Your Define logistic growth in biology images are ready. Define logistic growth in biology are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Define logistic growth in biology files here. Find and Download all free images.
If you’re looking for define logistic growth in biology pictures information connected with to the define logistic growth in biology topic, you have visit the ideal site. Our website frequently gives you hints for refferencing the highest quality video and image content, please kindly surf and locate more enlightening video content and graphics that fit your interests.
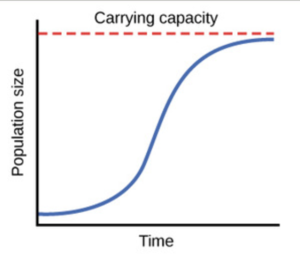
Define Logistic Growth In Biology. Logistic growth is when growth rate decreases as the population reaches carrying capacity. An important model related to carrying capacity K is the logistic growth curve. It is represented by an S-shaped growth curve. Populations growing according to logistic growth are observed in laboratory populations Paramecium and Daphnia as well as in nature fur seals.
 Logistic Models Rhea From projectrhea.org
Logistic Models Rhea From projectrhea.org
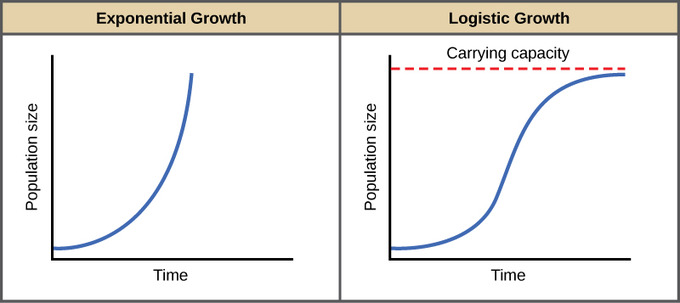
The formula given for logistic growth in the AP Biology formula booklet is. This leads to limitations on food space or other scarce resources. Exponential growth produces a J-shaped curve while logistic growth produces an S-shaped curve. An initial establishment phase in which growth is slow a rapid expansion phase in which the population grows relatively quickly and a a long entrenchment stage in which the population is close to its limiting population due to. Populations growing according to logistic growth are observed in laboratory populations Paramecium and Daphnia as well as in nature fur seals. A biological population with plenty of food space to grow and no threat from predators tends to grow at a rate that is proportional to the population that is in each unit of time a certain percentage of the individuals produce new individuals.
Explanation of logistic growth.
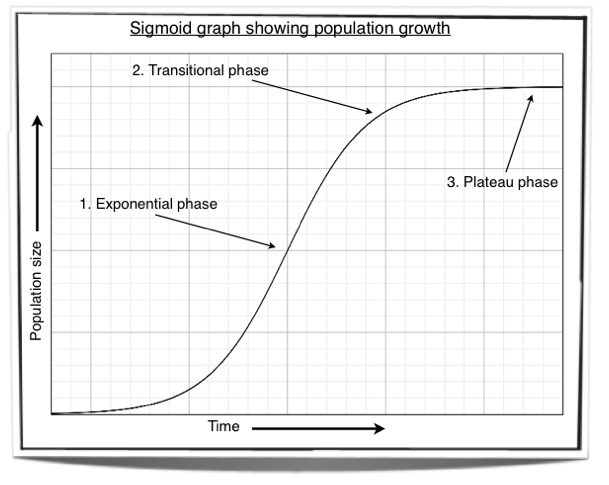
Definition of logistic growth model. The S-shaped pattern in which the growth of a population typically slows down as it approaches carrying capacity. Logistic model in the largest biology dictionary online. Mutualism is in essence the logistic growth equation mutualistic interaction. Logistic growth is population increase that happens in a manner that starts slowly as there are few individuals then increases in speed as numbers increase but then decreases to a halt as numbers get high enough that resources are depleted and cannot support further growth. Definition of logistic.
 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
1 p dp dt b kp where b equals the birth rate and k equals the death rate. Logistic growth assumes that systems grow exponentially until an upper limit or carrying capacity inherent in the system approaches at which point the growth rate slows and eventually saturates producing the characteristic S-shape curve Stone 1980. Of or relating to symbolic logic. From Biology Forums Dictionary. Logistic growth is a type of growth where the effect of limiting upper bound is a curve that grows exponentially at first and then slows down and hardly grows at all.
