Your Calculate d3mand curve from graph images are ready in this website. Calculate d3mand curve from graph are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Get the Calculate d3mand curve from graph files here. Download all free photos.
If you’re looking for calculate d3mand curve from graph images information related to the calculate d3mand curve from graph keyword, you have visit the right site. Our site frequently gives you suggestions for viewing the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly search and find more enlightening video articles and images that match your interests.
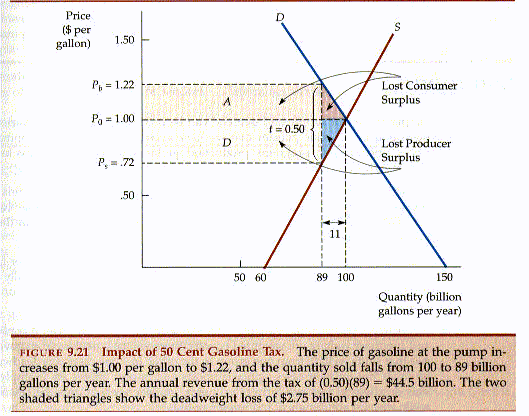
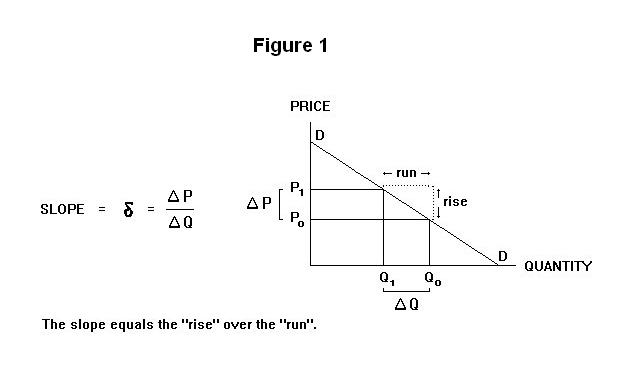
Calculate D3mand Curve From Graph. B is the slope of the demand in relationship to the price P P is the price. Q TR PQ MR 0 0 0 10 1040 400 20 2030 600 25 2525 625 30 3020. Then determine the equilibrium quantity where the demand curve meets the supply curve. We can measure consumer surplus with the following basic formula.
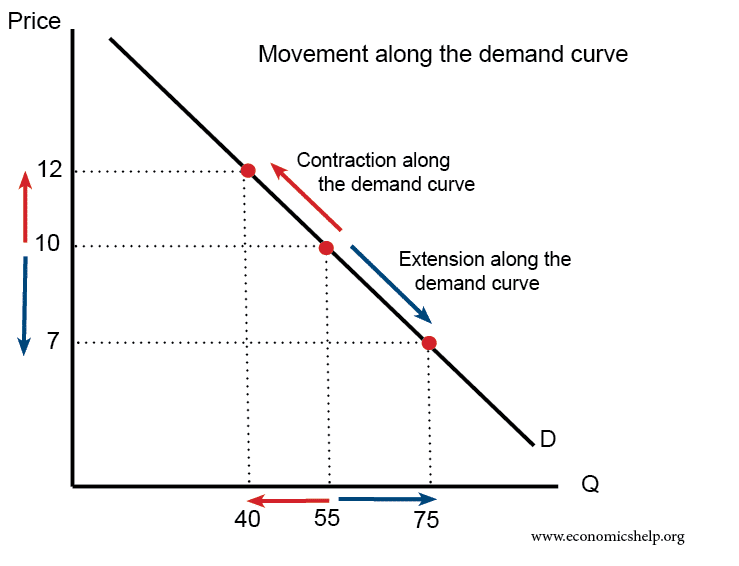
 Demand Curve Formula Economics Help From economicshelp.org
Demand Curve Formula Economics Help From economicshelp.org
Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. Qs -30 10P. Consumer surplus is the consumers gain from an exchange. In this case marginal revenue is equal to price as opposed to being strictly less than price and as a result the marginal revenue curve is the same as the demand curve. For normal daily goods there is an inverse or negative relationship between the desired quantity and the price. The formula for the Linear Demand Curve is.
You calculate it by dividing the change in total cost by the change in output.
