Your Elasticity calculations economics images are available. Elasticity calculations economics are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Download the Elasticity calculations economics files here. Get all royalty-free photos.
If you’re looking for elasticity calculations economics images information linked to the elasticity calculations economics interest, you have come to the right site. Our site frequently gives you suggestions for refferencing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly search and find more informative video articles and graphics that match your interests.
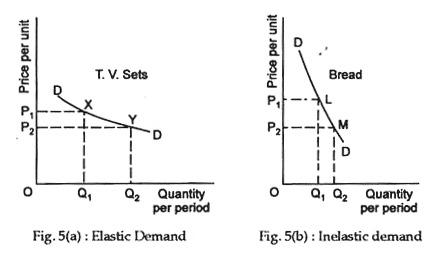
Elasticity Calculations Economics. We divide 2050 04 40. Get help with your Elasticity economics homework. In Figure 41a we were given two points and looked at elasticity as movements along a curve. For the arc elasticity method we calculate the price elasticity of demand using the average value of price barP and the average value of quantity demanded barQ.
 Price Income And Cross Elasticities Of Demand Edexcel Economics Revision From edexceleconomicsrevision.com
Price Income And Cross Elasticities Of Demand Edexcel Economics Revision From edexceleconomicsrevision.com
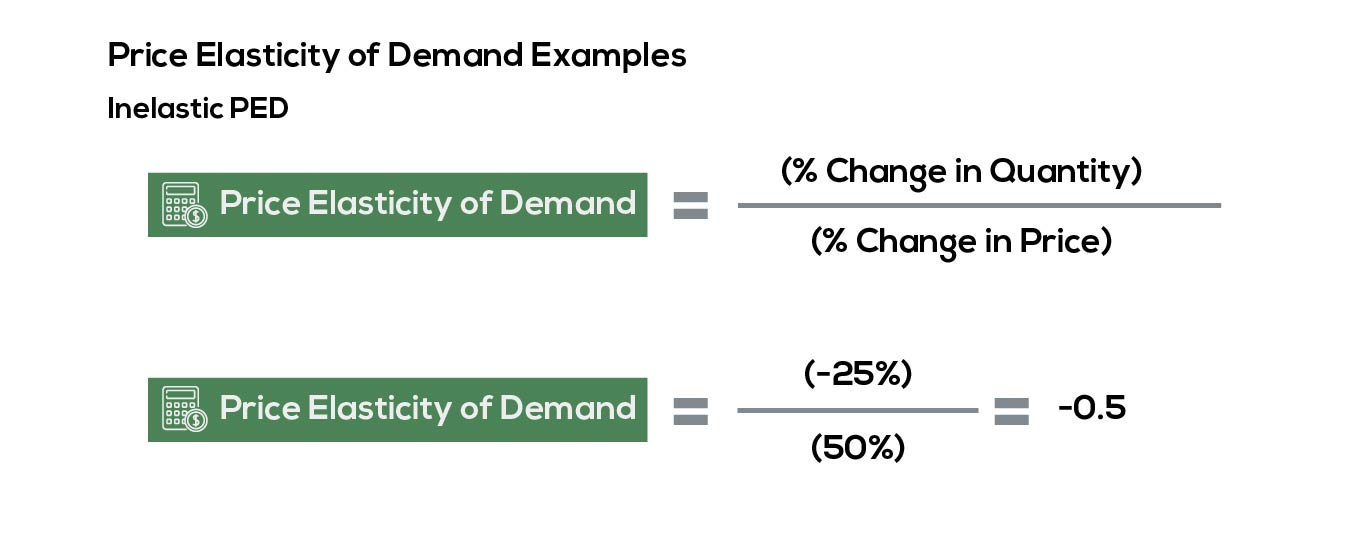
The formula for calculating elasticity is. Calculate the price elasticity of demand for this price change and calculate whether total revenue from the car park rises or falls. ¾If demand for a good is inelastic a higher price increases total revenue. That is by observing the relation between the price and the total outlay to know whether demand is relatively elastic e 1 or relatively inelastic e 1 or unitary elastic e 1. Table 41 shows how we calculate price elasticity The price increase is 20 percent with the resulting quantity decrease being 40 percent. Change in Price Price End Price Start Price Start.
