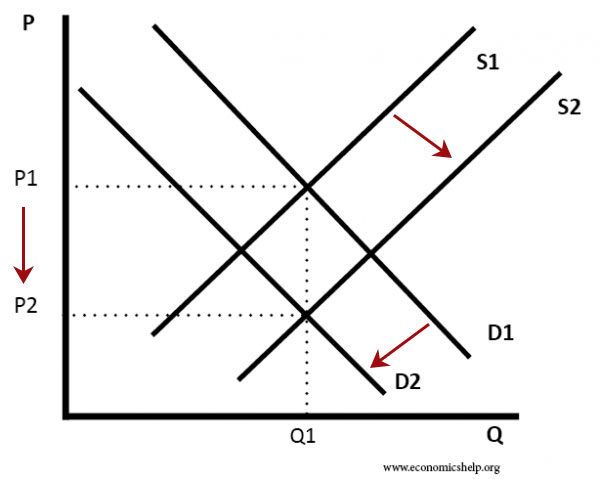
I Increase in Supply Shift to the Right. If all other things are unchanged what happens to the supply curve for DVD rentals if there is a an increase in wages paid to DVD rental store clerks b an increase in the price of DVD rentals or c an increase in the number of DVD rental stores. The point on the price axis is where the quantity demanded equals zero or where 0-3 32P. The equations above correspond to the supply curve shown earlier. Supply curve S sub 2 represents a shift based on increased supply.
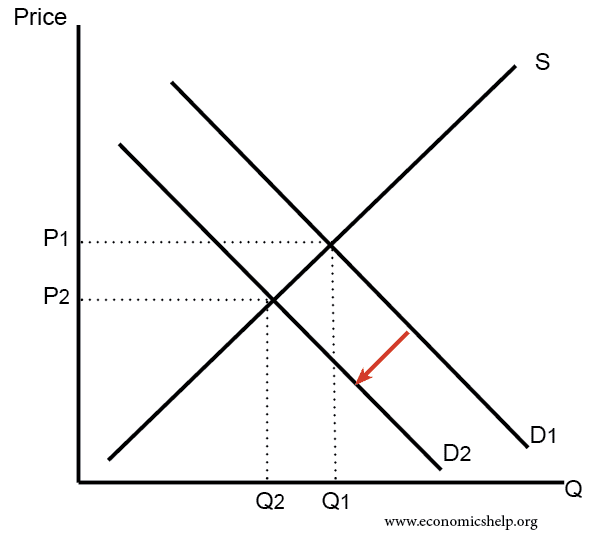 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
A Demand Curve is a diagrammatic illustration reflecting the price of a product or service and its quantity in demand in the market over a given period. An increase or decrease in market supply can cause the entire supply curve to shift to the right. How do we show an increase in demand graphically. The point on the price axis is where the quantity demanded equals zero or where 0-3 32P. What happens to the supply curve when the cost of production goes up.
