Your A decrease in supply is graphically represented by images are ready in this website. A decrease in supply is graphically represented by are a topic that is being searched for and liked by netizens today. You can Find and Download the A decrease in supply is graphically represented by files here. Find and Download all free vectors.
If you’re looking for a decrease in supply is graphically represented by images information related to the a decrease in supply is graphically represented by interest, you have visit the ideal site. Our website frequently gives you hints for seeking the maximum quality video and picture content, please kindly surf and find more informative video articles and graphics that match your interests.
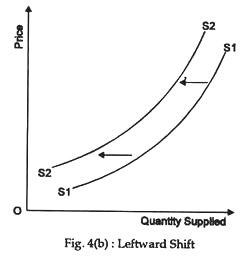
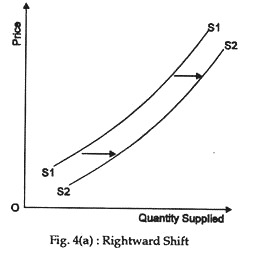
A Decrease In Supply Is Graphically Represented By. Likewise a decrease in supply will shift the supply curve up. So there are two possible changes in supply. Panel d of Figure 317 Changes in Demand and Supply shows that a decrease in supply shifts the supply curve to the left. An increase in costs of production causes the supply curve to increase.
 Practice Equilibrium Introduction To Business From courses.lumenlearning.com
Practice Equilibrium Introduction To Business From courses.lumenlearning.com
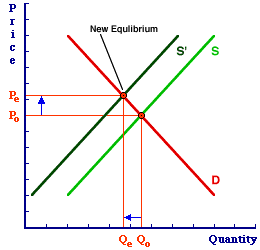
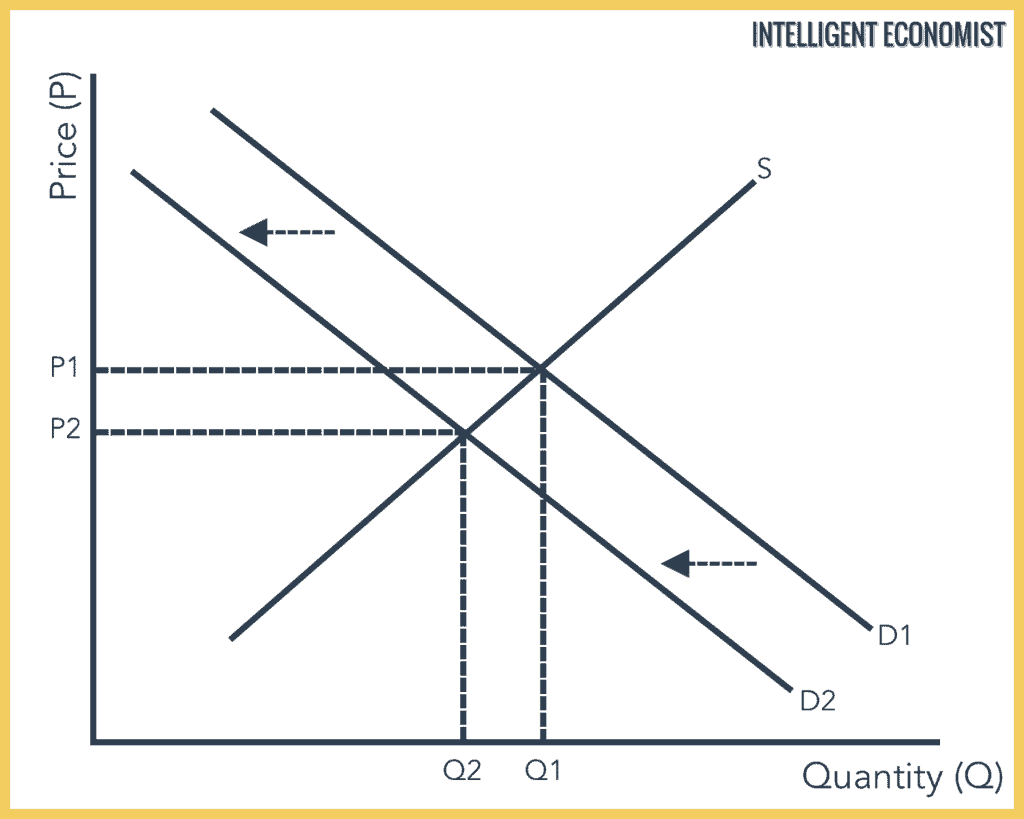
For any given demand a decrease in supply means that the market price will increase while the quantity sold will decrease. This new supply curve intersects the given demand curve at a point where the new equilibrium shows a. Change in supply. Change in supply includes an increase or decrease in supply. A shift of the entire supply curve caused by. Law of demand demand curve contraction 6.
