Your Cross price elasticity of demand problems and solutions images are available. Cross price elasticity of demand problems and solutions are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the Cross price elasticity of demand problems and solutions files here. Find and Download all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re searching for cross price elasticity of demand problems and solutions pictures information related to the cross price elasticity of demand problems and solutions topic, you have come to the right blog. Our website always provides you with suggestions for downloading the maximum quality video and image content, please kindly hunt and find more enlightening video articles and images that fit your interests.
Cross Price Elasticity Of Demand Problems And Solutions. Problem Set- Chapter 2 Solutions 1. This worked example asks you to compute two types of demand elasticities and then to draw conclusions from the results. The cross elasticity of demand is the proportional change in the quantity demanded of good X divided by the proportional change in the price of the related good Y. A cross-price elasticity of 063 implies that a 1 increase in the price of Pepsi would increase the quantity of Coke demanded by 063.
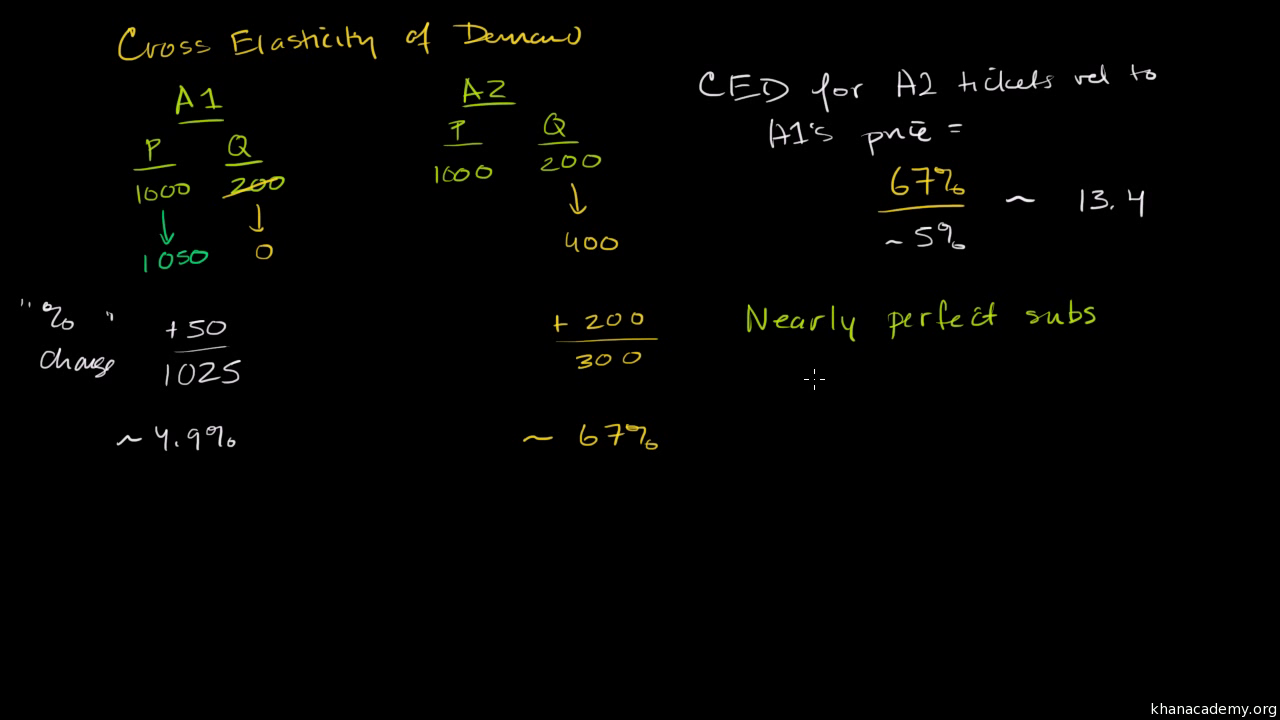 Cross Price Elasticity Of Demand Video Khan Academy From khanacademy.org
Cross Price Elasticity Of Demand Video Khan Academy From khanacademy.org
Are beer and nuts demand substitutes or demand complements. Cross-price elasticity measures how sensitive the demand of a product is over a shift of a corresponding product price. The cross elasticity of demand is the proportional change in the quantity demanded of good X divided by the proportional change in the price of the related good Y. This is all the information needed to compute the price elasticity of demand. The concept of cross elasticity of demand is of great importance in managerial decision making for formulating proper price strategy. So the percentage change in the price.
