Your Aggregate demand increase diagram images are ready. Aggregate demand increase diagram are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens now. You can Find and Download the Aggregate demand increase diagram files here. Download all free images.
If you’re searching for aggregate demand increase diagram pictures information linked to the aggregate demand increase diagram keyword, you have pay a visit to the right site. Our website frequently gives you suggestions for seeking the highest quality video and image content, please kindly surf and find more informative video articles and graphics that match your interests.
Aggregate Demand Increase Diagram. Aggregate demand AD refers to the amount of total spending on domestic goods and services in an economy. At point A at a price level of 118 11800 billion worth of goods and services will be demanded. Links output changes to changes in the price level Powell driving the bus. This chapter introduces you to the Aggregate Supply Aggregate Demand or ASAD model.
 Chapter 12 Aggregate Demand And Aggregate Supply Bryan S Blog From 14solvbr.wordpress.com
Chapter 12 Aggregate Demand And Aggregate Supply Bryan S Blog From 14solvbr.wordpress.com
I Gross capital investment ie. G is government expenditure. AD CIG X-M C Consumer expenditure on goods and services. We have seen that the formula for aggregate demand is AD C I G X M where M is the total value of imported goods. A higher tax rate leads to a new equilibrium at lower output by shifting the aggregate demand curve downwards. This model builds on the model for Aggregate Expenditure AE presented in Chapter 24 using the broader term aggregate demand to include explicit attention to the potential problem of inflation.
The Aggregate Demand Curve.
Does this mean that more imports will result in a lower level of aggregate demand. Aggregate demand AD is composed of various components. In contrast the vertical axis of an aggregate supply and aggregate demand diagram expresses the level of a price index like the Consumer Price Index or the GDP deflatorcombining a wide array of prices from across the economy. A shift to the right of the aggregate demand curve. In a linear aggregate demand model A. The aggregate supply curve determines the extent to which increases in aggregate demand lead to increases in real output or increases in prices.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
The chapter also adds in the role of. This model builds on the model for Aggregate Expenditure AE presented in Chapter 24 using the broader term aggregate demand to include explicit attention to the potential problem of inflation. An increase in government debt will shift the aggregate demand curve downwards. Well talk about that more in other articles but for now just think of aggregate demand as total spending. Why is there a minus sign in front of imports.
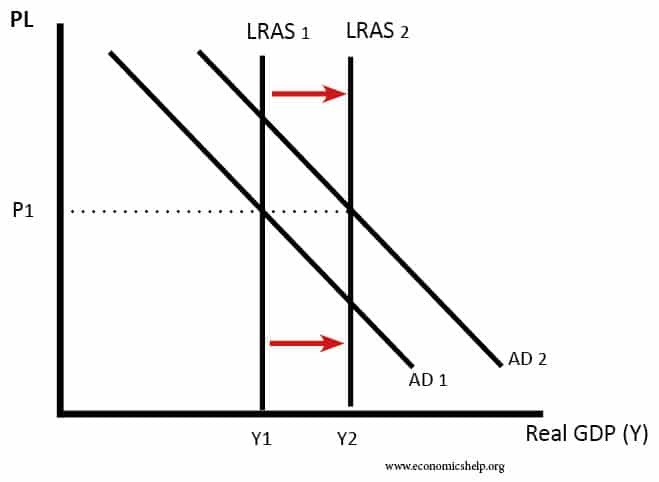 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Investment spending on capital goods eg. Strictly speaking AD is what economists call total planned expenditure. The Central Bank within the economy raises interest rates and tightens credit. Links output changes to changes in the price level Powell driving the bus. This chapter introduces you to the Aggregate Supply Aggregate Demand or ASAD model.