Formula How to calculate Arc Elasticity.
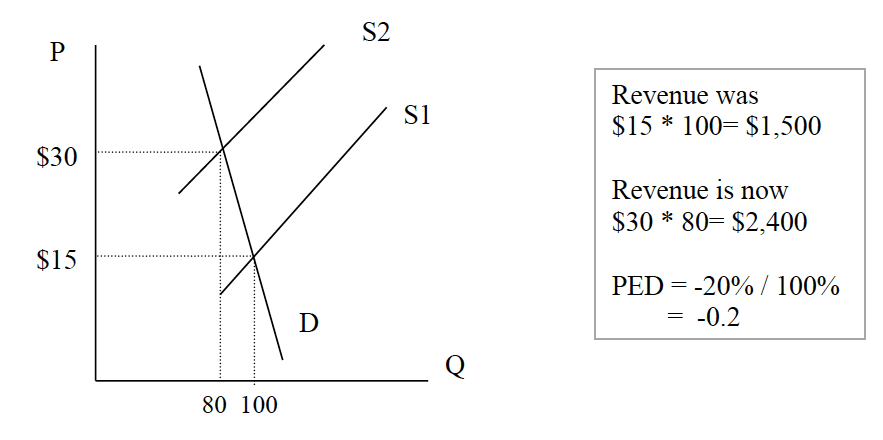
Elasticity Under Imperfect Competition D AR 0 Output Elastic Inelastic Unitary elasticity Perfectly Elastic Perfectly inelastic 0 Price Revenue PED ΔQdΔP At higher levels of the curve change in quantity going from 8 to 9 is 125 change in price going from 4 to 2 is -50 PED 12550 025. The price elasticity is greater than 1 and this good there- fore has price-elastic demand in the region from A to B. 4 2 8 9. PED change in the quantity demanded change in price. Formula How to calculate elasticity. PED is inelastic or -1 PED 0.
 Source: www2.palomar.edu
Source: www2.palomar.edu
Elasticity Economics Questions and Answers. To calculate elasticity instead of using simple percentage changes in quantity and price economists. Formula How to calculate Arc Elasticity. PED is the Price Elasticity of Demand. Change in Price P2 P1.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Table 41 shows how we calculate price elasticity The price increase is 20 percent with the resulting quantity decrease being 40 percent. The price elasticity of demand is evidently ED 4020 2. The price elasticity is greater than 1 and this good there- fore has price-elastic demand in the region from A to B. In such a case the decrease of the price is. Lastly if as price falls or rises the total outlay of the buyers remains constant then e 1.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
Elasticity and Total Revenue ¾If demand for a good is elastic an increase in price reduces total revenue. Q1 is the final quantity. Change in Price. Average Price P1 P2 2. In such a case when you decrease the price of the product the demand will increase but you will experience a drop in your overall revenue.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Displaystyletext Price Elasticity of Demandfrac text percent change in quantity text percent change in price Price Elasticity of. The average price is at the midpoint between the. Formula for Price Elasticity of Demand. To calculate a percentage we divide the change in quantity by initial quantity. The simplest way to apply the above two concepts in an equation is to simply divide the how much the band stretches the change in the length by the change in the force.
 Source: scielo.org.co
Source: scielo.org.co
Formula How to calculate Arc Elasticity. P r i c e E l a s t i c i t y o f D e m a n d p e r c e n t c h a n g e i n q u a n t i t y p e r c e n t c h a n g e i n p r i c e. Formula to calculate the price elasticity of demand. 51 THE PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND The Midpoint Method Percent change in price x 100 New price Initial price New Price Initial Price 2 To calculate the percentage change in the price divide the change in the price by the average price and then multiply by 100. In such a case the decrease of the price is.