Now let us assume that a surge of 50 in gasoline price resulted in a decline in the purchase of passenger vehicles by 10.
The average price is 5 a box. Another familiar term is cross elasticity price of demand XED this represents the change in demand of a product given a change in the. A cross-price elasticity of 063 implies that a 1 increase in the price of Pepsi would increase the quantity of Coke demanded by 063. Chapter 4 Elasticity. The price elasticity of demand measures how responsive the quantity demanded for a good is in response to a change in the price of another good while the. If XED 0 then the products are substitutes of each other.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Cross Elasticity of Demand Meaning. Cross elasticity of demand is referred to as the sensitivity of demand for one product to the price of another related product. Calculating Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand. A What happens to the demand for beer when the price of nuts goes up. Another familiar term is cross elasticity price of demand XED this represents the change in demand of a product given a change in the.
 Source: learncbse.in
Source: learncbse.in
Cross-price elasticity of demand is the more strongly the two goods are gross complements. The price elasticity of demand is 125. Cross elasticity of demand is an important concept of economics as it measures the change in demand for a good in relation to change in price of either substitute goods or complementary good where substitute goods refer to those goods which are direct competitor of each other that is one can use either of the two goods. A cross-price elasticity of 063 implies that a 1 increase in the price of Pepsi would increase the quantity of Coke demanded by 063. This worked example asks you to compute two types of demand elasticities and then to draw conclusions from the results.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
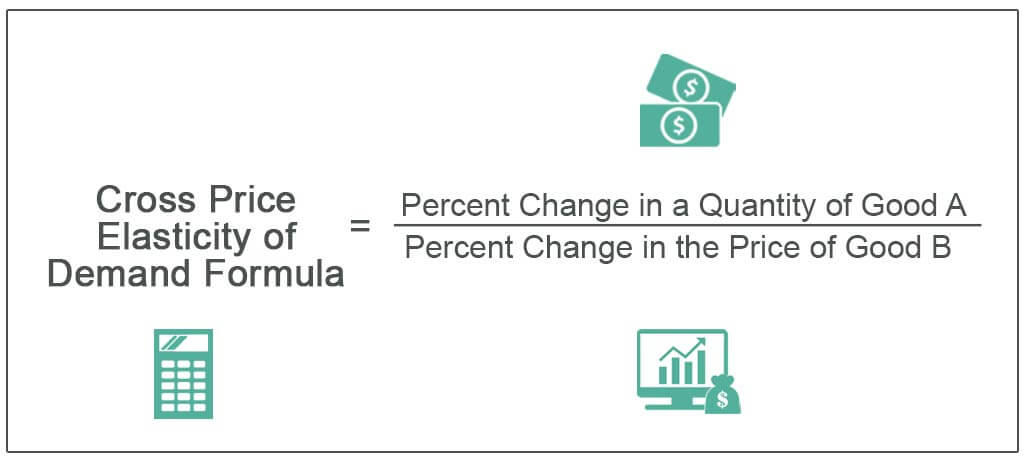
The cross elasticity of demand is the proportional change in the quantity demanded of good X divided by the proportional change in the price of the related good Y. It is the ratio of the percentage change in quantity demanded of good X and the percentage change in the price of good Y. Cross-price elasticity is the percentage change in quantity demanded caused by a 1 increase in the price of another. Cross elasticity of demand-Explanation with examples. The cross elasticity of demand.