DNdt rmax N K-NK This essentially means that the change in population over time ie. The slope of the graph the initial growth rate rmax times the number of individuals in the population N times the percentage left until we reach carrying capacity. Of or relating to symbolic logic. Of or relating to the philosophical attempt to reduce mathematics to logic. An initial establishment phase in which growth is slow a rapid expansion phase in which the population grows relatively quickly and a a long entrenchment stage in which the population is close to its limiting population due to.
 Source: bioprinciples.biosci.gatech.edu
Source: bioprinciples.biosci.gatech.edu
The growth curve of a population growing according to logistic growth is typically characterized by three phases. A biological population with plenty of food space to grow and no threat from predators tends to grow at a rate that is proportional to the population that is in each unit of time a certain percentage of the individuals produce new individuals. This logistic equation can also be seen to model physical growth provided K is interpreted rather naturally as the limiting physical dimension. In logistic growth a population will continue to grow until it reaches carrying capacity which is the maximum number of individuals the environment can support. Compare And Contrast Exponential And Logistic Growth - 9 images - biology exam 2 study guide bio 150 docx studying for difference between.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
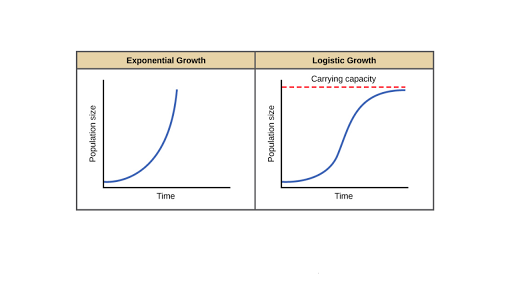
When resources are limited populations exhibit logistic growth. An initial establishment phase in which growth is slow a rapid expansion phase in which the population grows relatively quickly and a a long entrenchment stage in which the population is close to its limiting population due to. The geometric or exponential growth of all populations is eventually curtailed by food availability competition for other resources predation disease or some other ecological factorIf growth is limited by resources such as food the exponential growth of the population begins to slow as competition for those resources increases. Definition for Logistic growth. The growth curve of the exponential growth is J-shaped.
 Source: projectrhea.org
Source: projectrhea.org
1 p dp dt b kp where b equals the birth rate and k equals the death rate. 1 p dp dt b kp where b equals the birth rate and k equals the death rate. The geometric or exponential growth of all populations is eventually curtailed by food availability competition for other resources predation disease or some other ecological factorIf growth is limited by resources such as food the exponential growth of the population begins to slow as competition for those resources increases. Definition of logistic growth model. Logistic growth is population increase that happens in a manner that starts slowly as there are few individuals then increases in speed as numbers increase but then decreases to a halt as numbers get high enough that resources are depleted and cannot support further growth.

A biological population with plenty of food space to grow and no threat from predators tends to grow at a rate that is proportional to the population that is in each unit of time a certain percentage of the individuals produce new individuals. This is generally due to capacity and resource limitations. The Logistic growth refers to a population growth whose rate decreases with the increasing number of individuals and it becomes zero when the population becomes its maximum. It is represented by an S-shaped growth curve. Logistic model in the largest biology dictionary online.
 Source: ib.bioninja.com.au
Source: ib.bioninja.com.au
Exponential growth is possible when infinite natural resources are available which is not the case in the real world. It is represented by an S-shaped growth curve. It is parameterized by the initial population size or. The Logistic growth refers to a population growth whose rate decreases with the increasing number of individuals and it becomes zero when the population becomes its maximum. The growth curve of the exponential growth is J-shaped.
 Source: science.umd.edu
Source: science.umd.edu
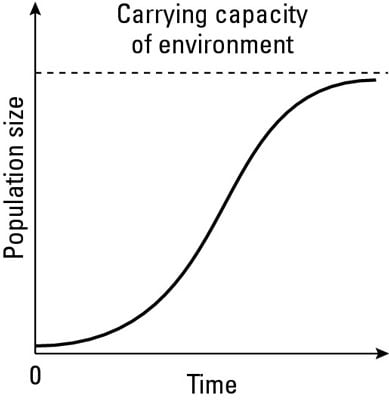
It is represented by an S-shaped growth curve. Logistic growth is when growth rate decreases as the population reaches carrying capacity. The logistic growth curve is initially very similar to the exponential growth curve. The S-shaped pattern in which the growth of a population typically slows down as it approaches carrying capacity. The Logistic growth refers to a population growth whose rate decreases with the increasing number of individuals and it becomes zero when the population becomes its maximum.
