Your Causes of rapid population growth in the twentieth century images are available. Causes of rapid population growth in the twentieth century are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Download the Causes of rapid population growth in the twentieth century files here. Get all royalty-free photos and vectors.
If you’re looking for causes of rapid population growth in the twentieth century pictures information connected with to the causes of rapid population growth in the twentieth century topic, you have pay a visit to the right blog. Our site frequently provides you with hints for downloading the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly search and locate more enlightening video articles and images that fit your interests.
Causes Of Rapid Population Growth In The Twentieth Century. Reasons for rapid expansion in population can be accredited to several factors such as fertility mortality migration and marriage. Via investments in education and reproductive health care. Geopolitical tensions between nations in all three of these groups are likely to arise over both fossil fuel coal oil and gas and low-carbon sources of energy. This is like adding the whole population of China to the worlds population.

SOME COUNTRIES ARE STILL EXPERIENCING EXPONENTIAL GROWTH BUT THE GROWTH RATE HAS SLOWED IN MANY COUNTRIES. The difficulties caused by rapid population growth are not primarily due to finite natural resources at least not for the world as a whole. That started in the industrial revolution when there were about a billion of us and we tapped into using fossil fuels to do large-scale agriculture. Population growth low fertility sustained productivity increases and rising consumption for the majority. Increasing population growth rates exacerbated pressures on land resources. For the last half-century we have lived in a world in which the population growth rate has been declining.
The chart shows that global population growth reached a peak in 1962 and 1963 with an annual growth rate of 22.
For the last half-century we have lived in a world in which the population growth rate has been declining. As mentioned poverty is also an underlying cause of rapid population growth. Population growth low fertility sustained productivity increases and rising consumption for the majority. Over the course of this transition declines in birth rates followed by declines in death rates bring about an era of rapid population growth. The human popula-tion will increase by 1 billion people in the next decade. 10 During the past 10 years the worlds food production has increased by 24 per cent outpacing the rate of population growth11 However this increase was not evenly distributed throughout the world.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Reasons for rapid expansion in population can be accredited to several factors such as fertility mortality migration and marriage. Rapid population expansion has had important demographic and social effects. Visualize trends in state federal minimum wage unemployment household earnings more. South America - South America - Effects of rapid population increase. Access to affordable and abundant energy underpins industrialisation the rise out of poverty economic growth and post-industrial society.

