Your Demand and supply curve after tax images are available in this site. Demand and supply curve after tax are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Demand and supply curve after tax files here. Download all royalty-free vectors.
If you’re looking for demand and supply curve after tax pictures information related to the demand and supply curve after tax topic, you have pay a visit to the ideal blog. Our website always provides you with suggestions for downloading the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly search and find more informative video articles and images that fit your interests.
Demand And Supply Curve After Tax. Vertical demand curve and an upward-sloping supply curve we can predict that a. Similarly the price the seller obtains falls but by less than the tax. And the demand for a good is given by Q_D 960 - 120P_D. While consumers may have other vacation choices sellers cant easily move their businesses.
 Negative Externailty Consumption Sugar Tax Economics Sugar Tax Tax From pinterest.com
Negative Externailty Consumption Sugar Tax Economics Sugar Tax Tax From pinterest.com
Rewrite the demand and supply equation as P 20 Q and P Q3. While consumers may have other vacation choices sellers cant easily move their businesses. And I must find the equilibrium quantity of the curves after the 2 tax has been taken into account for. In Figure 1a the supply is inelastic and the demand is elastic such as in the example of beachfront hotels. The price faced by consumers is 8 after the tax. The inverse demand curve or average revenue curve for the product of a perfectly competitive industry is give by p80-05Q where p is the.