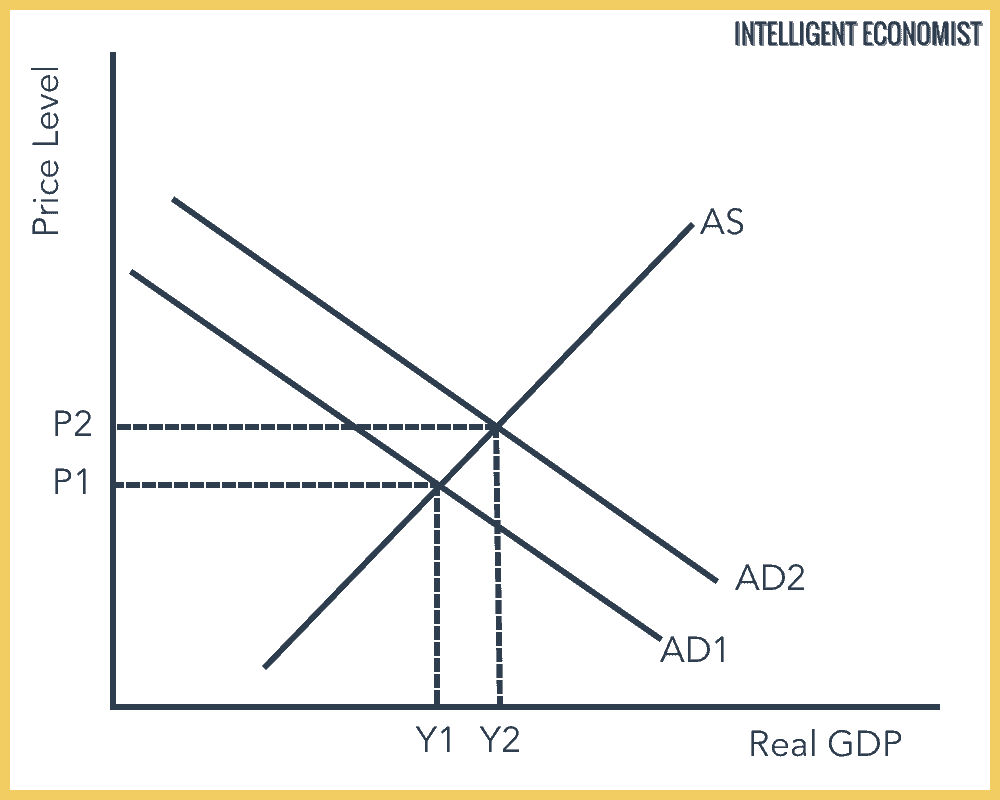 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Various points on the aggregate demand curve are found by adding the values of these components at different price levels. Aggregate demand AD is composed of various components. Strictly speaking AD is what economists call total planned expenditure. The aggregate demand curve for the data given in the table is plotted on the graph in Figure 71 Aggregate Demand. The