Ad Explore detailed reporting on the Economy in America from USAFacts. If anything rapid growth slows the accumulation of skills that encourage technological advance and. He believed that social exploitation and oppression of the less privileged people leads to poverty overcrowding unemployment environmental degradation that in turn causes over population. Ad Explore detailed reporting on the Economy in America from USAFacts. Human Population Growth.
 Source: freerangestats.info
Source: freerangestats.info
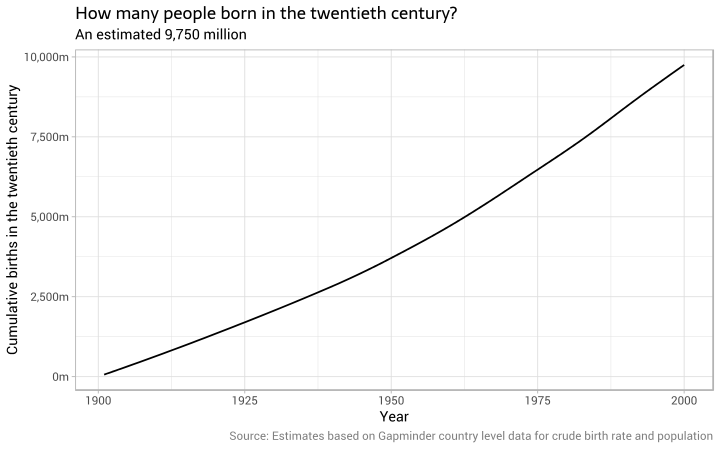
During the 1960s and early 1970s the average number of births per woman declined dramatically but overall population growth kept the total number of births at 100000-120000 per year. Its those social factors that require our intervention. Explain why human population size is likely to increase in the twenty-first century but not as rapidly as it did in the twentieth century. Peak population growth was reached in 1968 with an annual growth of 21. Does the demographic transition hold good for developing societies.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
With the new burst of population growth in developing countries after World War II economists returned to the Malthusian tradition. With the new burst of population growth in developing countries after World War II economists returned to the Malthusian tradition. As mentioned poverty is also an underlying cause of rapid population growth. The world population reached 5 billion in 1987 and 6 billion in 1999 and in October 2011 the global population was estimated at. Ad Explore detailed reporting on the Economy in America from USAFacts.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
According to Karl Marx population growth is a symptom rather than the cause of poverty resource depletion pollution and other social ills. The use of pesticides in LDCs for example was expected to increased between 400 to 600 in the last 25 years of the twentieth century. That started in the industrial revolution when there were about a billion of us and we tapped into using fossil fuels to do large-scale agriculture. The Effects on Biodiversity 3 Replies The massive growth in the human population through the 20th century has had more impact on biodiversity than any other single factor Sir David King science advisor to the UK government. The difficulties caused by rapid population growth are not primarily due to finite natural resources at least not for the world as a whole.
 Source: sociostudies.org
Source: sociostudies.org
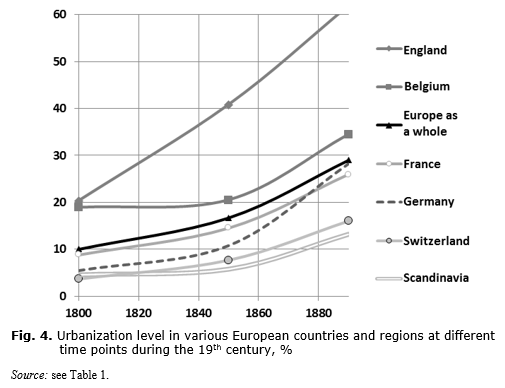
Malthus and the classical economists were writing at a time when in England population growth was accelerating. In South America the proportion of the. Births between 1950 and 1960. At the peak of population growth during the second stage the proportion of children tends to be high while in the third stage it is low. Population growth low fertility sustained productivity increases and rising consumption for the majority.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
This natural cause sometimes beneficial and sometimes disastrous depending on the conditions and locations could be. According to Karl Marx population growth is a symptom rather than the cause of poverty resource depletion pollution and other social ills. The use of pesticides in LDCs for example was expected to increased between 400 to 600 in the last 25 years of the twentieth century. Explain why human population size is likely to increase in the twenty-first century but not as rapidly as it did in the twentieth century. With the new burst of population growth in developing countries after World War II economists returned to the Malthusian tradition.
 Source: sociostudies.org
Source: sociostudies.org
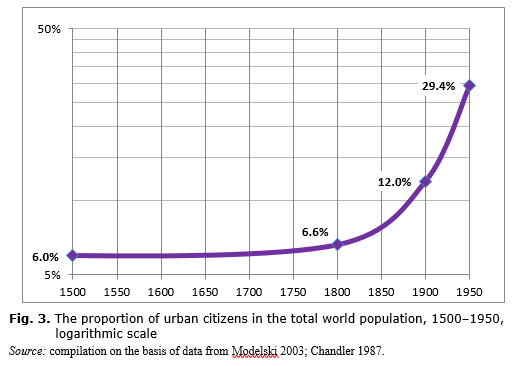
If anything rapid growth slows the accumulation of skills that encourage technological advance and. As mentioned poverty is also an underlying cause of rapid population growth. He believed that social exploitation and oppression of the less privileged people leads to poverty overcrowding unemployment environmental degradation that in turn causes over population. It peaked around half a century ago. This transition usually accompanies the development process that transforms an agricultural society into an industrial one.