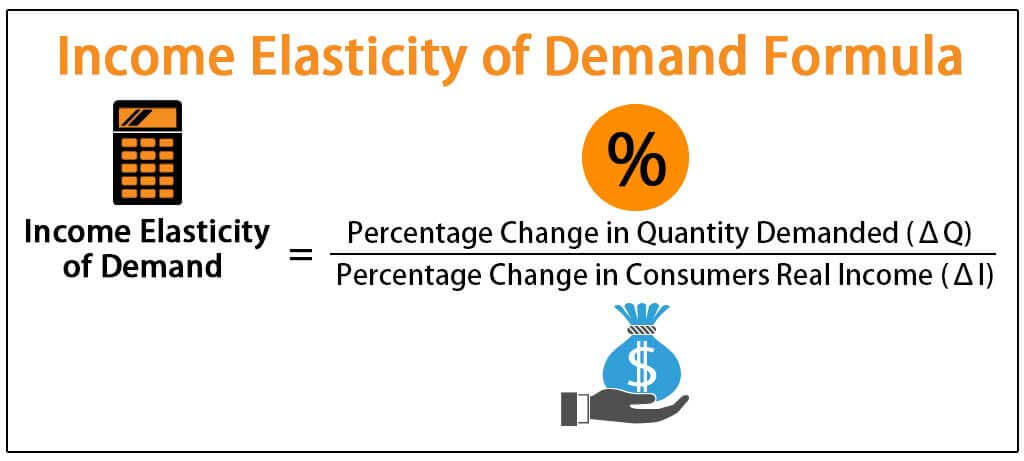
With M 1000 and P 2 the real money supply is 500.
A decrease in quantity demanded is graphically represented by. Change in quantity supplied. Economics questions and answers. Increase shift to the right in supply. A Decrease in Supply. A decrease in aggregate supply with no change in aggregate demand.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
Law of demand demand curve contraction 6. Panel d of Figure 317 Changes in Demand and Supply shows that a decrease in supply shifts the supply curve to the left. A decrease in supply. An increase in demand causes an increase in supply. Law of demand demand curve contraction 6.
 Source: investopedia.com
Source: investopedia.com
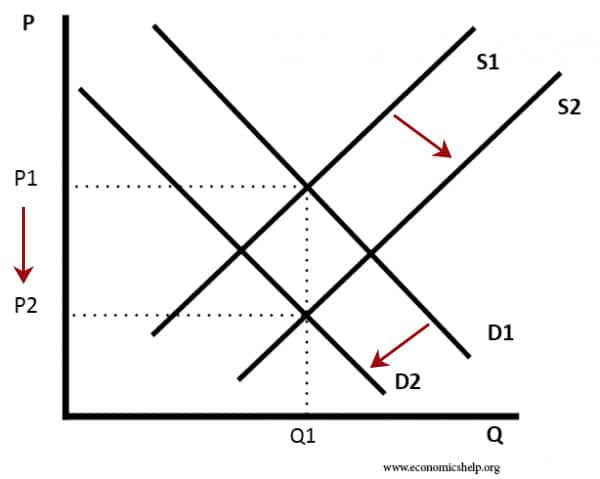
The graph below illustrates what a change in a determinant of aggregate supply will do to the position of the aggregate supply curve. Law of demand demand curve contraction 6. Change in quantity supplied. A Decrease in Supply. A decrease in aggregate supply with no change in aggregate demand.