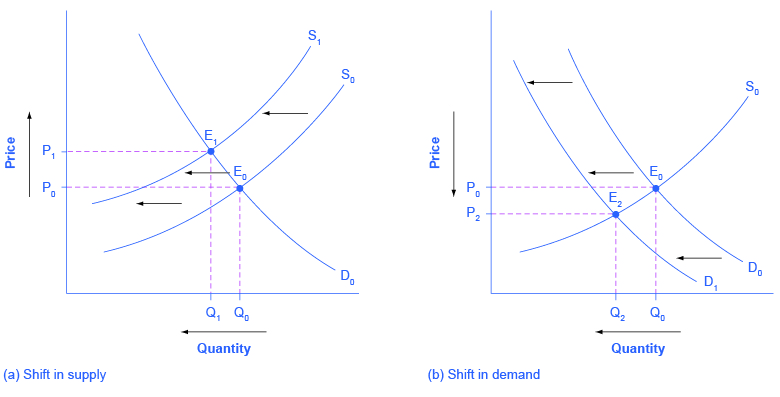 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
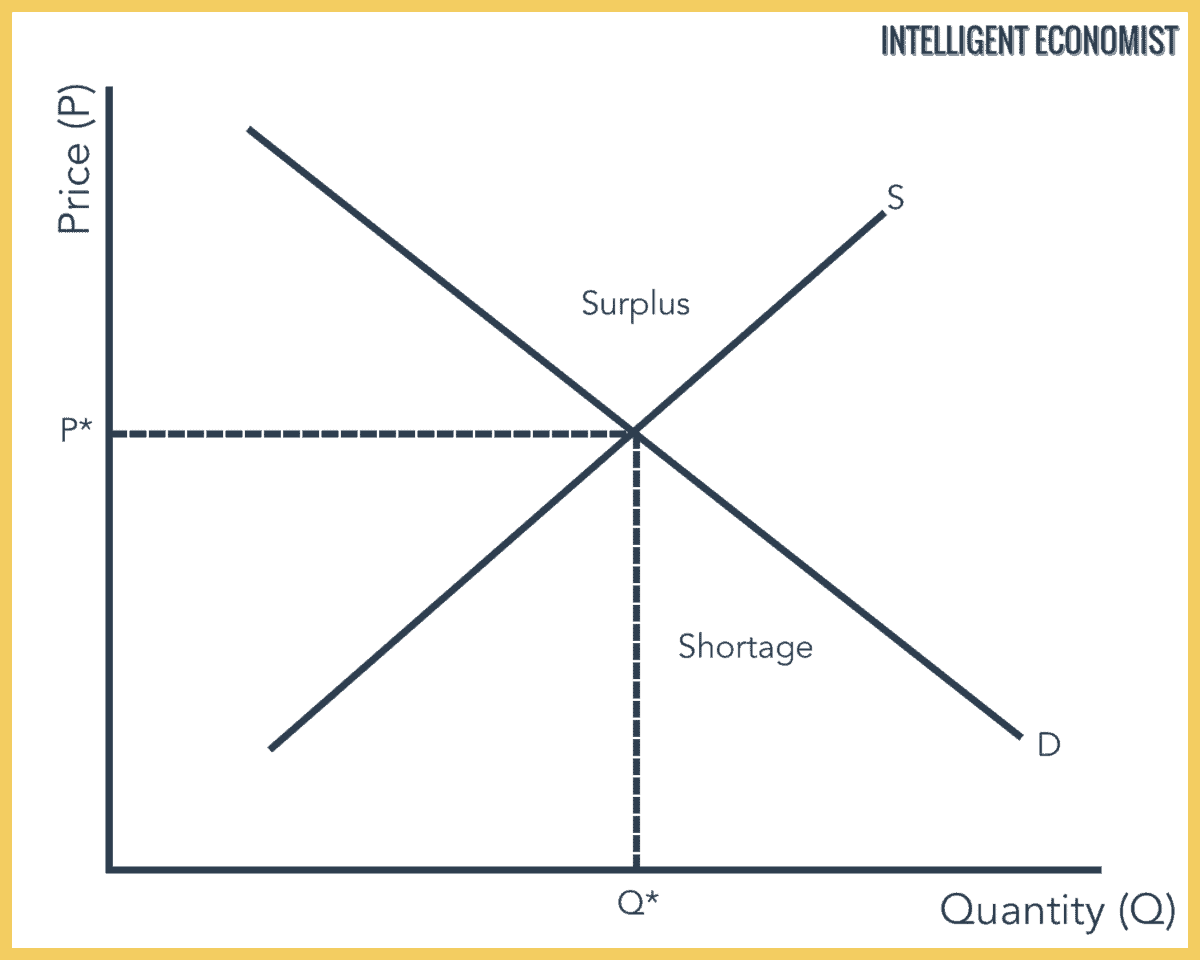
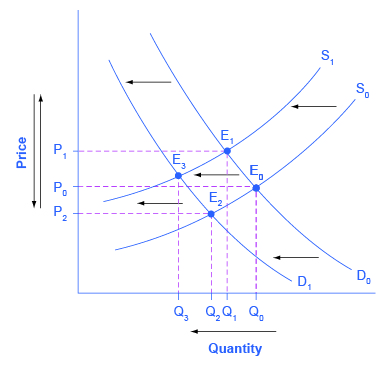
A decrease in supply is shown as a shift to the left. Instead we identify a market outcome usually an equilibrium price and quantity and then use that to identify consumer surplus and producer surplus. This can happen due to many factors that come under either shift or increase in demand supply or both. We can show this graphically as a leftward shift of supply from S 0 to S 1 which indicates that at any given price the quantity supplied decreases. In most cases we wont be looking at consumer surplus and producer surplus in relation to an arbitrary price.
