Your Collusive oligopoly diagram images are ready in this website. Collusive oligopoly diagram are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Collusive oligopoly diagram files here. Find and Download all free images.
If you’re looking for collusive oligopoly diagram images information related to the collusive oligopoly diagram topic, you have pay a visit to the right site. Our website frequently gives you hints for seeing the highest quality video and picture content, please kindly search and find more enlightening video content and images that match your interests.
Collusive Oligopoly Diagram. Figure 113 Monopoly Through Collusion shows a case in which the two firms are identical. 3rd degree price discrimination. The kinked demand curve of oligopoly was developed by Paul M. Non collusive oligopoly diagram.
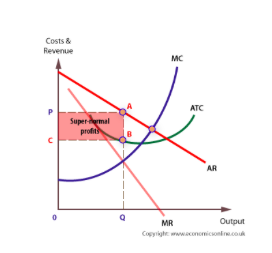 B Discuss The View That An Oligopoly Is Always Efficient In The Market 15 Quintessential Education Igcse Ib Tuition Specialists From qeducation.sg
B Discuss The View That An Oligopoly Is Always Efficient In The Market 15 Quintessential Education Igcse Ib Tuition Specialists From qeducation.sg
In this article we will discuss about the determination of price and output under collusive oligopoly. Figure-1 shows different oligopoly models. Collusive arrangements are generally. Sweezys Kinked Demand Curve Model. Oligopolists pursuing their individual self-interest would produce a greater quantity than a monopolist and charge a lower price. Collusive Oligopoly in Economics With Diagram In this article we will discuss about collusive oligopoly and how is price determined in this oligopoly.
Collusive arrangements are generally.
Collusive Oligopoly refers to a form of oligopoly in which the competing firms collude so as to minimize competition and maximize joint profit by reducing the uncertainties arising due to rivalry and selling the goods and service at a monopoly price. The kink exists because demand is more elastic at higher prices in comparison to low prices where demand is inelastic. A cartel is often. The kinked demand curve of oligopoly was developed by Paul M. Instead of laying emphasis on price-output determination the model explains the behavior of oligopolistic organizations. In this figure 174 the industry demand curve PD consisting of three firms are identical.
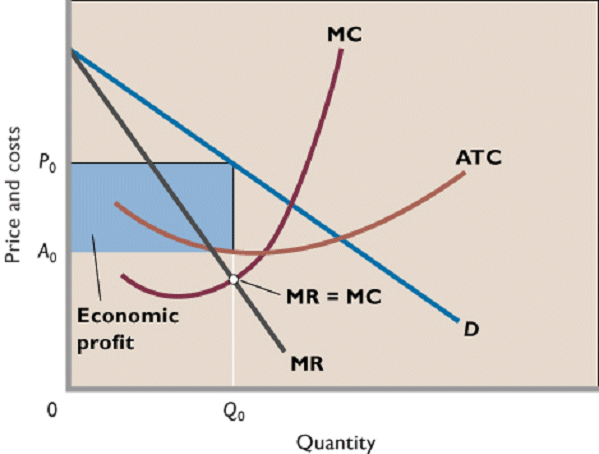 Source: www2.harpercollege.edu
Source: www2.harpercollege.edu
If firms in oligopoly collude and form a cartel. The idea of using a non-conventional demand curve to represent non-collusive oligopoly ie where sellers compete with. Characteristics of perfect competition. Pure oligopoly describes the situation where differentiation of the product is weak. Sweezys Kinked Demand Curve Model.