aggregate supply curve determines the extent to which increases in aggregate demand lead to increases in real output or increases in prices.
 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
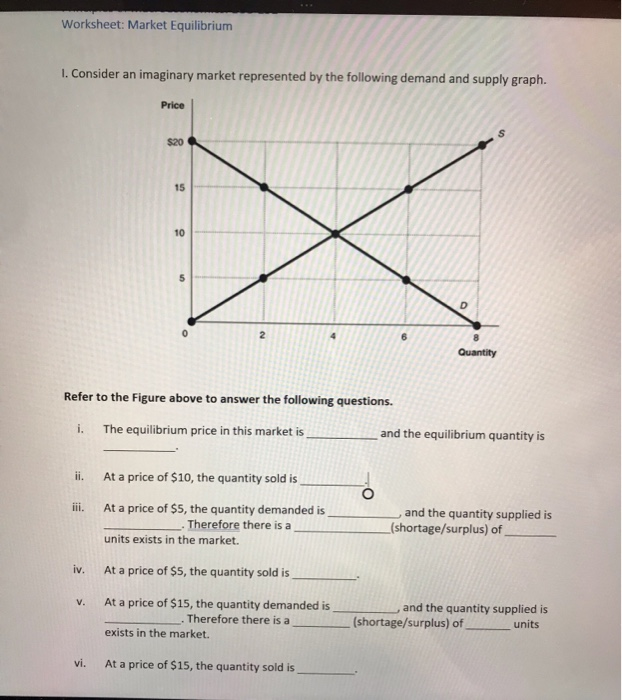
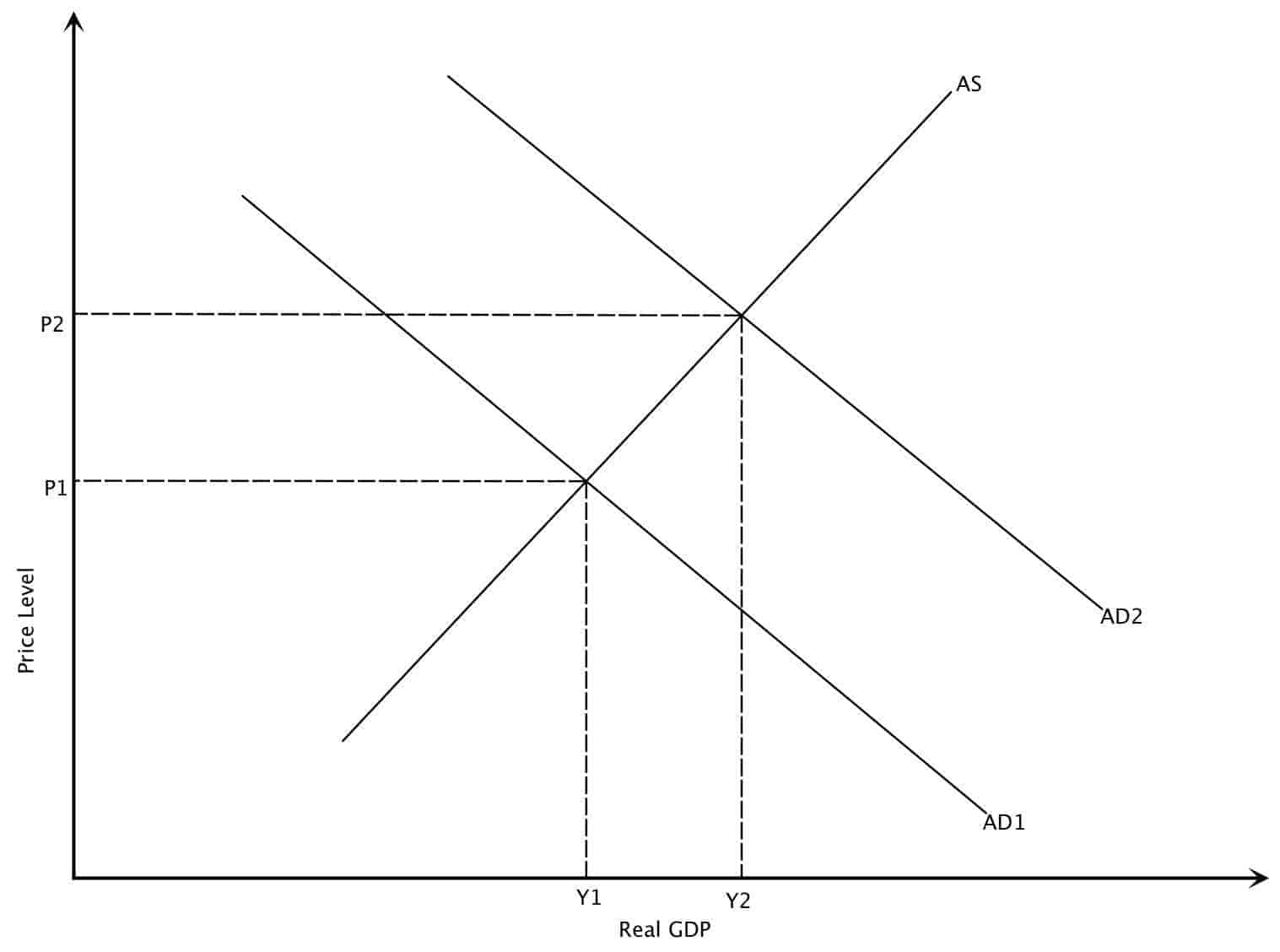
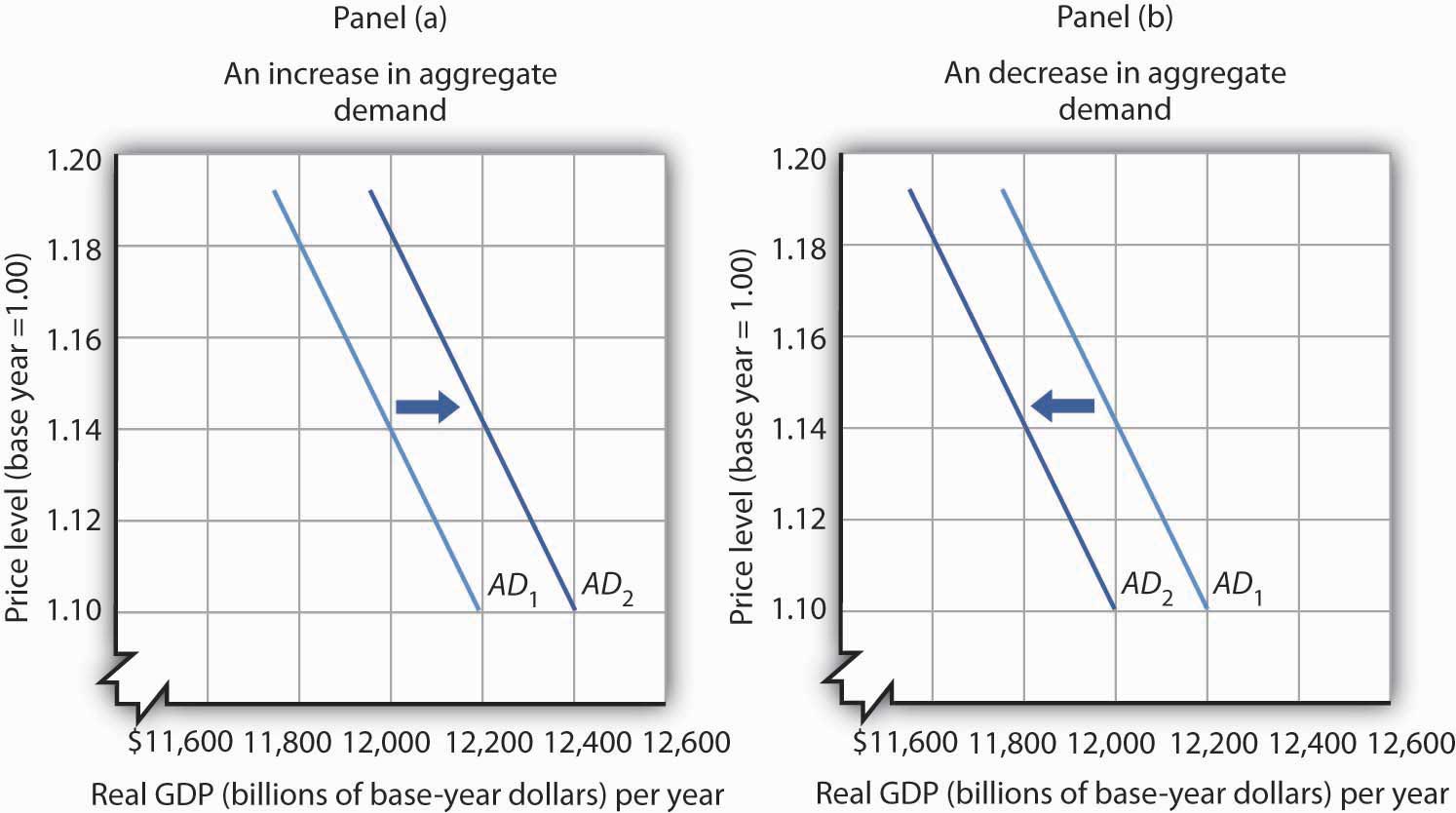
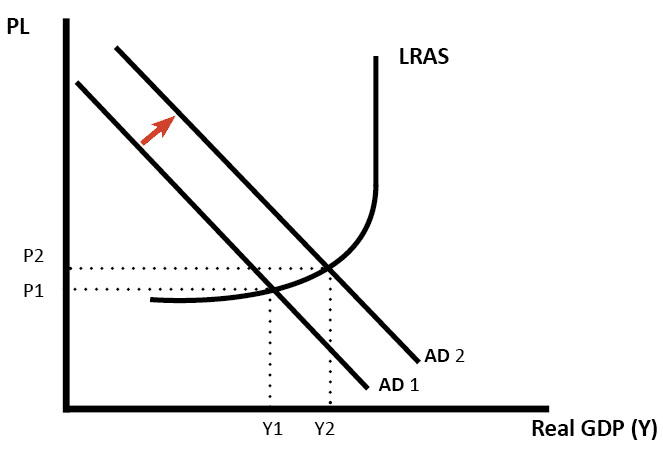
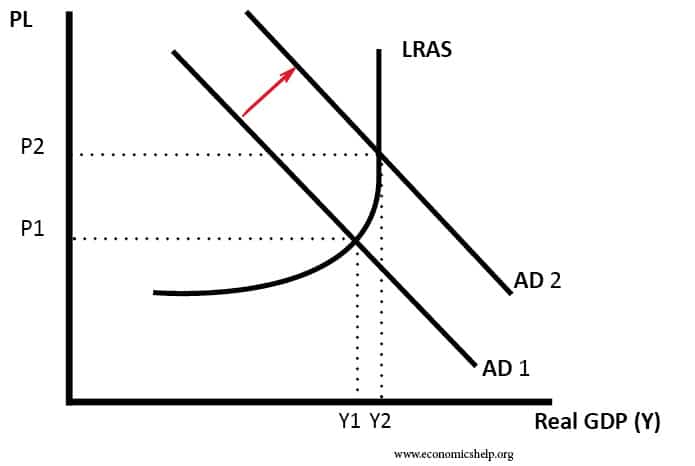
From AD 1 to AD 2 means that at the same price levels the quantity demanded of real GDP has increased. In a linear aggregate demand model A. A higher tax rate leads to a new equilibrium at lower output by shifting the aggregate demand curve downwards. The aggregate demand curve shifts to the right as a result of monetary expansion. Using an aggregate demand and aggregate supply diagram or model of the economy graphically illustrate and discuss the immediate effects of the following events upon the economy.
 Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Source: courses.lumenlearning.com
Aggregate demand or AD refers to the amount of total spending on domestic goods and services in an economy. A shift to the right of the aggregate demand curve. Aggregate demand AD is composed of various components. The aggregate demandaggregate supply model is a model that shows what determines total supply or total demand for the economy and how total demand and total supply interact at the macroeconomic level. Utilizing the aggregate demand curve a shift to the left a reduction in aggregate demand is perceived negatively while a shift to the right.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
At point A at a price level of 118 11800 billion worth of goods and services will be demanded. At point C a reduction in the. According to Keyns Aggregate Demand is equal to ADCIGX-M Where AD is aggregate demand. Why is there a minus sign in front of imports. Well talk about that more in other articles but for now just think of aggregate demand as total spending.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
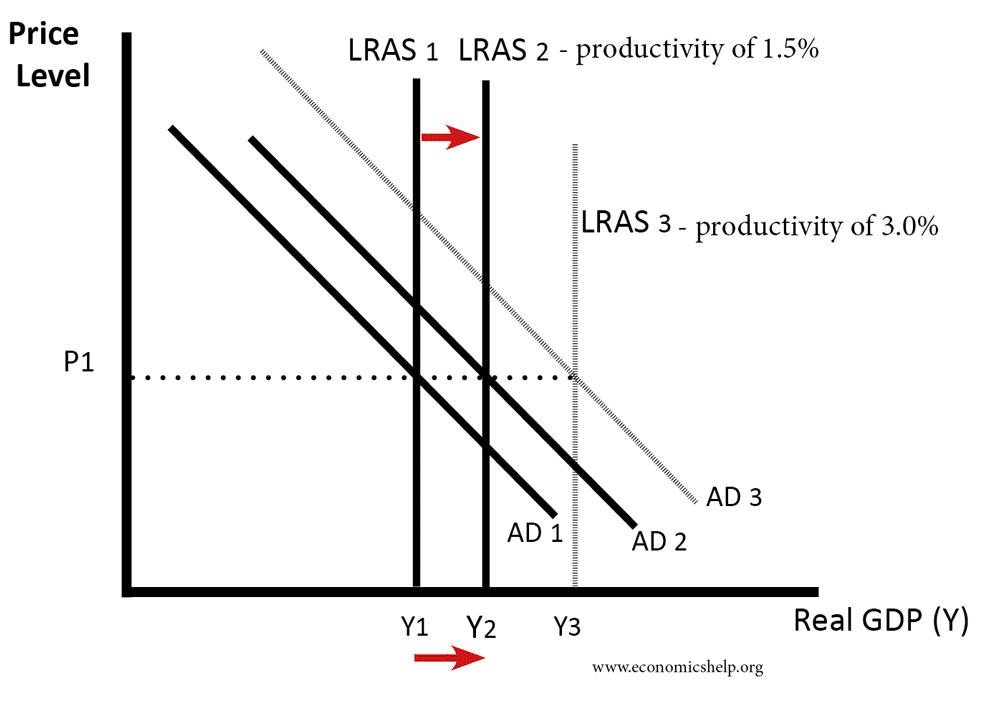
Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Adding Swings in the Overall Price Level to our Model of the Economy October 23rd 2019. An increase in government debt will shift the aggregate demand curve downwards. Strictly speaking AD is what economists call total planned expenditure. Does this mean that more imports will result in a lower level of aggregate demand. This leads to a proportionate increase in national output from OY 1 to OY 2 and no change in the general price level however when aggregate demand increases further from AD 2 to AD 3 it encounters less elastic conditions of aggregate supply.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
An increase in demand curve. Why is there a minus sign in front of imports. We have seen that the formula for aggregate demand is AD C I G X M where M is the total value of imported goods. We will further explain this distinction in the appendix The Expenditure-Output Model For now just think of aggregate demand as total spending. Utilizing the aggregate demand curve a shift to the left a reduction in aggregate demand is perceived negatively while a shift to the right.