 Source: penpoin.com
Source: penpoin.com
P r i c e E l a s t i c i t y o f D e m a n d p e r c e n t c h a n g e i n q u a n t i t y p e r c e n t c h a n g e i n p r i c e. If price rises from 50 to 70. The formula for calculating this economic indicator is. Table 41 shows how we calculate price elasticity The price increase is 20 percent with the resulting quantity decrease being 40 percent. ¾If demand for a good is inelastic a higher price increases total revenue.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Change in price 667 change in demand - 25 PED -25667 0375 ie. 41 Calculating Elasticity Mid-point Method. If price rises from 50 to 70. The four factors that affect price elasticity of demand are 1 availability of substitutes 2 if the good is. Formula for Price Elasticity of Demand.
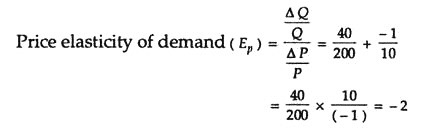 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Average Price P1 P2 2. We divide 2050 04 40. The term demand elasticity refers to the change in a products demand due to changes in other economic factors primarily consumer income and product price. Change in price 667 change in demand - 25 PED -25667 0375 ie. The formula for calculating this economic indicator is.
 Source: educba.com
Source: educba.com
Change in Price P2 P1. The price elasticity is greater than 1 and this good there- fore has price-elastic demand in the region from A to B. The three major forms of elasticity are price elasticity of demand cross-price elasticity of demand and income elasticity of demand. 51 THE PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND The Midpoint Method Percent change in price x 100 New price Initial price New Price Initial Price 2 To calculate the percentage change in the price divide the change in the price by the average price and then multiply by 100. Midpoint Elasticity Change in Quantity Average Quantity Change in Price Average Price Change in Quantity Q2 Q1.
 Source: investinganswers.com
Source: investinganswers.com
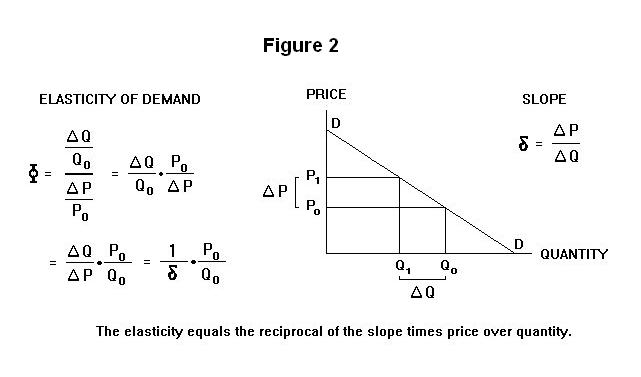
Midpoint Elasticity Change in Quantity Average Quantity Change in Price Average Price Change in Quantity Q2 Q1. Calculate the price elasticity of demand for this price change and calculate whether total revenue from the car park rises or falls. Elasticity Under Imperfect Competition D AR 0 Output Elastic Inelastic Unitary elasticity Perfectly Elastic Perfectly inelastic 0 Price Revenue PED ΔQdΔP At higher levels of the curve change in quantity going from 8 to 9 is 125 change in price going from 4 to 2 is -50 PED 12550 025. Lastly if as price falls or rises the total outlay of the buyers remains constant then e 1. The simplest way to apply the above two concepts in an equation is to simply divide the how much the band stretches the change in the length by the change in the force.