If a new tax is enacted the demand curve may be expected to shift depending on the tax.
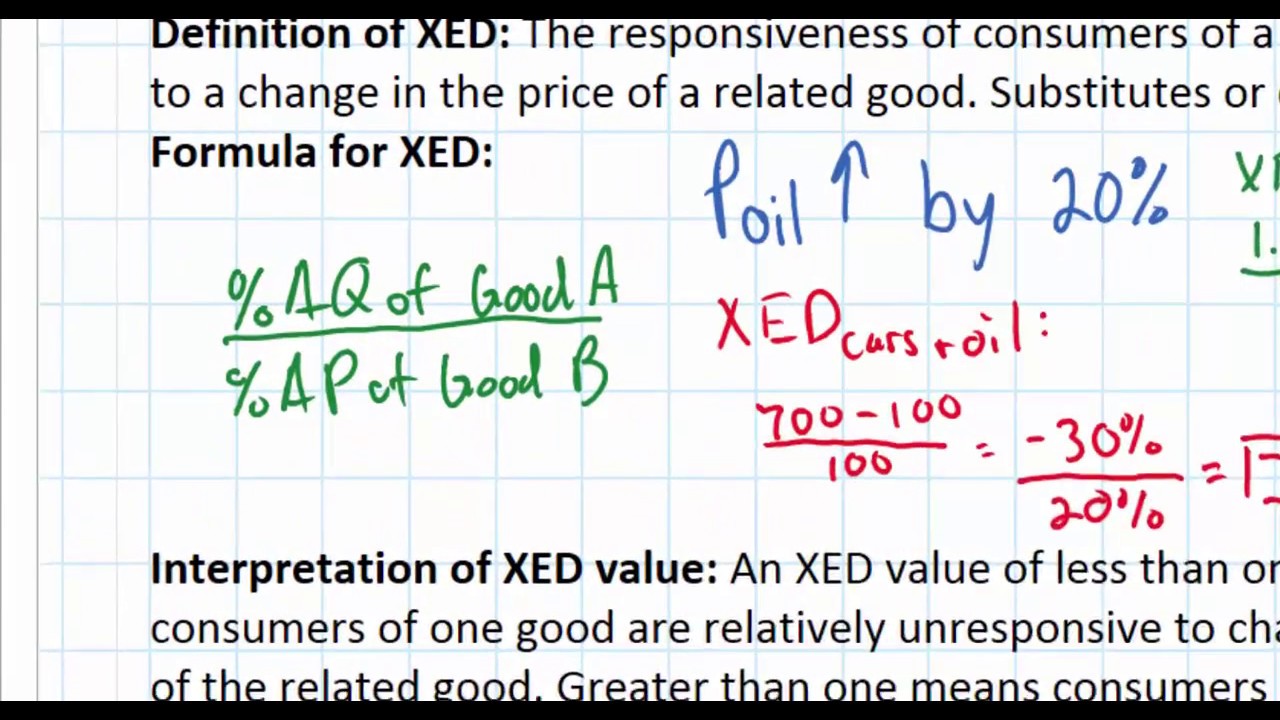
The vertical distance between the original and new supply curve is the amount of the tax. Hence the new equilibrium quantity after tax can be found from equating P Q3 4 and P 20 Q so Q3 4 20 Q which gives QT 12. Qs -30 10P. Taxes are among the market and regulatory conditions that define the demand curve. To consumers the tax increases the price of the good purchased moving them along the demand curve to a lower quantity demanded. The government decides to levy a tax of 2 per unit on the good to be paid by the seller.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
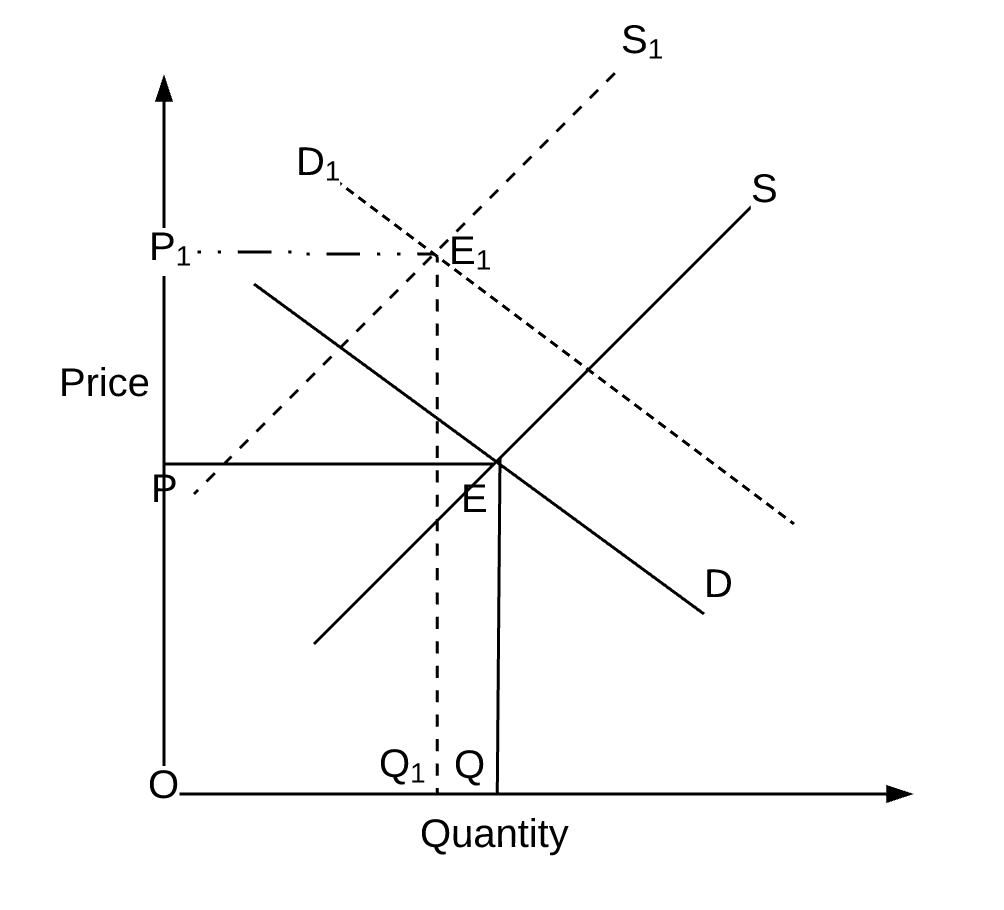
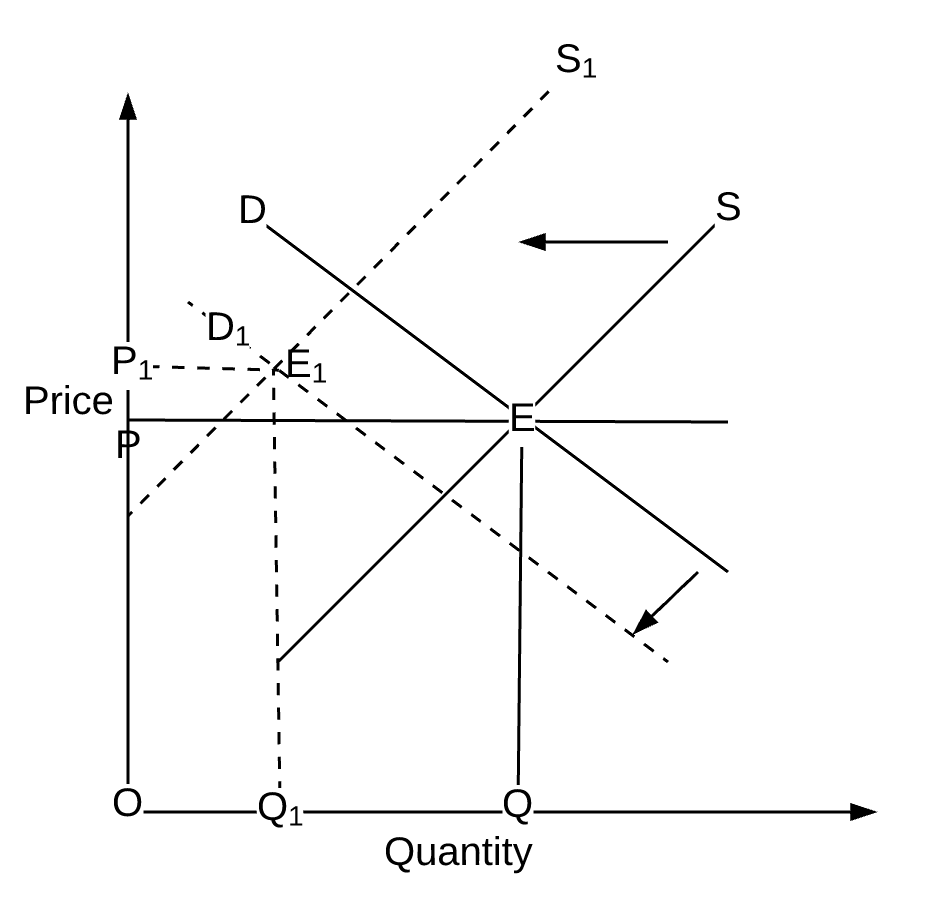
This intensive economics question goes over calculating equilibrium price and quantity then using those numbers to get consumer and producer surplus and finally implementing a tax to see how that will change the previous results. The demand curve because of the tax t. If a new tax is enacted the demand curve may be expected to shift depending on the tax. The new equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity is P_E1 6 Q_E1 14kg. After-tax S1 is the new supply curve and E1 is the new equilibrium.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
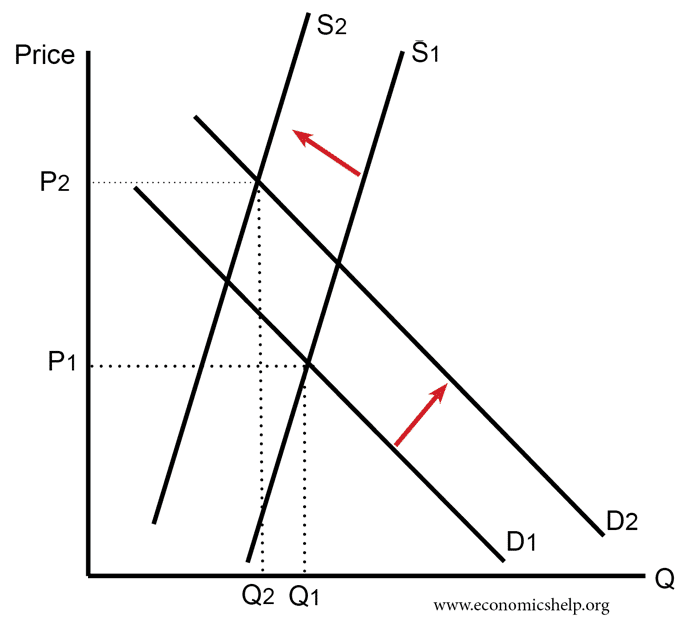