 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
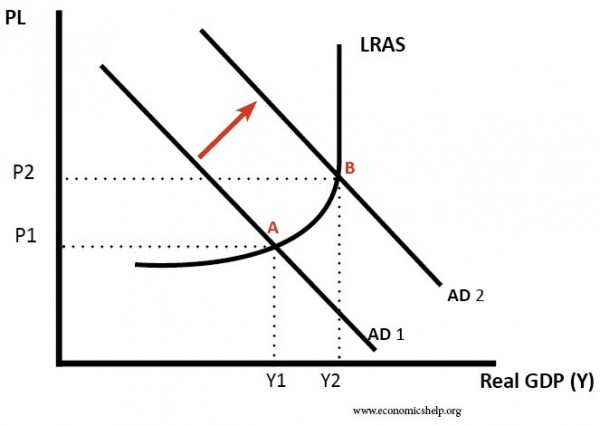
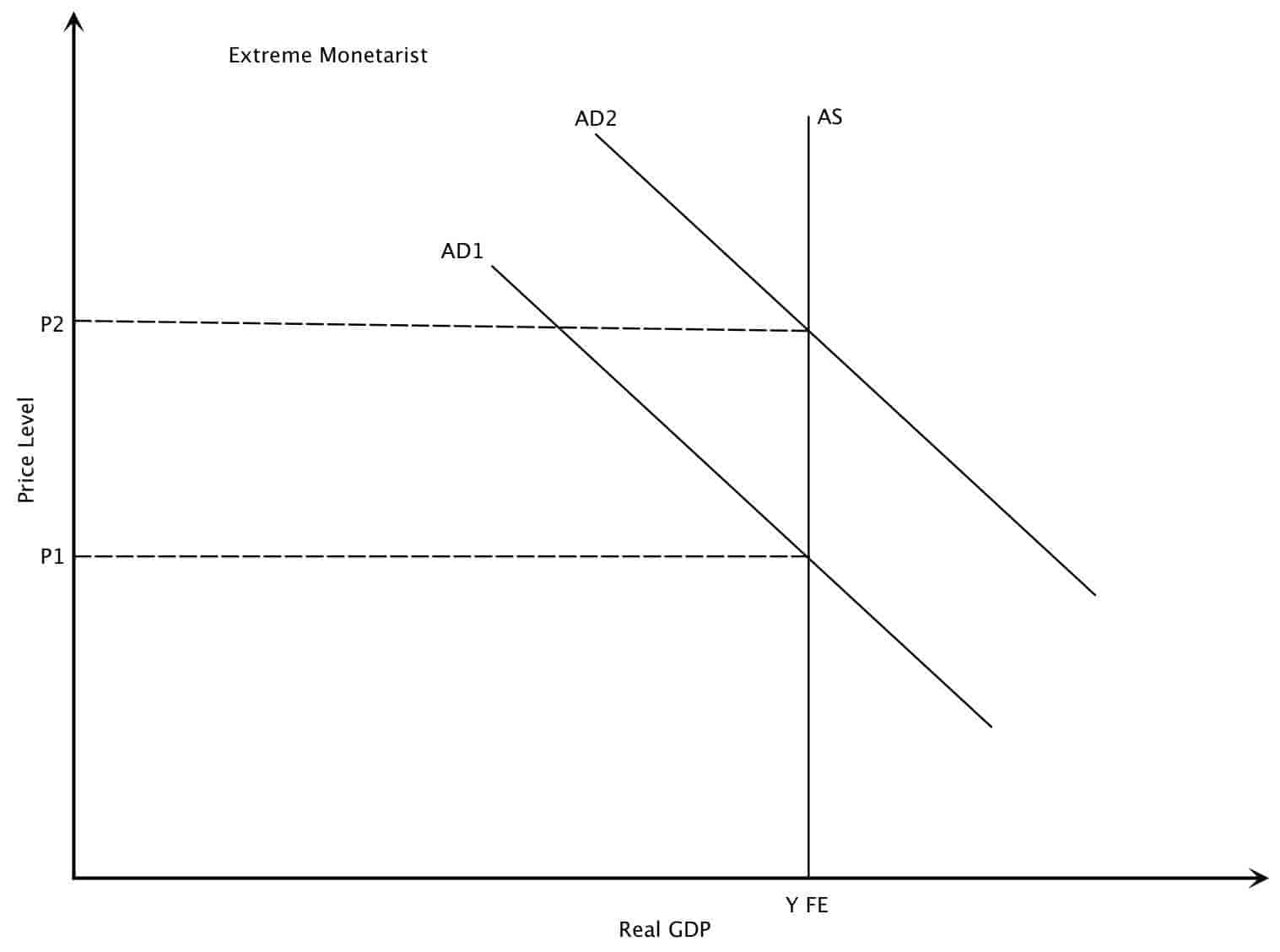
Does this mean that more imports will result in a lower level of aggregate demand. A higher tax rate leads to a new equilibrium at lower output by shifting the aggregate demand curve downwards. The Central Bank within the economy raises interest rates and tightens credit. Links output changes to changes in the price level Powell driving the bus. Assume now that aggregate demand in Fig.