A Decrease in Supply. A decrease in supply means that at each of the prices there is now a decrease in quantity suppliedmeaning that the curve shifts to the left Fig. B A rightward shift in the demand curve. We can clarify this result by actually looking at a shift in a supply curve for a translation service. D The number of sellers of good X.
 Source: medium.com
Source: medium.com
A decease in he quantity of a good service or resources supplied at every price. As we consider each of the determinants remember that those factors that cause an increase in AS will shift the curve outward and to the right and those factors that cause a decrease in AS will shift the curve. D A movement down and to the right along a demand curve. A decrease in supply means that at each of the prices there is now a decrease in quantity suppliedmeaning that the curve shifts to the left Fig. A decrease in quantity demanded is graphically represented by.
 Source: mlpp.pressbooks.pub
Source: mlpp.pressbooks.pub
All other factors are assumed constant. With M 1000 and P 2 the real money supply is 500. Such a decrease in supply cannot be represented by the original supply curve. A price decrease increases quantity supplied. Increase shift to the right in supply.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Panel d of Figure 310 Changes in Demand and Supply shows that a decrease in supply shifts the supply curve to the left. An increase in aggregate supply due to a decrease in input prices is represented by a shift to the right of the SAS curve. We can clarify this result by actually looking at a shift in a supply curve for a translation service. B an upward-sloping curve. A shift of the entire supply curve caused by.
 Source: youtube.com
Source: youtube.com
A decrease in quantity demanded is graphically represented by. With M 1000 and P 2 the real money supply is 500. A decrease in resource costs causes an increase in the supply curve. D a vertical line. This video shows how to graph a change in supply by shifting the supply curve.
 Source: amosweb.com
Source: amosweb.com
For any given demand a decrease in supply means that the market price will increase while the quantity sold will decrease. The real money supply is independent of the interest rate and is therefore represented by the vertical line. I Increase in Supply Shift to the Right. D a vertical line. A decease in he quantity of a good service or resources supplied at every price.