The new equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity is P_E1 6 Q_E1 14kg. Once you have had a go at the questions follow the link below to compare your answers. To consumers the tax increases the price of the good purchased moving them along the demand curve to a lower quantity demanded. Refer to the above figure in which S is the before-tax supply curve and S t is the supply curve after an excise tax is imposed. From the consideration of the graph we can see that after imposition of the tax the supply curve shifts up and to the left initial curve marked as S0 and the final one as S1.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
2 and reduce equilibrium output Refer to the figure in which S is the before-tax supply curve and St is the supply curve after an excise tax is imposed. The vertical distance between the original and new supply curve is the amount of the tax. And the demand for a good is given by Q_D 960 - 120P_D. Shifts from D to D. By introducing a tax the government essentially creates a wedge.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Therefore the price consumers pay and producers receive before the tax must be 2750 and the equilibrium quantity of pinckneys is 45. Shifts from D to D. Taxes are among the market and regulatory conditions that define the demand curve. With 4 tax on producers the supply curve after tax is P Q3 4. Vertical demand curve and an upward-sloping supply curve we can predict that a.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The price faced by consumers is 12 after the tax. A tax can be fully borne by consumers if. And a linear supply curve of the form. Using these demand and supply functions answer the following questions. In ugly-rose we can see that the consumers who have an inelastic demand loose a lot actually most of the total loss of surplus.