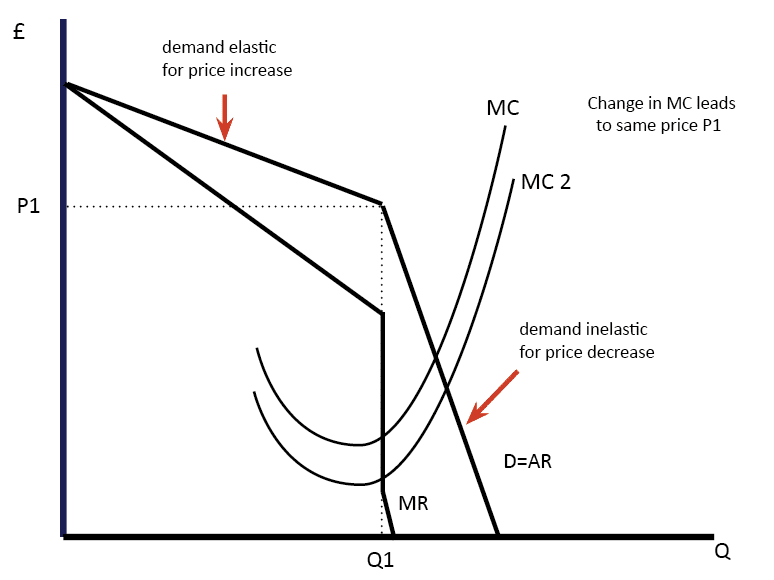 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
In the noncollusive oligopoly there is rivalry among the firms due to the interdependence. Instead of laying emphasis on price-output determination the model explains the behavior of oligopolistic organizations. The idea of using a non-conventional demand curve to represent non-collusive oligopoly ie where sellers compete with. Firms in an oligopoly may collude to set a price or output level for a market in order to maximize industry profits. Figure 113 Monopoly Through Collusion shows a case in which the two firms are identical.
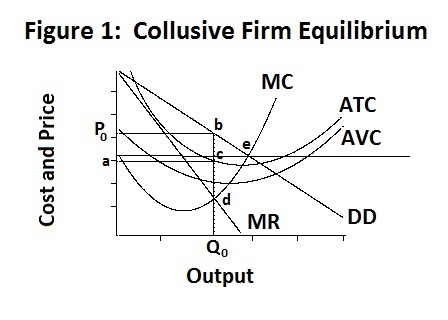 Source: economics.utoronto.ca
Source: economics.utoronto.ca
Non-collusive oligopoly Explain that the behaviour of firms in a non-collusive oligopoly is strategic in order to take account of possible actions by rivals Explain using a diagram the existence of price rigidities with reference to the kinked demand curve. Suppose an industry is a duopoly an industry with two firms. In contrast a collusive oligopoly involves collusion price agreements between firms. Two Typical Forms of Cartels With Diagram We saw that in the absence of collusion the monopoly solution in the industry the solution at which the joint industry profit is maximized can be achieved under the rare conditions that. Instead of laying emphasis on price-output determination the model explains the behavior of oligopolistic organizations.
 Source: qeducation.sg
Source: qeducation.sg
In a model of collusive oligopoly we discuss the economics of agreement between the firms in an undifferentiated oligopolistic industry. In this the oligopolists enter into a contract to establish the levels of price and output in. 49 rows Collusive Oligopoly. The kink exists because demand is more elastic at higher prices in comparison to low prices where demand is inelastic. Let us discuss different oligopoly models as shown in Figure-1.

Many buyers and sellers price takers Characteristics of perfect competition. In contrast a collusive oligopoly involves collusion price agreements between firms. Evaluating the Costs and Benefits of Collusion - Revision Video. Let us discuss different oligopoly models as shown in Figure-1. The collusive models of oligopoly suggest that duopolists or oligopolists can gain by colluding ie by choosing the output level which maximises total industry profits and then sharing the profits among themselves.
 Source: biznewske.com
Source: biznewske.com
Non-collusive oligopoly Explain that the behaviour of firms in a non-collusive oligopoly is strategic in order to take account of possible actions by rivals Explain using a diagram the existence of price rigidities with reference to the kinked demand curve. One approach to the analysis of oligopoly is to assume that firms in the industry collude selecting the monopoly solution. The kink exists because demand is more elastic at higher prices in comparison to low prices where demand is inelastic. Collusive Oligopoly or Cartel Model Microeconomics. Since each firm is a price-searcher each.