 Source: economics.utoronto.ca
Source: economics.utoronto.ca
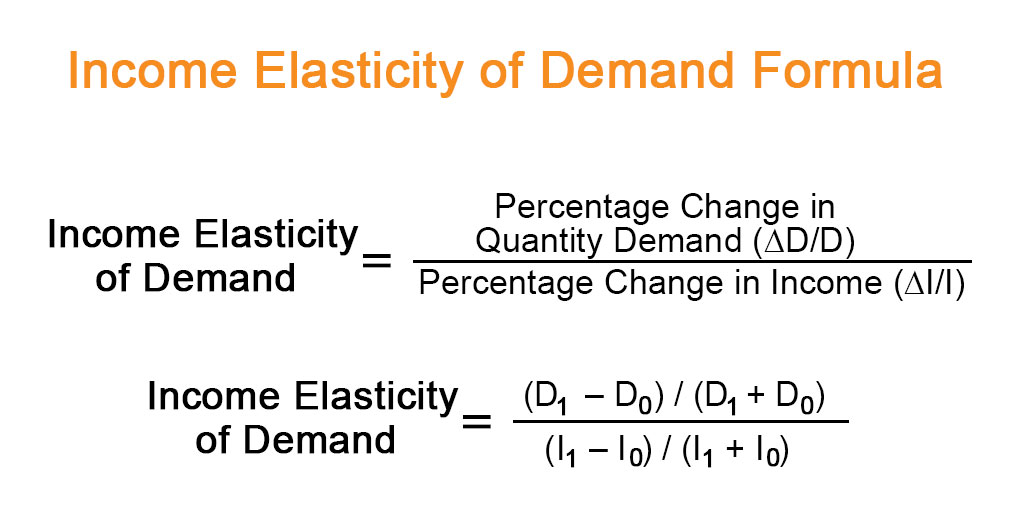
To calculate elasticity instead of using simple percentage changes in quantity and price economists. The three major forms of elasticity are price elasticity of demand cross-price elasticity of demand and income elasticity of demand. Midpoint Elasticity Change in Quantity Average Quantity Change in Price Average Price Change in Quantity Q2 Q1. Average Price P1 P2 2. We divide 2050 04 40.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The PED calculator employs the midpoint formula to determine the price elasticity of demand. How to calculate price elasticity of demand. If price rises from 50 to 70. Elasticity Definitions and Formulas. Elasticity is a general measure of the responsiveness of an economic variable in response to a change in another economic variable.
 Source: edexceleconomicsrevision.com
Source: edexceleconomicsrevision.com
Formula to calculate the price elasticity of demand. PED Q N - Q I Q N Q I 2 P N - P I P N P I 2 Where. Average Price P1 P2 2. Formula to calculate the price elasticity of demand. Elasticity Under Imperfect Competition D AR 0 Output Elastic Inelastic Unitary elasticity Perfectly Elastic Perfectly inelastic 0 Price Revenue PED ΔQdΔP At higher levels of the curve change in quantity going from 8 to 9 is 125 change in price going from 4 to 2 is -50 PED 12550 025.
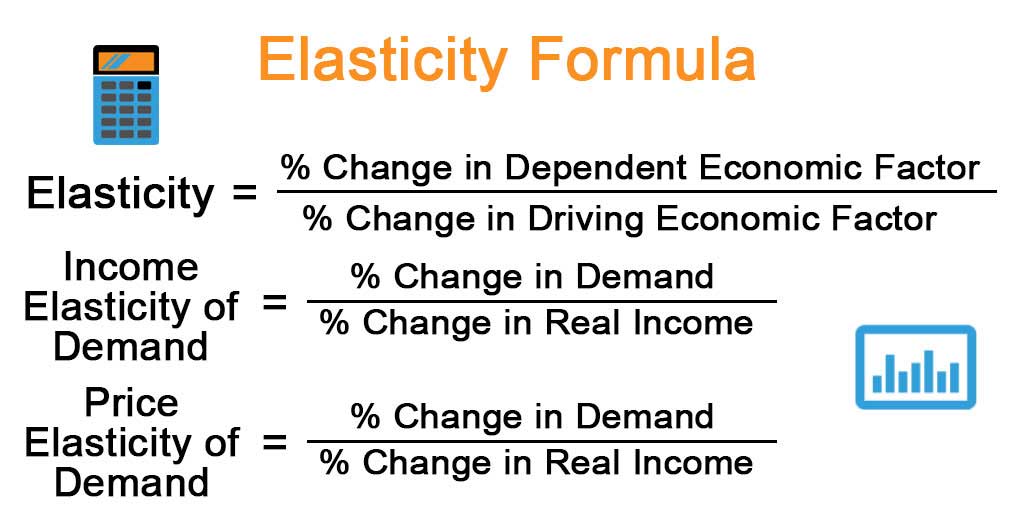 Source: educba.com
Source: educba.com
The three major forms of elasticity are price elasticity of demand cross-price elasticity of demand and income elasticity of demand. Access the answers to hundreds of Elasticity economics questions that are explained in a way that. Formula How to calculate elasticity. 51 THE PRICE ELASTICITY OF DEMAND The Midpoint Method Percent change in price x 100 New price Initial price New Price Initial Price 2 To calculate the percentage change in the price divide the change in the price by the average price and then multiply by 100. Demand is price inelastic Total revenue.