When looking at a demand-supply graph the demand curve is always going to be sloping downward due to the law of diminished marginal utility. This situation still follows the rule that the marginal revenue curve is twice as steep as the demand curve since twice a slope of zero is still a slope of zero. Then determine the equilibrium quantity where the demand curve meets the supply curve. The Math Science. Price Elasticity Calculator Midpoint Method. Calculating marginal revenue from a linear demand curve The blue curve on the following graph represents the demand curve facing a firm that can set its own prices.

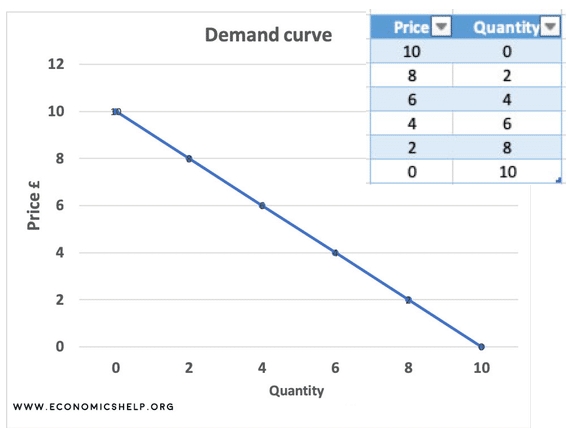
Calculate the quantities demanded and supplied for prices from 3 - 15. Then determine the equilibrium quantity where the demand curve meets the supply curve. Calculating marginal revenue from a linear demand curve The blue curve on the following graph represents the demand curve facing a firm that can set its own prices. A quick visual on how to graph the demand curve. Consider the graph below.

Point Elasticity along a Constant Elasticity Demand Curve. You can draw many of these for each time period on the same sheet to analyze and compare. In addition regarding consumer and producer surplus. When looking at a demand-supply graph the demand curve is always going to be sloping downward due to the law of diminished marginal utility. Assume a linear demand function of the form.
 Source: financetrain.com
Source: financetrain.com
What is the General Form of Inverse Demand Function. If the Inverse Demand Function is. Q 800 - P 10. The Math Science. Q is the quantity of demand.
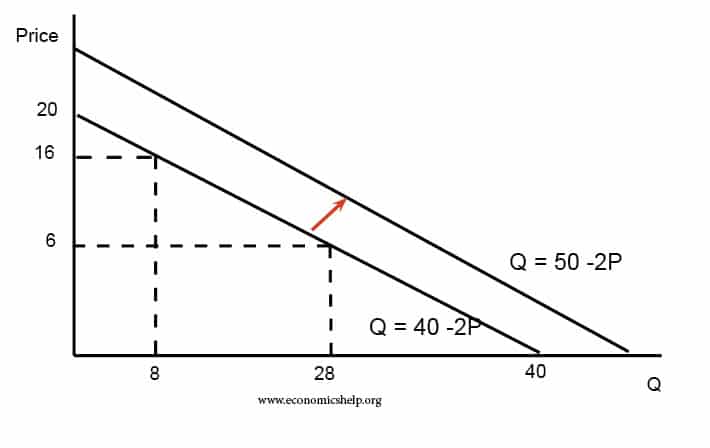
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
You will identify the equilibrium pricing at this point. Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. The graph is calculated using a linear function that is defined as P a - bQ where P equals the price of the product Q equals the quantity demanded of the product and a is equivalent to non-price factors that. Qd a bP Q. P f-1 Q Example of Inverse Demand Function.
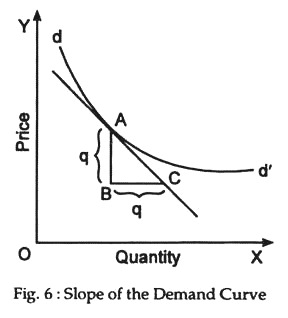 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
A is the effect of all influences on demand other than price. When plotted on a graph marginal costs will typically produce a. Point Elasticity along a Constant Elasticity Demand Curve math version Supply Elasticity. This situation still follows the rule that the marginal revenue curve is twice as steep as the demand curve since twice a slope of zero is still a slope of zero. The Inverse Demand Curve is.