 Source: saylordotorg.github.io
Source: saylordotorg.github.io
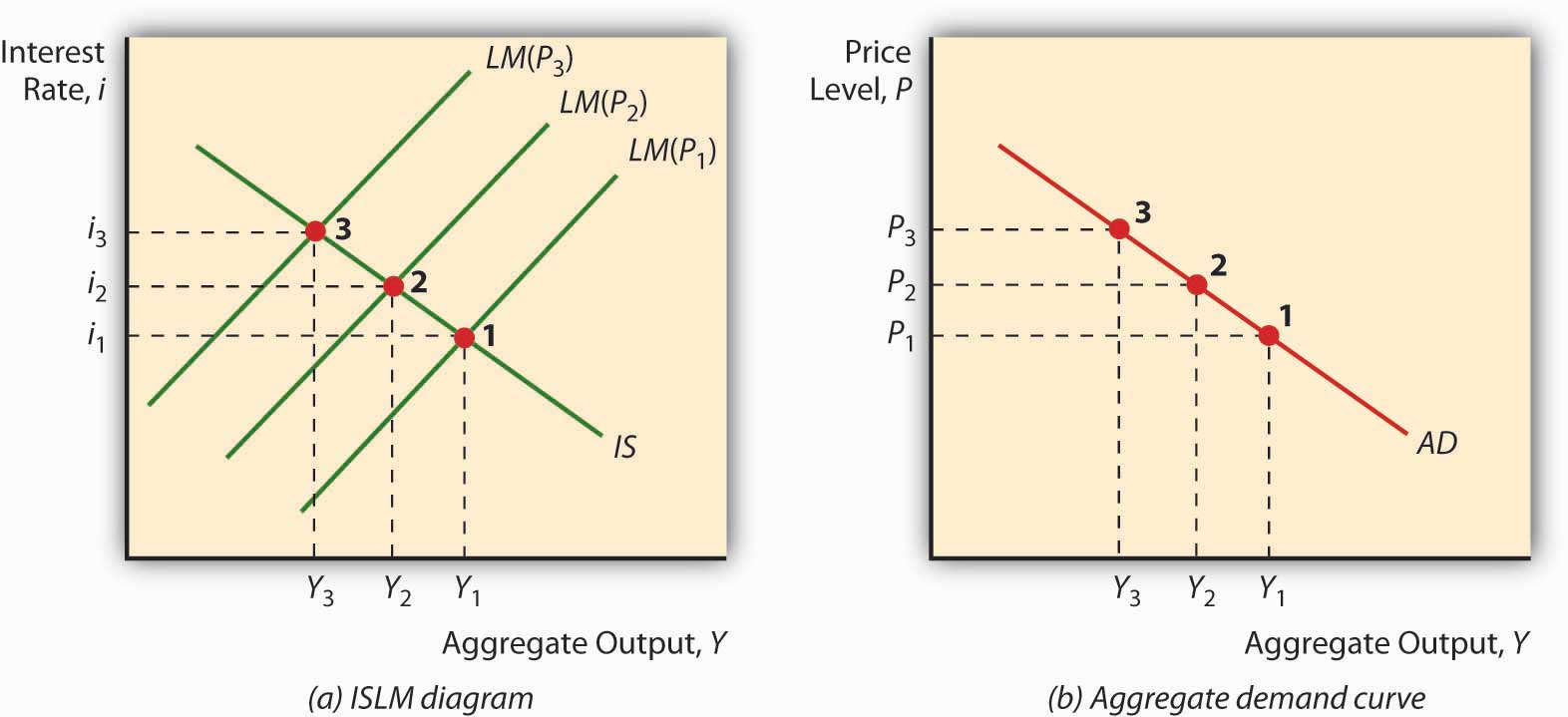
Various points on the aggregate demand curve are found by adding the values of these components at different price levels. This chapter introduces you to the Aggregate Supply Aggregate Demand or ASAD model. Aggregate demand AD is the total demand for goods and services produced within the economy over a period of time. X-M is net exports. The aggregate demand curve shifts to the right as a result of monetary expansion.
 Source: 14solvbr.wordpress.com
Source: 14solvbr.wordpress.com
Well talk about that more in other articles but for now just think of aggregate demand as total spending. The aggregate demand curve shifts to the right as a result of monetary expansion. This chapter introduces you to the Aggregate Supply Aggregate Demand or ASAD model. From AD 1 to AD 2 means that at the same price levels the quantity demanded of real GDP has increased. The equation used to calculate aggregate demand is.