10 During the past 10 years the worlds food production has increased by 24 per cent outpacing the rate of population growth11 However this increase was not evenly distributed throughout the world. Population growth low fertility sustained productivity increases and rising consumption for the majority. With the new burst of population growth in developing countries after World War II economists returned to the Malthusian tradition. The world population reached 5 billion in 1987 and 6 billion in 1999 and in October 2011 the global population was estimated at. Peak population growth was reached in 1968 with an annual growth of 21.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Reasons for rapid expansion in population can be accredited to several factors such as fertility mortality migration and marriage. 10 During the past 10 years the worlds food production has increased by 24 per cent outpacing the rate of population growth11 However this increase was not evenly distributed throughout the world. Our Growing Population It is estimated that the world population is about 26 billion people on October 24 October 1945 the founding date of the United Nations. It peaked around half a century ago. During the 1960s and early 1970s the average number of births per woman declined dramatically but overall population growth kept the total number of births at 100000-120000 per year.
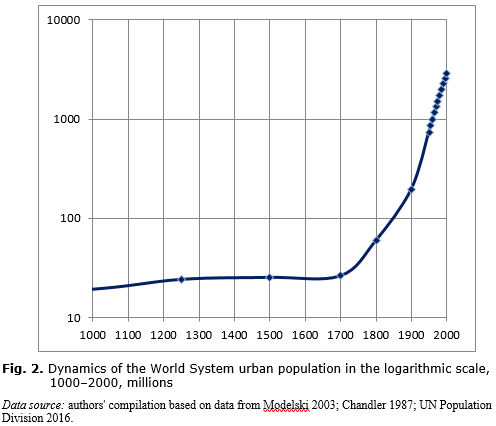 Source: sociostudies.org
Source: sociostudies.org
That started in the industrial revolution when there were about a billion of us and we tapped into using fossil fuels to do large-scale agriculture. Human Population Growth. But since then world population growth has halved. The growth in human. Social factors are at the base of both poverty and population growth.

South America - South America - Effects of rapid population increase. Increasing population growth rates exacerbated pressures on land resources. Does the demographic transition hold good for developing societies. Social factors are at the base of both poverty and population growth. The world population reached 5 billion in 1987 and 6 billion in 1999 and in October 2011 the global population was estimated at.

In an even more speeded-up form Russia and the Soviet Union in their century of industrialization that began in the 1880s illustrated the link between industrialization and population. It peaked around half a century ago. Its population grew rapidly after 1870 during its industrializing phase and leveled off equally rapidly after World War II. This transition usually accompanies the development process that transforms an agricultural society into an industrial one. This is like adding the whole population of China to the worlds population.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
In South America the proportion of the. Births between 1950 and 1960. The human popula-tion will increase by 1 billion people in the next decade. If anything rapid growth slows the accumulation of skills that encourage technological advance and. The Effects on Biodiversity 3 Replies The massive growth in the human population through the 20th century has had more impact on biodiversity than any other single factor Sir David King science advisor to the UK government.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
SOME COUNTRIES ARE STILL EXPERIENCING EXPONENTIAL GROWTH BUT THE GROWTH RATE HAS SLOWED IN MANY COUNTRIES. Since then the increase of the world population has slowed and today grows by just over 1 per year. South America - South America - Effects of rapid population increase. Our Growing Population It is estimated that the world population is about 26 billion people on October 24 October 1945 the founding date of the United Nations. Two examples are especially illuminating.

But neither does rapid population growth itself automati-cally trigger technological advance and adaptation. It peaked around half a century ago. Ad Explore detailed reporting on the Economy in America from USAFacts. The growth in human. Social factors are at the base of both poverty and population growth.
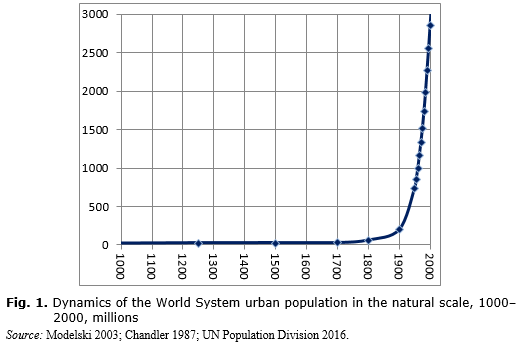 Source: sociostudies.org
Source: sociostudies.org
This is like adding the whole population of China to the worlds population. Our Growing Population It is estimated that the world population is about 26 billion people on October 24 October 1945 the founding date of the United Nations. Malthus and the classical economists were writing at a time when in England population growth was accelerating. Voluntary migration of the rural population has been accompanied by aggressive re-planning schemes in which rural villages are demolished and new manufacturing settlements built at rapid pace for former agricultural families to move in to. Ad Explore detailed reporting on the Economy in America from USAFacts.

Responding to the high population pressure coupled with extreme poverty the government became more involved in family planning. The growth in human. During the 1960s and early 1970s the average number of births per woman declined dramatically but overall population growth kept the total number of births at 100000-120000 per year. As mentioned poverty is also an underlying cause of rapid population growth. Population growth low fertility sustained productivity increases and rising consumption for the majority.
This site is an open community for users to do submittion their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title causes of rapid population growth in the twentieth century by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.