 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
So there are two possible changes in supply. The downward sloping line represents the money demand function which is 1000 100r. This new supply curve intersects the given demand curve at a point where the new equilibrium shows a. Likewise a decrease in supply will shift the supply curve up. For any given demand a decrease in supply means that the market price will increase while the quantity sold will decrease.
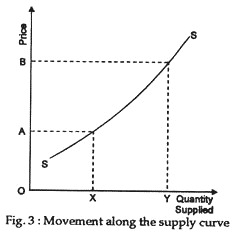 Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Source: economicsdiscussion.net
Such a decrease in supply cannot be represented by the original supply curve. A a horizontal line. Decrease shift to the left in supply. Panel d of Figure 310 Changes in Demand and Supply shows that a decrease in supply shifts the supply curve to the left. C A movement up and to the left along a demand curve.
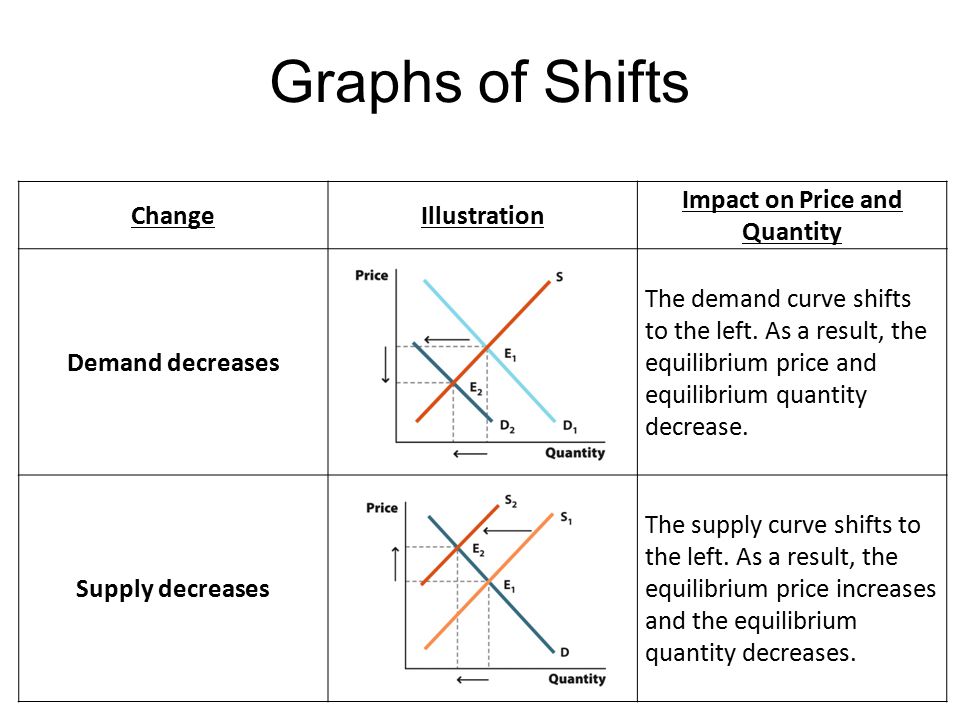 Source: slideplayer.com
Source: slideplayer.com
Panel d of Figure 317 Changes in Demand and Supply shows that a decrease in supply shifts the supply curve to the left. A decease in he quantity of a good service or resources supplied at every price. B an upward-sloping curve. A decrease in supply means that at each of the prices there is now a decrease in quantity suppliedmeaning that the curve shifts to the left Fig. The equilibrium price rises to 7 per pound.
 Source: investopedia.com
Source: investopedia.com
This new supply curve intersects the given demand curve at a point where the new equilibrium shows a. The equilibrium price rises to 7 per pound. The equilibrium price rises to 7 per pound. As we consider each of the determinants remember that those factors that cause an increase in AS will shift the curve outward and to the right and those factors that cause a decrease in AS will shift the curve. The graph below illustrates what a change in a determinant of aggregate supply will do to the position of the aggregate supply curve.
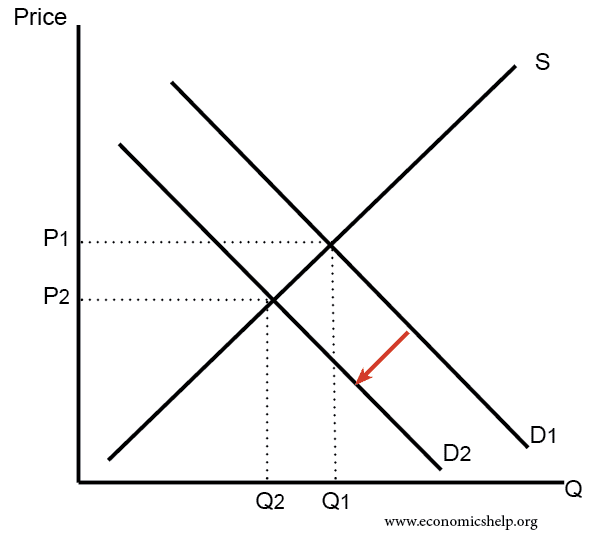 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
All other factors are assumed constant. A shift of the entire supply curve caused by. All other factors are assumed constant. Such a decrease in supply cannot be represented by the original supply curve. D A movement down and to the right along a demand curve.