 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Are beer and nuts demand substitutes or demand complements. The price rises from 4 to 6 a box a rise of 2 a box. Qd 700 2P P N 01I where P is the price of beer P N is the price of nuts and I is average consumer income. She charges 10 per pound for her hand made chocolate. Cross Elasticity of Demand Meaning.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
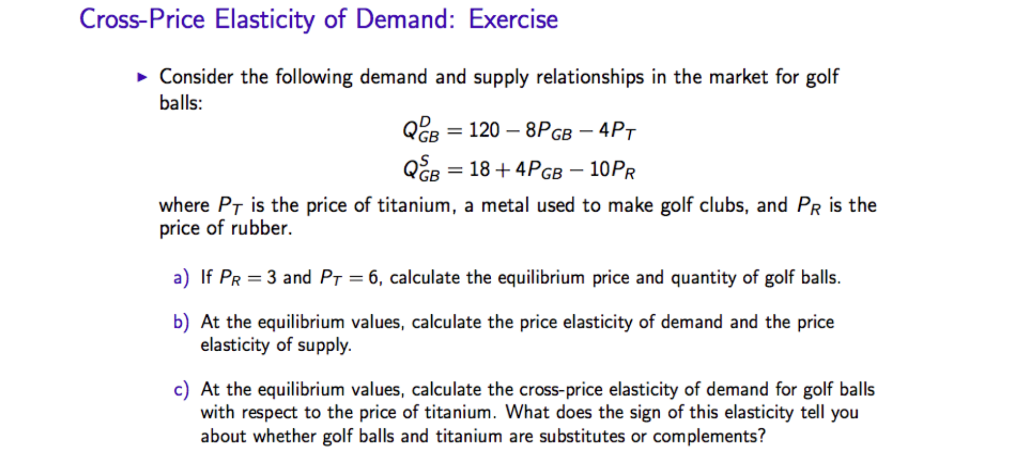
Ch 2 Problem 21 The demand for beer in Japan is given by the following equation. A cross-price elasticity of 063 implies that a 1 increase in the price of Pepsi would increase the quantity of Coke demanded by 063. Our mission is to provide a free world-class education to. You the economist have calculated the elasticity of demand for chocolate in her town to be 25. B percentage change in quantity demanded of one good divided by percentage change in price.
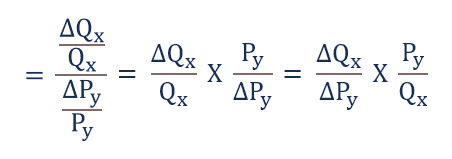 Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
Source: corporatefinanceinstitute.com
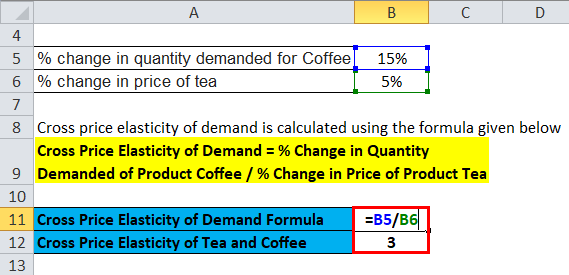
Cross-price elasticity is the percentage change in quantity demanded caused by a 1 increase in the price of another. Are beer and nuts demand substitutes or demand complements. Cross Price Elasticity of Demand Definition. The cross elasticity of demand is the proportional change in the quantity demanded of good X divided by the proportional change in the price of the related good Y. Anna owns the Sweet Alps Chocolate store.
 Source: studocu.com
Source: studocu.com
Multi-product firms often use this concept to measure the effect of change in price of one product on the demand for other products. Cross-price elasticity is the percentage change in quantity demanded caused by a 1 increase in the price of another. Cross Elasticity of Demand Meaning. The average price is 5 a box. The initial price and quantity of widgets demanded is P1 12 Q1 8.
 Source: educba.com
Source: educba.com
Change in Quantity 40 - 5050 -020 -20 Change in Price 600 - 400400 050 50 Elasticity -2050 -04 04 The elasticity of demand is 04 elastic. Cross-price elasticity is the percentage change in quantity demanded caused by a 1 increase in the price of another. The average price is 5 a box. Let us take the simple example of gasoline and passenger vehicles. To find the quantity when the price is 10 a box we use the same formula.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
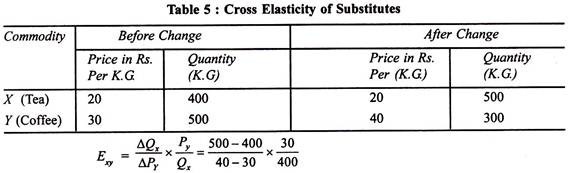
To find the quantity when the price is 10 a box we use the same formula. Cross-price elasticity of demand is the more strongly the two goods are gross complements. Often in the market some goods can relate to one another. For example Maruti Udyog Ltd. Produces Maruti Vans Alto and Maruti SX-4.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
The concept of cross elasticity of demand is of great importance in managerial decision making for formulating proper price strategy. Another familiar term is cross elasticity price of demand XED this represents the change in demand of a product given a change in the. Cross price elasticity of demand Formula Q 1X u2013 Q 0X Q 1X Q 0X P 1Y u2013 P 0Y P 1Y P 0Y Examples Example 1. The price elasticity of demand is 125. The subsequent price and quantity is P2 9 Q2 10.