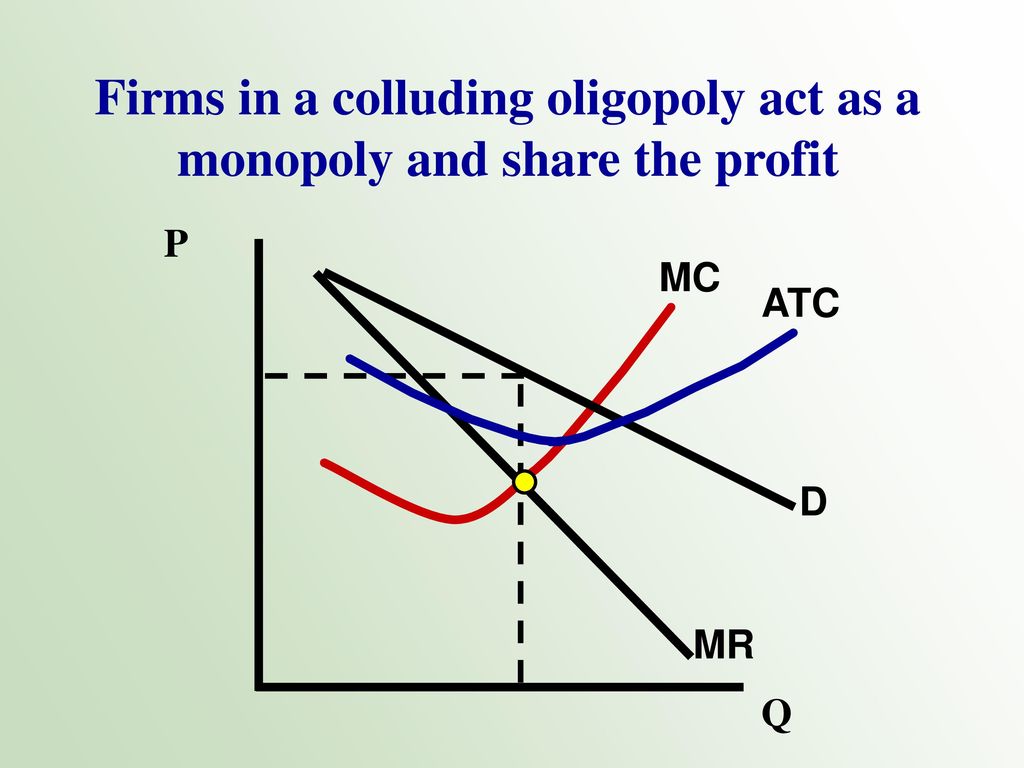 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
On the other hand in collusive oligopoly the rival firms enter into a collusion to maximise joint profit by reducing the uncertainty due to rivalry. Collusive oligopoly refers to a market where there is co-operation among the sellers ie coordination of prices. Collusive Oligopoly refers to a form of oligopoly in which the competing firms collude so as to minimize competition and maximize joint profit by reducing the uncertainties arising due to rivalry and selling the goods and service at a monopoly price. If firms in oligopoly collude and form a cartel. In the noncollusive oligopoly there is rivalry among the firms due to the interdependence.
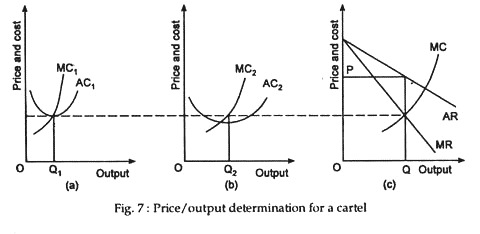 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Collusive Oligopoly refers to a form of oligopoly in which the competing firms collude so as to minimize competition and maximize joint profit by reducing the uncertainties arising due to rivalry and selling the goods and service at a monopoly price. The idea of using a non-conventional demand curve to represent non-collusive oligopoly ie where sellers compete with. A each firm knows the monopoly price that is has a correct knowledge of the market demand and of. Price stability in a non-collusive oligopoly can be explained by the kinked oligopoly diagram. Definition of Collusive Oligopoly.