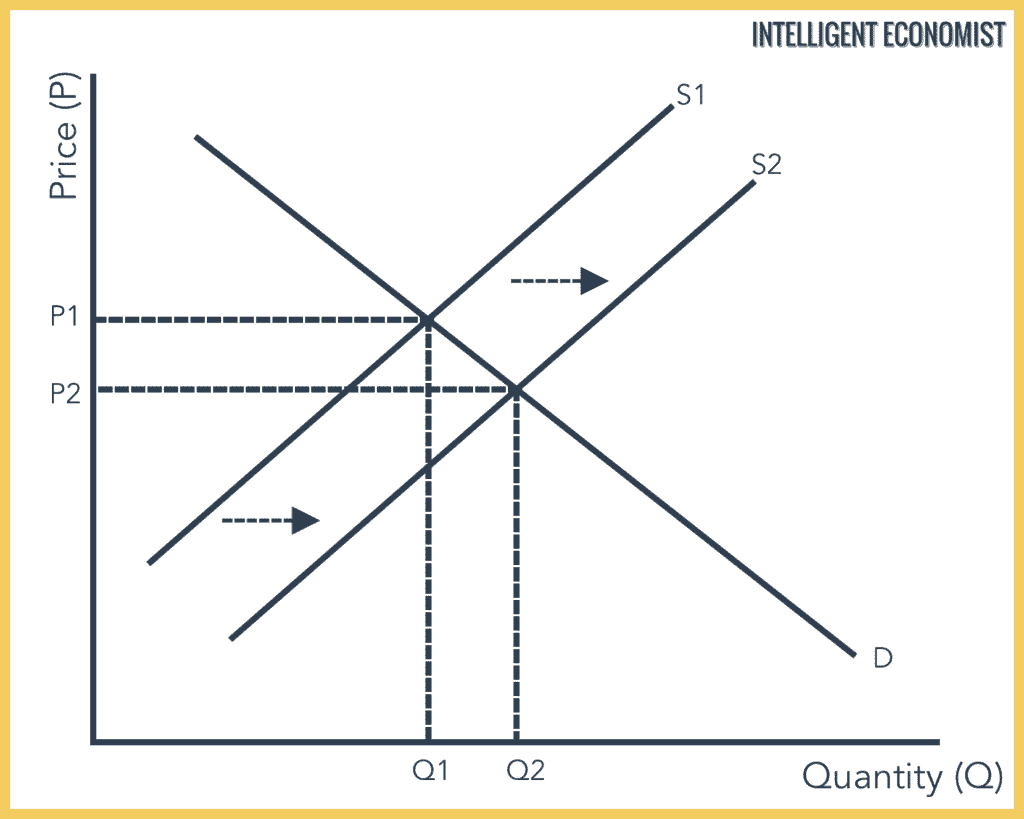 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
As we consider each of the determinants remember that those factors that cause an increase in AS will shift the curve outward and to the right and those factors that cause a decrease in AS will shift the curve. D A movement down and to the right along a demand curve. A Decrease in Supply. Law of demand demand curve contraction 6. D The number of sellers of good X.
 Source: intelligenteconomist.com
Source: intelligenteconomist.com
3 A decrease in real money supply caused by an increase in the price level is graphically represented by A a shift of the AD-curve to the right B a shift of the AD-curve to the left C movement along the AD-curve to the right D movement along the AD-curve to the left E a shift of the AS-curve to the right 4. This is represented on a demand supply graph as. Because of this counter intuitive result I like to think of an increase in supply as a rightward shift and a decrease in supply as a leftward shift. C The supply of good X. B A rightward shift in the demand curve.
 Source: toppr.com
Source: toppr.com
The supply curve is also graphed in two dimensions. Panel d of Figure 317 Changes in Demand and Supply shows that a decrease in supply shifts the supply curve to the left. Decrease shift to the left in supply. It will lead to a shift in supply curve. For any given demand a decrease in supply means that the market price will increase while the quantity sold will decrease.
 Source: economicshelp.org
Source: economicshelp.org
B A rightward shift in the demand curve. What happens to supply when income increases. The supply curve shifts left up. A a horizontal line. A decrease in quantity demanded is graphically represented by.
 Source: personal.psu.edu
Source: personal.psu.edu
Change in supply includes an increase or decrease in supply. It is graphically represented by a shift in the supply curve. A leftward shift of the supply curve. Panel d of Figure 317 Changes in Demand and Supply shows that a decrease in supply shifts the supply curve to the left. A A leftward shift in the demand curve.
This site is an open community for users to share their favorite wallpapers on the internet, all images or pictures in this website are for personal wallpaper use only, it is stricly prohibited to use this wallpaper for commercial purposes, if you are the author and find this image is shared without your permission, please kindly raise a DMCA report to Us.
If you find this site adventageous, please support us by sharing this posts to your own social media accounts like Facebook, Instagram and so on or you can also bookmark this blog page with the title a decrease in supply is graphically represented by by using Ctrl + D for devices a laptop with a Windows operating system or Command + D for laptops with an Apple operating system. If you use a smartphone, you can also use the drawer menu of the browser you are using. Whether it’s a Windows, Mac, iOS or Android operating system, you will still be able to bookmark this website.