 Source: acqnotes.com
Source: acqnotes.com
As the tax affects supply the supply curve tends to shift upward thus establishing the new equilibrium with the same demand curve. Therefore the new price has to be established for the new supply curve equation and the new supply equation is equalized to demand equation to determine new equilibrium price. A tax on buyers is thought to shift the demand curve to the leftreduce consumer demandbecause the price of goods relative to their value to consumers has gone up. None of the above. The effect of the tax on the supply-demand equilibrium is to shift the quantity toward a point where the before-tax demand minus the before-tax supply is the amount of the tax.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
As the tax affects supply the supply curve tends to shift upward thus establishing the new equilibrium with the same demand curve. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. The government decides to levy a tax of 2 per unit on the good to be paid by the seller. And I must find the equilibrium quantity of the curves after the 2 tax has been taken into account for. A tax on buyers is thought to shift the demand curve to the leftreduce consumer demandbecause the price of goods relative to their value to consumers has gone up.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
AP is owned by the College Board which does not endorse this site or the above reviewStudy Questions1 Show supply demand with an equilibrium price and. In ugly-rose we can see that the consumers who have an inelastic demand loose a lot actually most of the total loss of surplus. A tax can be fully borne by consumers if. The new equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity is P_E1 6 Q_E1 14kg. While consumers may have other vacation choices sellers cant easily move their businesses.

With 4 tax on producers the supply curve after tax is P Q3 4. The tax size predicts the new level of quantity supplied which is reduced in comparison to the initial level. The price faced by consumers is 12 after the tax. 200 the vertical distance between the two supply curves 2. Therefore the price consumers pay and producers receive before the tax must be 2750 and the equilibrium quantity of pinckneys is 45.
 Source: assignmentexpert.com
Source: assignmentexpert.com
In Figure 1a the supply is inelastic and the demand is elastic such as in the example of beachfront hotels. A tax on buyers is thought to shift the demand curve to the leftreduce consumer demandbecause the price of goods relative to their value to consumers has gone up. Qs -30 10P. Due to the tax the new equilibrium price P1 is higher and the equilibrium quantity Q1 is lower. And the demand for a good is given by Q_D 960 - 120P_D.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
After-tax S1 is the new supply curve and E1 is the new equilibrium. A tax on buyers is thought to shift the demand curve to the leftreduce consumer demandbecause the price of goods relative to their value to consumers has gone up. And the demand for a good is given by Q_D 960 - 120P_D. A tax can be fully borne by consumers if. The variation of the surplus of each agents is quite telling.
 Source: sanandres.esc.edu.ar
Source: sanandres.esc.edu.ar
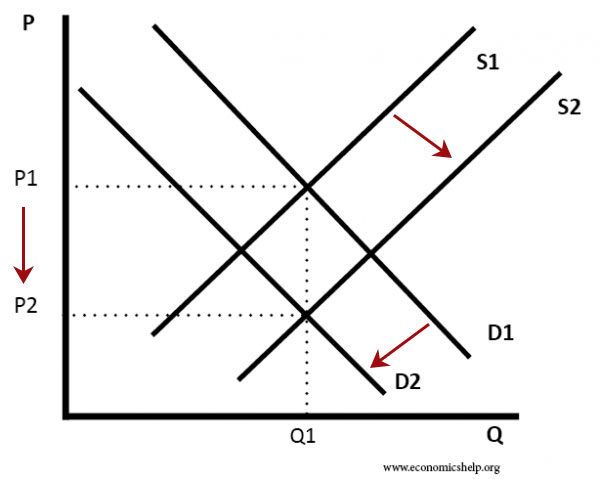
After tax the supply curve. The variation of the surplus of each agents is quite telling. Assume a linear demand function of the form. The more elastic the demand and supply curves the lower the tax revenue. The demand curve and shifted supply curve create a new equilibrium which is burdened by the tax.