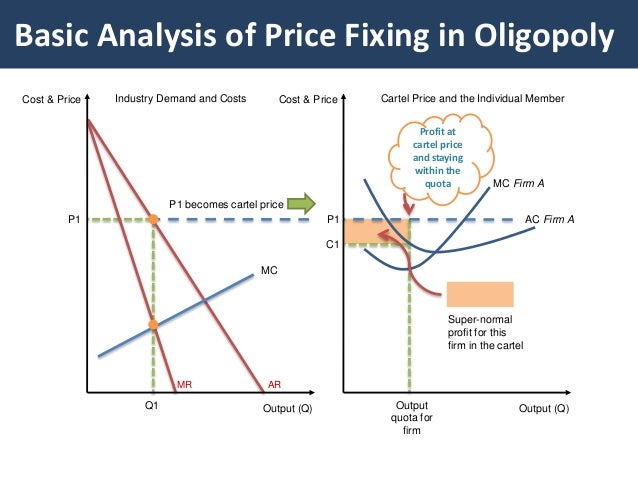 Source: pt.slideshare.net
Source: pt.slideshare.net
Under the assumptions stated above the equilibrium of the industry under collusive oligopoly is explained with the help of a diagram. Sweezys Kinked Demand Curve Model. Pricing and output in a pure oligopoly can be collusive or non-collusive. In a model of collusive oligopoly we discuss the economics of agreement between the firms in an undifferentiated oligopolistic industry. When there is product differentiation ie differentiated oligopoly two or few sellers may recognise that their prices are closely interrelated.

Oligopolists pursuing their individual self-interest would produce a greater quantity than a monopolist and charge a lower price. When there is product differentiation ie differentiated oligopoly two or few sellers may recognise that their prices are closely interrelated. Since each firm is a price-searcher each. Sweezys Kinked Demand Curve Model. Collusive arrangements are generally.
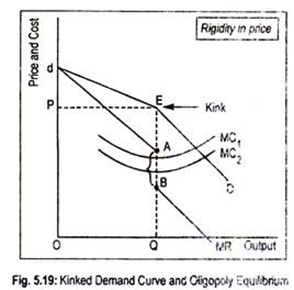 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Figure 113 Monopoly Through Collusion shows a case in which the two firms are identical. In a model of collusive oligopoly we discuss the economics of agreement between the firms in an undifferentiated oligopolistic industry. The kinked demand curve of oligopoly was developed by Paul M. In this the oligopolists enter into a contract to establish the levels of price and output in. One approach to the analysis of oligopoly is to assume that firms in the industry collude selecting the monopoly solution.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
The collusive models of oligopoly suggest that duopolists or oligopolists can gain by colluding ie by choosing the output level which maximises total industry profits and then sharing the profits among themselves. Definition of Collusive Oligopoly. Figure-1 shows different oligopoly models. NON-COLLUSIVE OLIGOPOLY Oligopoly can be of two types. Sweezys Kinked Demand Curve Model.
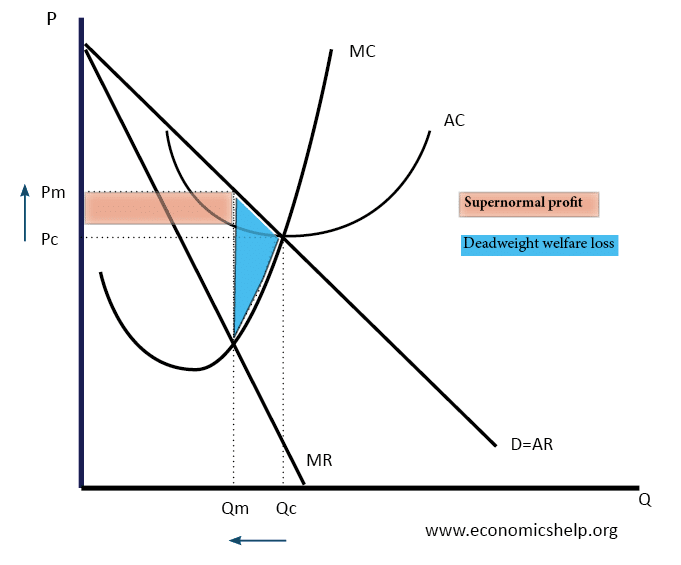 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
49 rows Collusive Oligopoly. Evaluating the Costs and Benefits of Collusion - Revision Video. NON-COLLUSIVE OLIGOPOLY Oligopoly can be of two types. Collusive Oligopoly or Cartel Model Microeconomics. Figure-1 shows different oligopoly models.