 Source: wallstreetmojo.com
Source: wallstreetmojo.com
Calculating Cross-Price Elasticity of Demand. Anna owns the Sweet Alps Chocolate store. The cross-price elasticity of demand is defined as a the percentage change in the supply for one good a shift in the supply curve divided by the percentage change in the price of a related. Another familiar term is cross elasticity price of demand XED this represents the change in demand of a product given a change in the. Cross elasticity of demand is an important concept of economics as it measures the change in demand for a good in relation to change in price of either substitute goods or complementary good where substitute goods refer to those goods which are direct competitor of each other that is one can use either of the two goods.
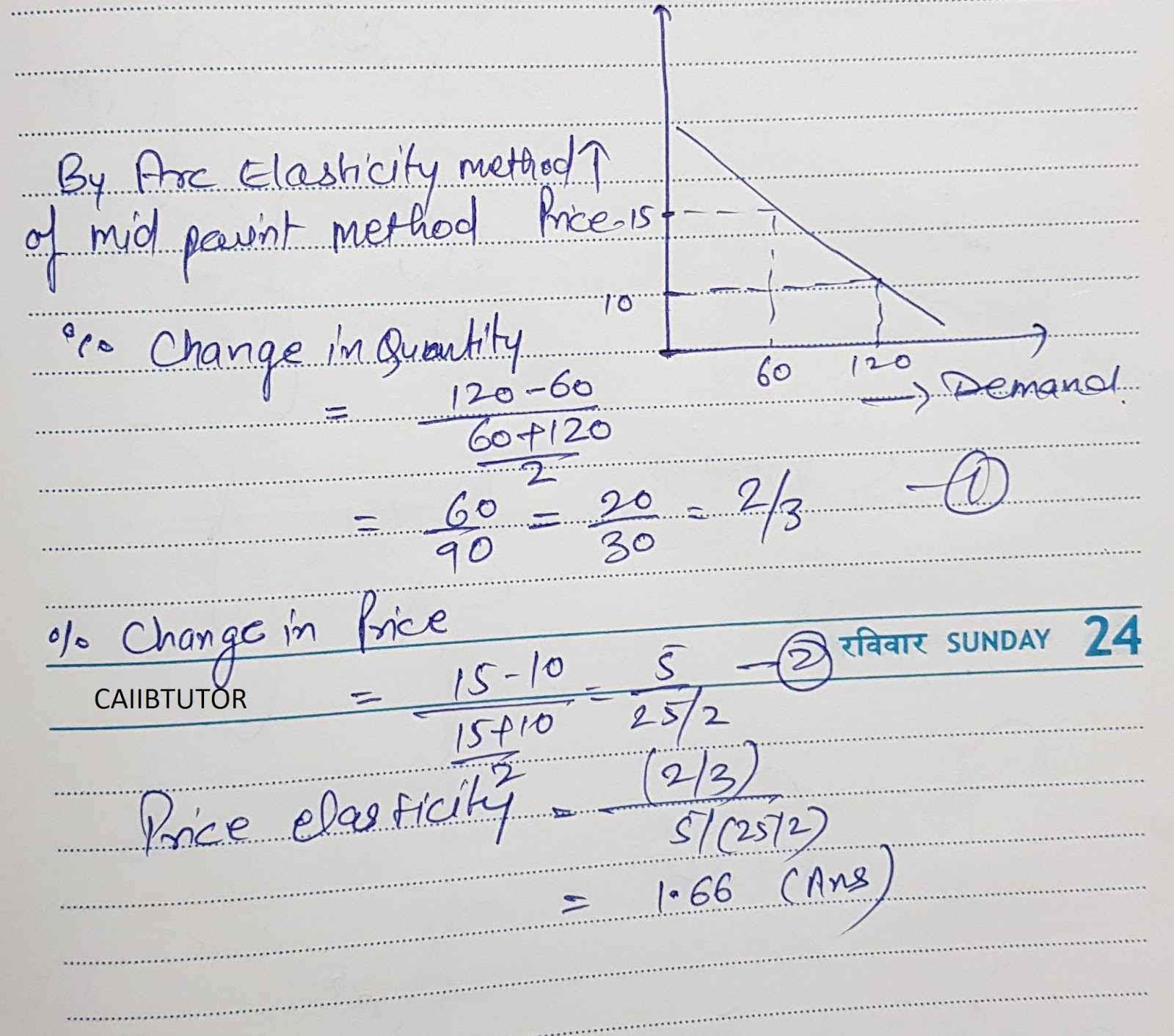 Source: caiibtutor.blogspot.com
Source: caiibtutor.blogspot.com
She charges 10 per pound for her hand made chocolate. Cross elasticity of demand is referred to as the sensitivity of demand for one product to the price of another related product. Ch 2 Problem 21 The demand for beer in Japan is given by the following equation. So the percentage change in the price. Our mission is to provide a free world-class education to.