 Source: investopedia.com
Source: investopedia.com
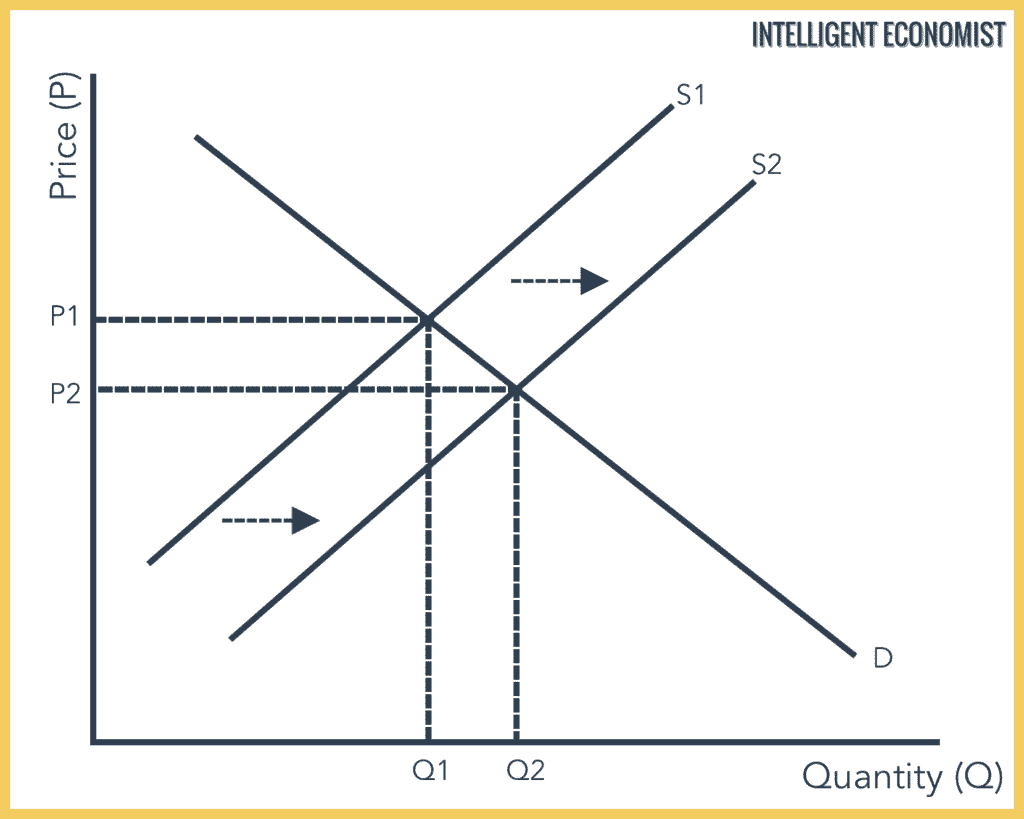
University of California Merced ECONOMICS 11. Where there were previously 7 sellers and 5 new sellers enters the market its effect on the market will be that the supply curve will shift to the right as shown in the figure below. This can happen due to many factors that come under either shift or increase in demand supply or both. If other factors relevant to supply do change then the entire supply curve will shift. The following supply curve graph tracks the relationship between supply demand and the price of modern-day HDTVs.