 Source: pinterest.com
Source: pinterest.com
The price faced by consumers is 11 after the tax. Therefore the price consumers pay and producers receive before the tax must be 2750 and the equilibrium quantity of pinckneys is 45. Taxes on supply and demand The VAT on the suppliers will shift the supply curve to the left symbolizing a reduction in supply similar to firms facing higher input costs. Hence the new equilibrium quantity after tax can be found from equating P Q3 4 and P 20 Q so Q3 4 20 Q which gives QT 12. With 4 tax on producers the supply curve after tax is P Q3 4.
 Source: assignmentexpert.com
Source: assignmentexpert.com
2 and reduce equilibrium output Refer to the figure in which S is the before-tax supply curve and St is the supply curve after an excise tax is imposed. Therefore the price consumers pay and producers receive before the tax must be 2750 and the equilibrium quantity of pinckneys is 45. Hence the new equilibrium quantity after tax can be found from equating P Q3 4 and P 20 Q so Q3 4 20 Q which gives QT 12. The new equilibrium price and the equilibrium quantity is P_E1 6 Q_E1 14kg. 49 rows A specific tax will shift the supply curve upwards by 5.
 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
From the consideration of the graph we can see that after imposition of the tax the supply curve shifts up and to the left initial curve marked as S0 and the final one as S1. Before the tax is implemented the equilibrium price and quantity occur at the intersection of the demand and the supply curves. The variation of the surplus of each agents is quite telling. None of the above. If a new tax is enacted the demand curve may be expected to shift depending on the tax.
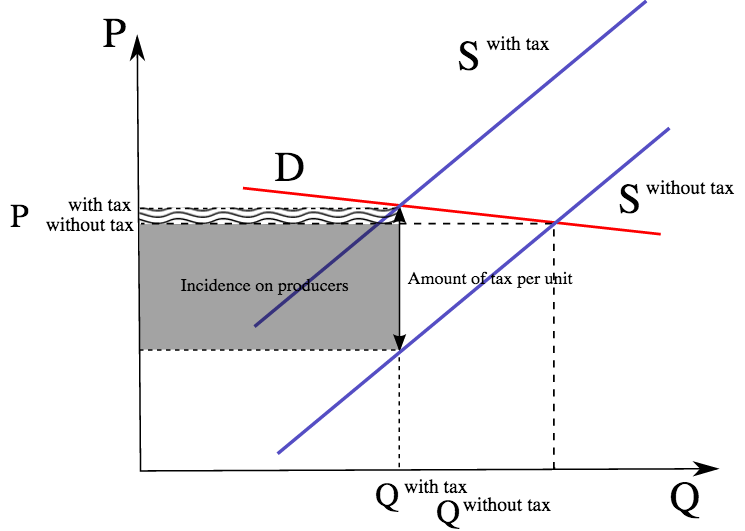
In Figure 1 a demand curve is added into this instance of competitive market. Calculating impact of a tax - example. This intensive economics question goes over calculating equilibrium price and quantity then using those numbers to get consumer and producer surplus and finally implementing a tax to see how that will change the previous results. A tax increases the price a buyer pays by less than the tax. In Figure 1 a demand curve is added into this instance of competitive market.
 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
After tax the supply curve. Taxes are among the market and regulatory conditions that define the demand curve. Due to the tax the new equilibrium price P1 is higher and the equilibrium quantity Q1 is lower. This intensive economics question goes over calculating equilibrium price and quantity then using those numbers to get consumer and producer surplus and finally implementing a tax to see how that will change the previous results. Price consumers pay after tax 3500.
 Source: tr.pinterest.com
Source: tr.pinterest.com
2 and reduce equilibrium output Refer to the figure in which S is the before-tax supply curve and St is the supply curve after an excise tax is imposed. Taxes on supply and demand The VAT on the suppliers will shift the supply curve to the left symbolizing a reduction in supply similar to firms facing higher input costs. Shifts from D to D. A tax can be fully borne by consumers if. 49 rows A specific tax will shift the supply curve upwards by 5.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site beneficial, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title demand and supply curve after tax by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.