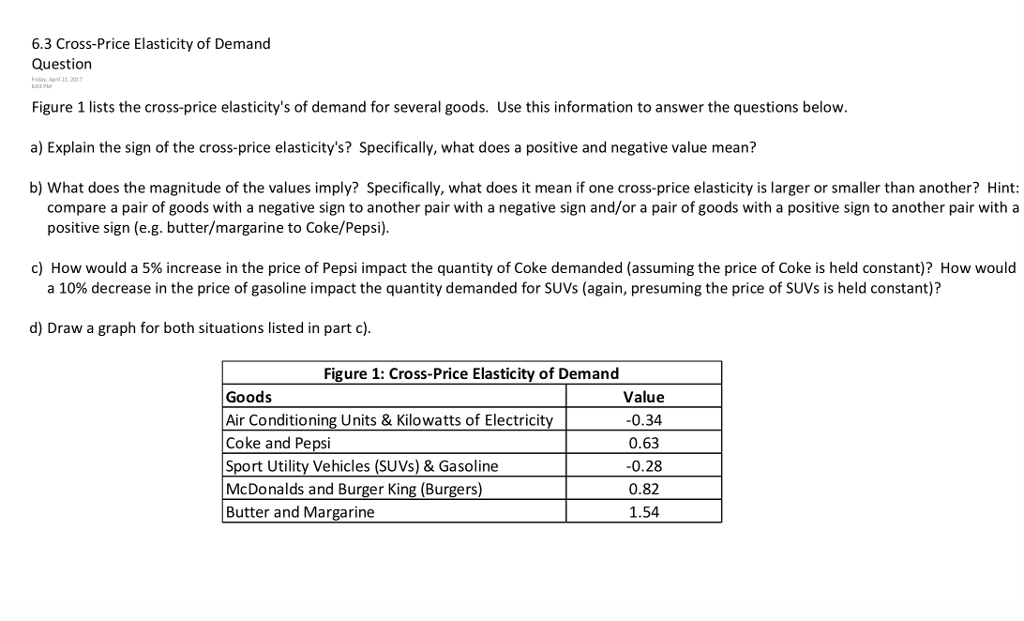 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
The price elasticity of demand is 125. Cross elasticity of demand-Explanation with examples. A cross-price elasticity of 063 implies that a 1 increase in the price of Pepsi would increase the quantity of Coke demanded by 063. Cross-price elasticity of demand is the more strongly the two goods are gross complements. Cross elasticity of demand is an important concept of economics as it measures the change in demand for a good in relation to change in price of either substitute goods or complementary good where substitute goods refer to those goods which are direct competitor of each other that is one can use either of the two goods.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Anna owns the Sweet Alps Chocolate store. Another familiar term is cross elasticity price of demand XED this represents the change in demand of a product given a change in the. Often in the market some goods can relate to one another. It is the ratio of the percentage change in quantity demanded of good X and the percentage change in the price of good Y. The price elasticity of demand is 125.