 Source: bobbyrb.wordpress.com
Source: bobbyrb.wordpress.com
The Central Bank within the economy raises interest rates and tightens credit. G is government expenditure. AD CIG X-M C Consumer expenditure on goods and services. The Aggregate Demand Curve. A higher tax rate leads to a new equilibrium at lower output by shifting the aggregate demand curve downwards.

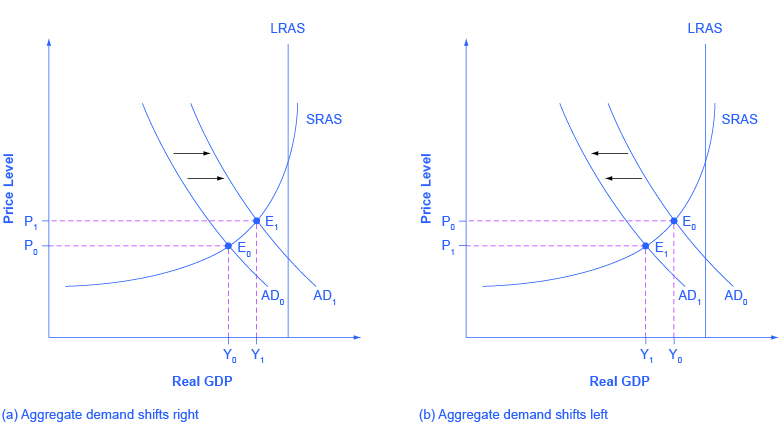
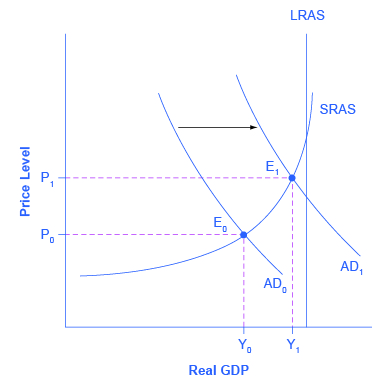
Aggregate demand AD is composed of various components. An illustration of the two ways in which the aggregate demand curve can shift is provided in Figure. The vertical axis of a microeconomics demand and supply diagram expresses a price or wage or rate of return for an individual good or service. Various points on the aggregate demand curve are found by adding the values of these components at different price levels. The Aggregate Demand Curve.
 Source: khanacademy.org
Source: khanacademy.org
1 1-C1 1-1m is the size of the multiplier in an open economy. The aggregate supply curve determines the extent to which increases in aggregate demand lead to increases in real output or increases in prices. Links output changes to changes in the price level Powell driving the bus. Ad Over 27000 video lessons and other resources youre guaranteed to find what you need. Does this mean that more imports will result in a lower level of aggregate demand.
 Source: textbook.stpauls.br
Source: textbook.stpauls.br
At point C a reduction in the. G is government expenditure. The aggregate demandaggregate supply model is a model that shows what determines total supply or total demand for the economy and how total demand and total supply interact at the macroeconomic level. Does this mean that more imports will result in a lower level of aggregate demand. A higher tax rate leads to a new equilibrium at lower output by shifting the aggregate demand curve downwards.
 Source: college.cengage.com
Source: college.cengage.com
The aggregate demandaggregate supply model is one of the fundamental diagrams in this course like the budget constraint diagram that we introduced in the Choice in a World of Scarcity chapter and the supply and demand diagram in the Demand and Supply chapter because it provides an overall framework for bringing these factors together in one diagram. Aggregate demand AD is composed of various components. Targeting output and. The aggregate demand curve for the data given in the table is plotted on the graph in Figure 71 Aggregate Demand. The equation used to calculate aggregate demand is.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
Utilizing the aggregate demand curve a shift to the left a reduction in aggregate demand is perceived negatively while a shift to the right. A higher tax rate leads to a new equilibrium at lower output by shifting the aggregate demand curve downwards. Links output changes to changes in the price level Powell driving the bus. Aggregate Demand and Aggregate Supply Adding Swings in the Overall Price Level to our Model of the Economy October 23rd 2019. Why is there a minus sign in front of imports.
 Source: researchgate.net
Source: researchgate.net
The aggregate demandaggregate supply model is a model that shows what determines total supply or total demand for the economy and how total demand and total supply interact at the macroeconomic level. 1 1-C1 1-1m is the size of the multiplier in an open economy. X-M is net exports. We have seen that the formula for aggregate demand is AD C I G X M where M is the total value of imported goods. Ad Over 27000 video lessons and other resources youre guaranteed to find what you need.
This site is an open community for users to submit their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site serviceableness, please support us by sharing this posts to your preference social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also save this blog page with the title aggregate demand increase diagram by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.