 Source: ibguides.com
Source: ibguides.com
It is parameterized by the initial population size or. Logistic growth of a population size occurs when resources are limited thereby setting a maximum number an environment can support. Logistic growth equation which is shown later to provide an extension to the exponential model. A population constrained by resources that approaches its carrying capacity will experience this. The logistic growth curve is initially very similar to the exponential growth curve.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Exponential growth produces a J-shaped curve while logistic growth produces an S-shaped curve. Logistic growth equation which is shown later to provide an extension to the exponential model. McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Scientific Technical Terms 6E Copyright 2003 by The McGraw-Hill Companies Inc. Logistic growth describes the growth rate of a species or a number of species in which the rate decreases as the total number grows. In logistic growth population expansion decreases as resources become scarce and it levels off when the carrying capacity of the environment is reached resulting in an S-shaped curve.
 Source: dummies.com
Source: dummies.com
In logistic growth a population will continue to grow until it reaches carrying capacity which is the maximum number of individuals the environment can support. The logistic growth curve is initially very similar to the exponential growth curve. It is parameterized by the initial population size or. Populations growing according to logistic growth are observed in laboratory populations Paramecium and Daphnia as well as in nature fur seals. In logistic growth a population will continue to grow until it reaches carrying capacity which is the maximum number of individuals the environment can support.
 Source: blendspace.com
Source: blendspace.com
This logistic equation can also be seen to model physical growth provided K is interpreted rather naturally as the limiting physical dimension. Logistic growth describes the growth rate of a species or a number of species in which the rate decreases as the total number grows. This is possible for some situations like population where there is usually some type of upper bound. A population constrained by resources that approaches its carrying capacity will experience this. Mutualism is in essence the logistic growth equation mutualistic interaction.

Logistic model in the largest biology dictionary online. Carrying capacity can be defined as maximum number of individuals in a population that can be supported by the environment. The Logistic growth refers to a population growth whose rate decreases with the increasing number of individuals and it becomes zero when the population becomes its maximum. Compare And Contrast Exponential And Logistic Growth - 9 images - biology exam 2 study guide bio 150 docx studying for difference between. The logistic growth curve is initially very similar to the exponential growth curve.
 Source: xaktly.com
Source: xaktly.com
In logistic growth a populations per capita growth rate gets smaller and smaller as population size approaches a maximum imposed by limited resources in the environment known as the carrying capacity. Explanation of logistic growth. It is represented by an S-shaped growth curve. A biological population with plenty of food space to grow and no threat from predators tends to grow at a rate that is proportional to the population that is in each unit of time a certain percentage of the individuals produce new individuals. Logistic growth equation which is shown later to provide an extension to the exponential model.
 Source: britannica.com
Source: britannica.com
It is represented by an S-shaped growth curve. Carrying capacity can be defined as maximum number of individuals in a population that can be supported by the environment. In logistic growth a population will continue to grow until it reaches carrying capacity which is the maximum number of individuals the environment can support. What is the definition of logistic growth in biology. From Biology Forums Dictionary.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
In logistic growth population expansion decreases as resources become scarce and it levels off when the carrying capacity of the environment is reached resulting in an S-shaped curve. Entry 1 of 2 1 a. Logistic model in the largest biology dictionary online. A population constrained by resources that approaches its carrying capacity will experience this. An important model related to carrying capacity K is the logistic growth curve.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Populations growing according to logistic growth are observed in laboratory populations Paramecium and Daphnia as well as in nature fur seals. The geometric or exponential growth of all populations is eventually curtailed by food availability competition for other resources predation disease or some other ecological factorIf growth is limited by resources such as food the exponential growth of the population begins to slow as competition for those resources increases. Explanation of logistic growth. Definition for Logistic growth. In logistic growth a populations per capita growth rate gets smaller and smaller as population size approaches a maximum imposed by limited resources in the environment known as the carrying capacity.
It is represented by an S-shaped growth curve. McGraw-Hill Dictionary of Scientific Technical Terms 6E Copyright 2003 by The McGraw-Hill Companies Inc. It is represented by an S-shaped growth curve. The slope of the graph the initial growth rate rmax times the number of individuals in the population N times the percentage left until we reach carrying capacity. Such type of population growth is termed as logistic growth.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title define logistic growth in biology by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.