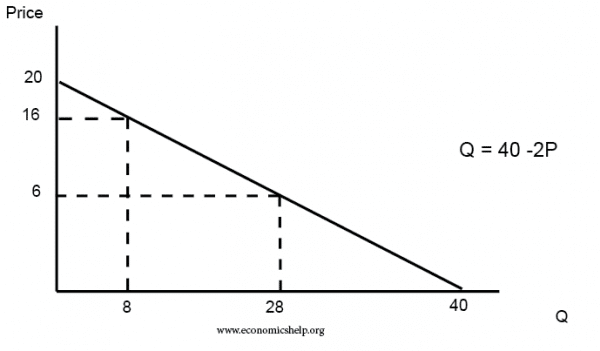 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
In the graph the equilibrium point is denoted by F and the quantity by OB. Aggregate demand is the sum of individual demand curves of all buyers inside and outside of a countryAn individual demand curve represents the quantity of a commodity that a consumer is willing to buy based on price in graph form. Qd a bP Q. Consumer surplus Maximum price willing to spend Actual price. Q a - bP.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
Q is the quantity of demand. We can measure consumer surplus with the following basic formula. Once you have had a go at the questions follow the link below to compare your answers. What is the General Form of Inverse Demand Function. When looking at a demand-supply graph the demand curve is always going to be sloping downward due to the law of diminished marginal utility.

How to Calculate Consumer Surplus. The Inverse Demand Curve is. KGJS rendering software released under the MIT. It postulates that in a competitive market the unit price for a particular good or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets will vary until it. Using these demand and supply functions answer the following questions.
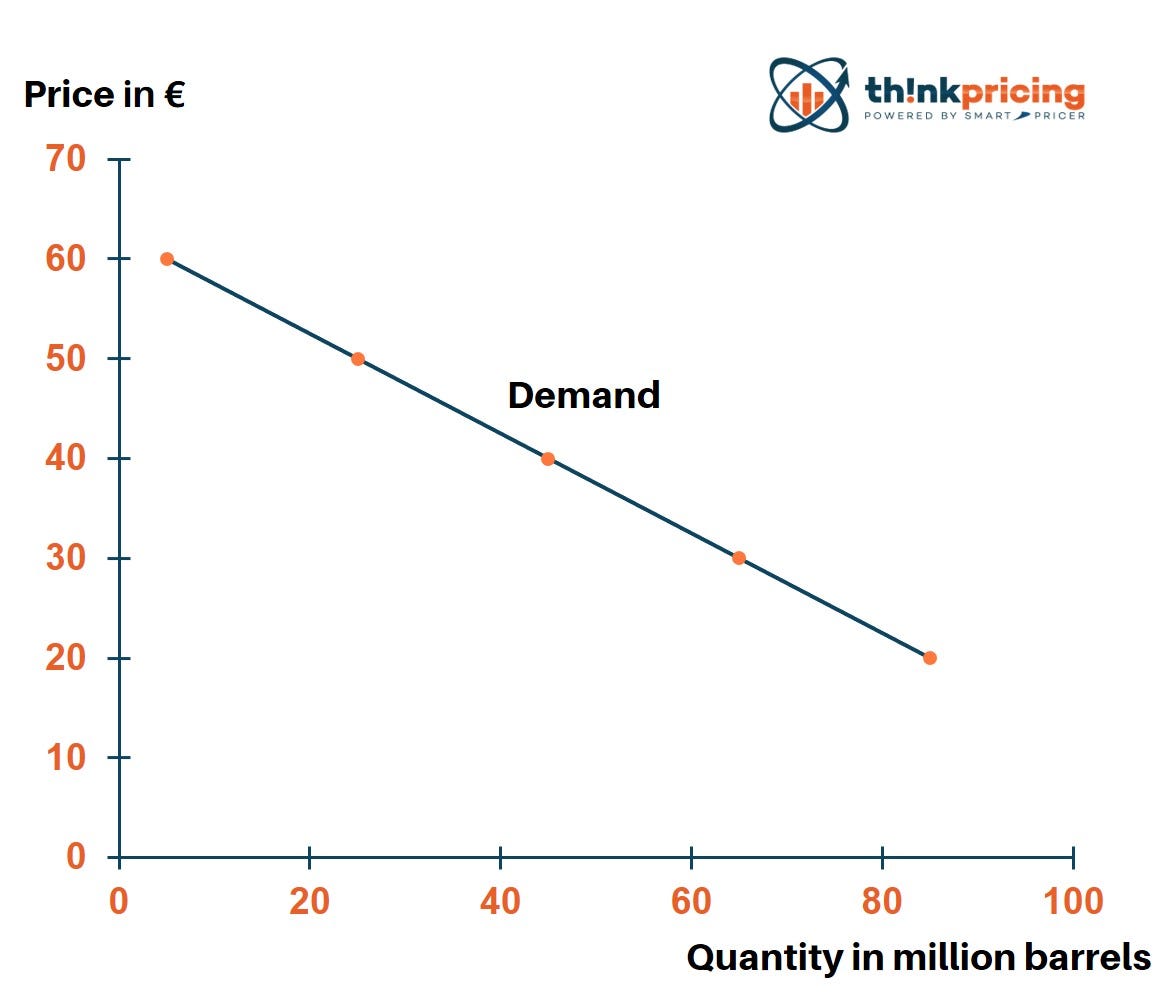 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
Equilibrium price 5. Qd 120 - 5P. Supply and Demand Calculator. B is the slope of the demand in relationship to the price P P is the price. Q a - bP.