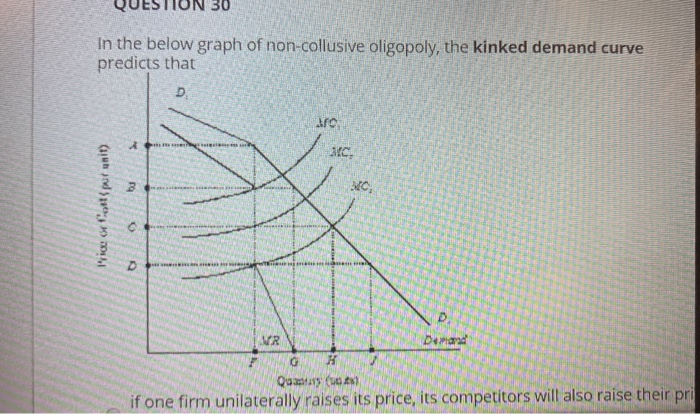 Source: chegg.com
Source: chegg.com
Pricing and output in a pure oligopoly can be collusive or non-collusive. On the other hand in collusive oligopoly the rival firms enter into a collusion to maximise joint profit by reducing the uncertainty due to rivalry. Under the assumptions stated above the equilibrium of the industry under collusive oligopoly is explained with the help of a diagram. Sweezys Kinked Demand Curve Model. The kink exists because demand is more elastic at higher prices in comparison to low prices where demand is inelastic.
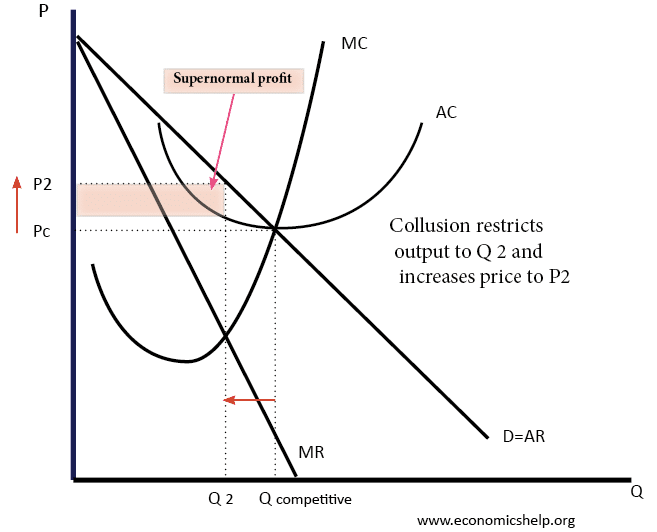 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Suppose an industry is a duopoly an industry with two firms. Oligopolists pursuing their individual self-interest would produce a greater quantity than a monopolist and charge a lower price. Collusive arrangements are generally. A each firm knows the monopoly price that is has a correct knowledge of the market demand and of. Many buyers and sellers price takers Characteristics of perfect competition.
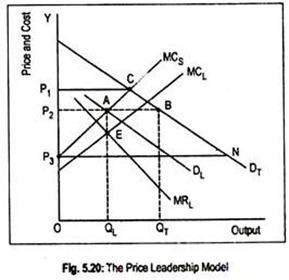 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Instead of laying emphasis on price-output determination the model explains the behavior of oligopolistic organizations. Collusive arrangements are generally. Figure 113 Monopoly Through Collusion shows a case in which the two firms are identical. One of the important features of oligopoly market is price rigidity. Suppose an industry is a duopoly an industry with two firms.
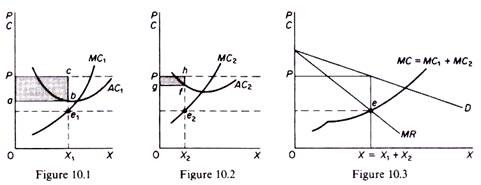 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Firms in an oligopoly may collude to set a price or output level for a market in order to maximize industry profits. Pricing and output in a pure oligopoly can be collusive or non-collusive. The kink exists because demand is more elastic at higher prices in comparison to low prices where demand is inelastic. One of the important features of oligopoly market is price rigidity. Definition of Collusive Oligopoly.
 Source: sanandres.esc.edu.ar
Source: sanandres.esc.edu.ar
One of the important features of oligopoly market is price rigidity. So is the case with. Consumers and producers have perfect information. In contrast a collusive oligopoly involves collusion price agreements between firms. Figure 113 Monopoly Through Collusion shows a case in which the two firms are identical.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title collusive oligopoly diagram by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.