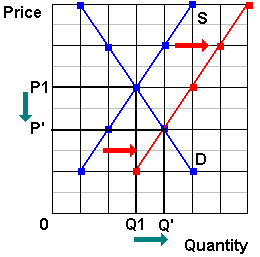 Source: www2.harpercollege.edu
Source: www2.harpercollege.edu
The video discusses several factors that could lead to a change in supply. Draw a graph of a supply curve for pizza. How do we show an increase in demand graphically. Panel b of Figure 2512 An Increase in the Money Supply shows an economy with a money supply of M which is in equilibrium at an interest rate of r 1. Usually the demand curve diagram comprises X and Y axis where the former represents the price of the service or product and the latter shows the quantity of the said entity in demand.
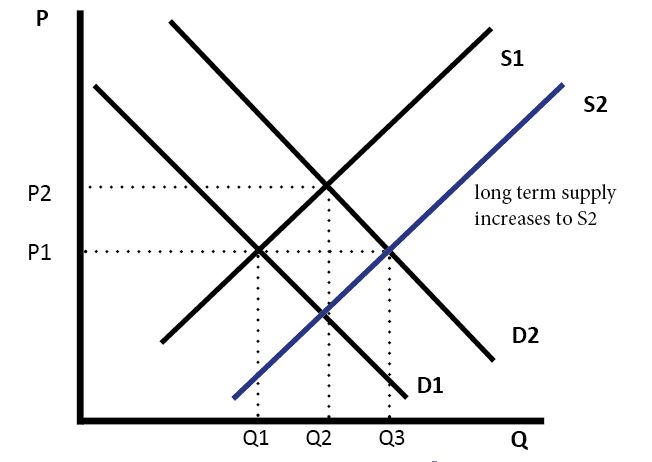 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
A Demand Curve is a diagrammatic illustration reflecting the price of a product or service and its quantity in demand in the market over a given period. If all other things are unchanged what happens to the supply curve for DVD rentals if there is a an increase in wages paid to DVD rental store clerks b an increase in the price of DVD rentals or c an increase in the number of DVD rental stores. We can show this graphically as a leftward shift of supply from S 0 to S 1 which indicates that at any given price the quantity supplied decreases. In most cases we wont be looking at consumer surplus and producer surplus in relation to an arbitrary price. Shifts in Aggregate Supply.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Change in supply includes an increase or decrease in supply. Students who viewed this also studied. Pick a quantity like Q 0. This means that quantity supplied goes up with an increase in supply — as long as price remains the same — which intuitively makes sense. A supply curve shows how quantity supplied will change as the price rises and falls assuming ceteris paribus so that no other economically relevant factors are changing.
 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
By keeping the price the same on both supply curves we can see that a downward shift in the supply curve an increase in supply causes the quantity supplied to increase. I Increase in Supply Shift to the Right. Students who viewed this also studied. A decrease in supply is shown as a shift to the left. The following supply curve graph tracks the relationship between supply demand and the price of modern-day HDTVs.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
This video shows how to graph a change in supply by shifting the supply curve. The equations above correspond to the supply curve shown earlier. This preview shows page 1 - 2 out of 2 pages. In this example 50-inch HDTVs are being sold for 475. They never seem to be static and are always fluctuating.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
As the price falls to the new equilibrium level the quantity of coffee demanded increases to 30 million pounds of coffee per month. Students who viewed this also studied. If other factors relevant to supply do change then the entire supply curve will shift. Pick a quantity like Q 0. Higher prices for key inputs shifts AS to the left.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
This video shows how to graph a change in supply by shifting the supply curve. In this example at a price of 20000 the quantity supplied decreases from 18 million on the original supply curve S 0 to 165 million on the supply curve S 1 which is labeled as point L. As the price of a given commodity increases. Supply curve S sub 1 represents a shift based on decreased supply. In the case of a competitive free market the market equilibrium is located at the intersection of the supply.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
As the price falls to the new equilibrium level the quantity of coffee demanded increases to 30 million pounds of coffee per month. Thus a graphical representation of market equilibrium for gold would always keep changing. What happens to the supply curve when the cost of production goes up. Supply curve S sub 1 represents a shift based on decreased supply. Students who viewed this also studied.