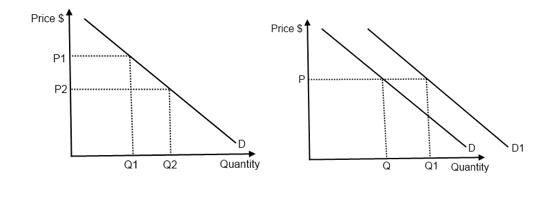 Source: ibguides.com
Source: ibguides.com
Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. The Calculator helps calculating the market equilibrium given Supply and Demand curves. A is the effect of all influences on demand other than price. A quick visual on how to graph the demand curve. Q is the quantity of demand.
 Source: economics.utoronto.ca
Source: economics.utoronto.ca
Use the graph input tool to help you answer the following questions. For normal daily goods there is an inverse or negative relationship between the desired quantity and the price. Point Elasticity along a Constant Elasticity Demand Curve math version Supply Elasticity. The Inverse Demand Curve is. View the full answer.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
B is the slope of the demand in relationship to the price P P is the price. The consumer surplus is the area below the demand curve but above the equilibrium price and up to the quantity demand. At equilibrium the price would be 5 with a quantity demand of 500. Style your graph and add images if necessary. This situation still follows the rule that the marginal revenue curve is twice as steep as the demand curve since twice a slope of zero is still a slope of zero.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
49 rows A linear demand curve can be plotted using the following equation. At equilibrium the price would be 5 with a quantity demand of 500. Point Elasticity along a Constant Elasticity Demand Curve. The Math Science. We can measure consumer surplus with the following basic formula.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Calculating marginal revenue from a linear demand curve The blue curve on the following graph represents the daily demand curve facing a firm that can set its own prices. It postulates that in a competitive market the unit price for a particular good or other traded item such as labor or liquid financial assets will vary until it. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. 49 rows A linear demand curve can be plotted using the following equation. Mark the demand and supply data for each price to get the demand and supply curves.

Consider the graph below. In this case marginal revenue is equal to price as opposed to being strictly less than price and as a result the marginal revenue curve is the same as the demand curve. When looking at a demand-supply graph the demand curve is always going to be sloping downward due to the law of diminished marginal utility. Consumer surplus Maximum price willing to spend Actual price. Q fP then the general form of Inverse Demand Functionis.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
The demand curve is a graph used in economics to demonstrate the relationship between the price of a product and the demand for that same product. You will identify the equilibrium pricing at this point. This situation still follows the rule that the marginal revenue curve is twice as steep as the demand curve since twice a slope of zero is still a slope of zero. Consumer surplus Maximum price willing to spend Actual price. Price Elasticity Calculator Midpoint Method.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
Firstly plot graph for the supply curve and the initial demand curve with a price on the ordinate and quantity on the abscissa. We can measure consumer surplus with the following basic formula. When looking at a demand-supply graph the demand curve is always going to be sloping downward due to the law of diminished marginal utility. You will identify the equilibrium pricing at this point. How to Calculate Consumer Surplus.
 Source: study.com
Source: study.com
Once you enter a value in a white field the. Price Elasticity Calculator Midpoint Method. You will not be graded on any changes you make to this graph. The Math Science. Qs -30 10P.
This site is an open community for users to do sharing their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site convienient, please support us by sharing this posts to your favorite social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title calculate d3mand curve from graph by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.