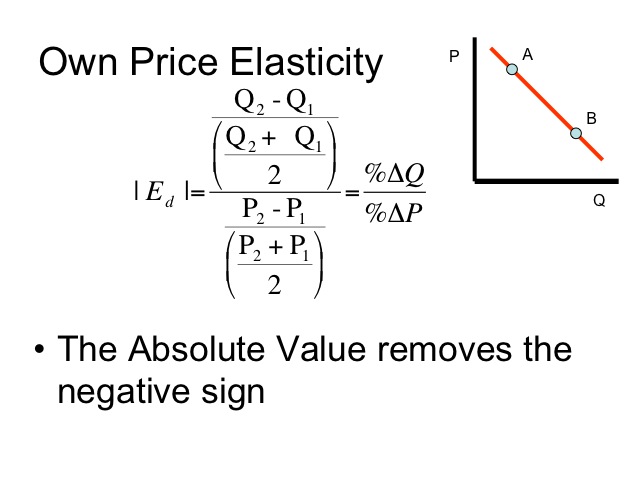 Source: courses.byui.edu
Source: courses.byui.edu
In such a case the decrease of the price is. 41 Calculating Elasticity Mid-point Method. The price elasticity is greater than 1 and this good there- fore has price-elastic demand in the region from A to B. The simplest way to apply the above two concepts in an equation is to simply divide the how much the band stretches the change in the length by the change in the force. Formula for Price Elasticity of Demand.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Elasticity Definitions and Formulas. Table 41 shows how we calculate price elasticity The price increase is 20 percent with the resulting quantity decrease being 40 percent. That is by observing the relation between the price and the total outlay to know whether demand is relatively elastic e 1 or relatively inelastic e 1 or unitary elastic e 1. Formula for Price Elasticity of Demand. The price elasticity is greater than 1 and this good there- fore has price-elastic demand in the region from A to B.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
To calculate a percentage we divide the change in quantity by initial quantity. Access the answers to hundreds of Elasticity economics questions that are explained in a way that. PED is the Price Elasticity of Demand. Elasticity Under Imperfect Competition D AR 0 Output Elastic Inelastic Unitary elasticity Perfectly Elastic Perfectly inelastic 0 Price Revenue PED ΔQdΔP At higher levels of the curve change in quantity going from 8 to 9 is 125 change in price going from 4 to 2 is -50 PED 12550 025. ¾If demand for a good is unit-elastic an increase in price does not change total revenue.
 Source: educba.com
Source: educba.com
The formula for calculating this economic indicator is. Formula How to calculate elasticity. Change in Quantity Quantity End Quantity Start Quantity Start. Sales effect Price effect. PED Q1 Q0 Q1 Q0 P1 P0 P1 P0 Q0 is the initial quantity.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title elasticity calculations economics by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.