 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
This can happen due to many factors that come under either shift or increase in demand supply or both. By keeping the price the same on both supply curves we can see that a downward shift in the supply curve an increase in supply causes the quantity supplied to increase. A decrease in supply is shown as a shift to the left. This video shows the effect of an increase in supply or a decrease in supply on equilibrium price and quantityTo see how revenue is calculated watch here h. Pick a quantity like Q 0.
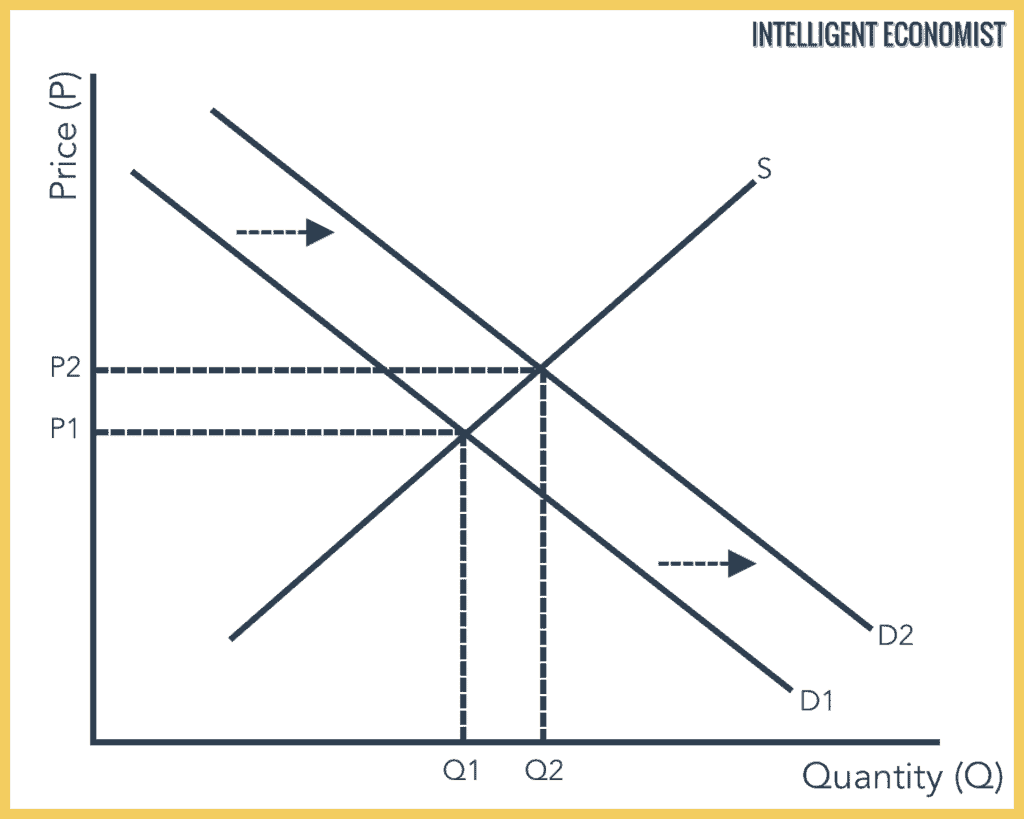 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Now suppose the bond purchases by the Fed as shown in Panel a result in an increase in the money supply to M. In this example at a price of 20000 the quantity supplied decreases from 18 million on the original supply curve S 0 to 165 million on the supply curve S 1 which is labeled as point L. Increase shift to the right in supply. The video discusses several factors that could lead to a change in supply. Supply curve S sub 1 represents a shift based on decreased supply.
 Source: investopedia.com
Source: investopedia.com
In this example at a price of 20000 the quantity supplied decreases from 18 million on the original supply curve S 0 to 165 million on the supply curve S 1 which is labeled as point L. A Demand Curve is a diagrammatic illustration reflecting the price of a product or service and its quantity in demand in the market over a given period. Usually the demand curve diagram comprises X and Y axis where the former represents the price of the service or product and the latter shows the quantity of the said entity in demand. It may be due to the change in the price of related goods income taste and preference of consumers etc. The supply curve is the visual representation of the law of supply.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title how do we show an increase in supply graphically by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