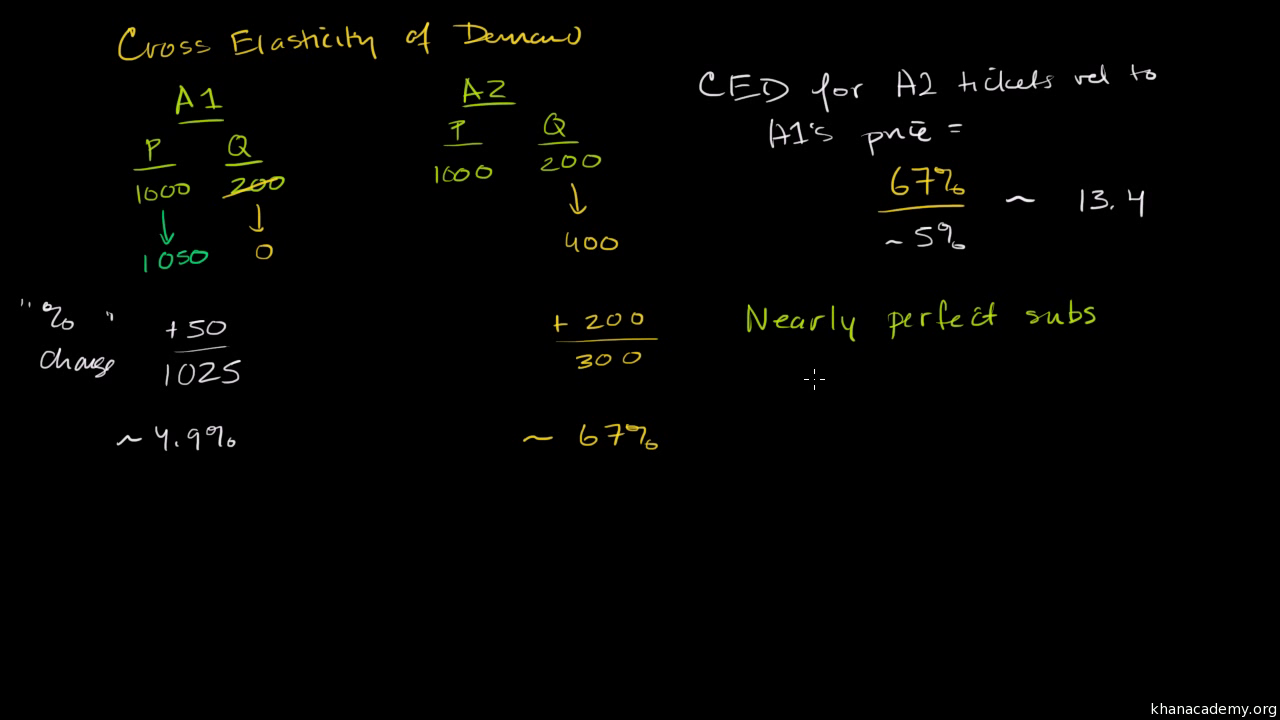 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
The cross elasticity of demand. Solutions to Problems. The initial price and quantity of widgets demanded is P1 12 Q1 8. Therefore a 5 increase in the price of Pepsi would increase the quantity of Coke demanded by five times as much that is by 5 063 315. The average price is 5 a box.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
If XED 0 then the products are substitutes of each other. Cross-price elasticity measures how sensitive the demand of a product is over a shift of a corresponding product price. Cross-price elasticity of demand AP is a registered trademark of the College Board which has not reviewed this resource. The initial price and quantity of widgets demanded is P1 12 Q1 8. The price rises from 4 to 6 a box a rise of 2 a box.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Our mission is to provide a free world-class education to. If XED 0 then the products are substitutes of each other. The cross elasticity of demand is the proportional change in the quantity demanded of good X divided by the proportional change in the price of the related good Y. Cross price elasticity of demand XED QXQX PYPY Where QX Quantity of product X PY Price of the product Change in the quantity demandedprice From this formula the following can be deduced. Calculate the cross-price elasticity of demand in this.
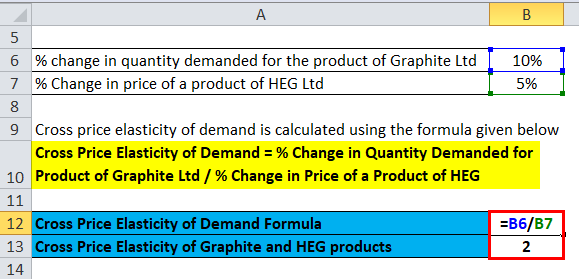 Source: educba.com
Source: educba.com
You the economist have calculated the elasticity of demand for chocolate in her town to be 25. Problem Set- Chapter 2 Solutions 1. To find the quantity when the price is 10 a box we use the same formula. Change in Quantity 40 - 5050 -020 -20 Change in Price 600 - 400400 050 50 Elasticity -2050 -04 04 The elasticity of demand is 04 elastic. Chapter 4 Elasticity.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site good, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title cross price elasticity of demand problems and solutions by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.